Dural Sinuses, Meninges, and Vasculature Flashcards
1
Q
- Cranial meninges
A
- Dense regular CT layers (3)
- Separate soft tissue of brain from cranial bones
- Contain and circulate CSF
- Parts form some of the veins
*
2
Q
- What are the 3 layers of the cranial meninges from superficial to deep?
A
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia mater
3
Q
- Dura Mater
A
- Two fibrous layers
- Strongest
- Two layers:
- Periosteal layer-more superficial layer, attaches to periosteum
- Meningeal layer-deep to periosteal layer
- Fused with periosteal layer; except in two layers separate to form large blood-filled spaces called dural venous sinuses
4
Q
- Arachnoid
A
- Immediately internal to the dura mater
- Collagen and elastic fibers=arachnoid trabeculae
5
Q
- Space between the arachnoid and overlying dura mater is called the _ space
- Space immediately deep to the arachnoid space is the _ space
A
- Subdural
- Subrarachnoid
6
Q
- Pia Mater
A
- Innermost layer
- Follows sulci and gyri-adhered to actual brain
- Delicate thin layer of CT
- Means gentle mother-so here’s a picture of my mom

7
Q
- Cranial Dural Spta
A
- _ layer of the dura mater extends as flat partitions (_) deep into cranial cavity at four locations
- Membranous partitions separate specific parts of the brain and provide additional stabilization and support to the entire brain
- Falx cerebri
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Falx cerebelli
- Diaphragma Cerebelli
- In the septa are dural venous sinuses (superior and inferior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, sigmoid sinus, and transverse sinus)
8
Q
- Dural Septa and Dural Venous Sinuses
A

9
Q
- Arterial supply to the meninges comes from the _ artery which is a branch of the external carotid a.
- What are the sub-branches of the arterial supply to the meninges
- This artery enters the skull via _
A
- Middle meningeal a.
- Frontal (anterior) branch
- Parietal (posterior) branch
- Foramen spinosum
10
Q
- Innveration of the meninges
A
- Middle frontal portion of brain-Opthalmic N (V1)
- Lateral frontal portion of brain- Maxillary N (V2) and Mandibular N (V3)
- Posteromedial-Opthalmic N (V1) and Cervical Spinal Nerves (Deeper-C2,C3)
- Posterolateral-Mandibular N (V3)

11
Q

A
- Superior sagittal sinus
- Inferior sagittal sinus
- Straight sinus
- Confluence of the sinuses
- Occipital sinus
- Sigmoid sinus
- Cavernous sinus
- Anterior intercavernous sinus
- Posterior intercavernous sinus
- Sphenoparietal sinus
- Superior petrosal sinus
- Inferior petrosal sinus
12
Q

A
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Diaphragma sellae
- Falx cerebri
- Falx cerebelli
13
Q
- Cavernous sinus associated structures
A
- CN III, IV, first part of V, VI
- Internal carotid a.
- Pituitary gland

14
Q
- What nerve is less tightly compacted in the cavernous sinus and is more prone to damage with a thrombus of the cavernous sinus and internal carotid a.?
A
- Abducent n. (CN VI)

15
Q
- The internal carotid artery has what three parts in the brain
A
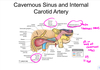
16
Q
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Functions
- Where is it formed
- What does it contain
A
- Buoyancy
- Protection
- Environmental stability
- Formed in choroid plexus in each ventricle
- Produced by secretion from ependymal cells that originate from the blood plasma
- More Na+, H+, and Ca2+ but less K+ than plasma
17
Q
- CSF drains into the _ and then into the dural venous sinus, which then drains into the internal jugular v.
A
- Arachnoid granulations
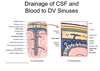
18
Q
_ joins the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein posterior to medial end of clavicle
A
- Internal jugular v.
19
Q
- Internal jugular v.
- Emerges thru _ as continuation of sigmoid sinus
- Descends behind and lateral to _ inside the carotid sheath
A
- Jugular foramen
- Internal carotid a.
20
Q
- What LNs are located in the I region of the cervical LNs?
A
- Submental and submandibular LNs
21
Q
- What LNs are located in region II of the cervical LNs?
A
- Deep cervical LNs (upper lateral group)
22
Q
- What LNs are located in the III region of the cervical LNs?
A
- Deep cervical LNs (middle lateral group)
23
Q
What LNs are located in the IV region of the cervical LNs?
A
- Deep cervical LNs (lower lateral group)
24
Q
- What LNs are located in the V region of the cervical LNs?
A
- LNs of the posterior cervical triangle
25
Q
- What LNs are located in the VI region of the cervical LNs?
A
- Anterior cervical LNs
26
Q
- Cervical LNs
A

27
Q
- At what two sites do the lymphatic pathways in the cervical region intersect?
- What is clinically significant if these LNs are affected compared to peripheral LNs?
A
- Jugulofacial venous junction
- Jugulosubclavian venous junction
- Could indicate malignancy rather than localized pathology
28
Q
- What are the two bulbs of the internal jugular v?
A
- Superior bulb
- Inferior bulb (bicuspid valve above)

29
Q
- _ assists in draining the cavernous sinus; leaves thru anterior part of jugular foramen and joins the internal jugular v below the superior bulb
A
- Inferior petrosal sinus
30
Q
- _ is formed by union of supraorbital and supratrochlear veins at medial canthus to form the angular v
- Communicates with the cavernous sinus thru superior opthalmic v
- Descends on the face posterior to the facial a. to lower border of mandible
- Joined by anterior division of retromandibular v.oins pterygoid plexus thru deep facial v
A
- Facial v
31
Q
- _ is formed by the union of superficial temporal and maxillary veins
- Passes downwards in substance of parotid gland
- Has two divisions
A
- Retromandibular v.
32
Q
What are the two divisions of the retromandibular vein?
A
- Anterior
- Joins the facial v
- Posterior division
- Pierces deep fascia and joins posterior auricular to form external jugular v.
33
Q
- _ v passes backward between the sphenomandibular ligament and neck of the mandible
- Unites with the superficial temporal v to form the retromandibular v.
A
- Maxillary v
34
Q
- Pterygoid plexus
A
- Small veins around and within laeral pterygoid muscle in infratemporal region
- Drain into maxillary veins which join superficial temporal vein to form retromandibular
- Acts as a peripheral pump-aids venous return by pumping action of muscle every time mouth is opened
Yawning-prolonged and forcible contraction of lateral pterygoid to open mouth, accompanied by contraction of diaphragm and stretching of limbs-reflex triggered by venous stagnation
35
Q
_ veins
Drain pharyngeal plexus on outer surface of pharynx
End in internal jugular v, facial, lingual or superior thyroid veins
A
- Pharyngeal veins
36
Q
- _ leaves the superior pole of the thyroid gland and empties in the face or internal jugular
- _ is short and wide, passes thru middle of pole directly into internal jugular v
- _ joins internal jugular, but more often vertebral or posterior auricular
A
- Superior thyroid v.
- Middle thyroid v.
- Occipital v.
37
Q
- _ vein starts below chin, passes beneath platysma to suprasternal notch
A
- Anterior jugular v.
38
Q
- _ vein
- Begins behind angle of mandible by union of posterior auricular and posterior division of the retromandibular veins
- Descends obliquely, deep to platysma, receives posterior external jugular v
- Pierces deep fascia just above clavicle and drains into the subclavian v.
A
- External jugular v
39
Q
Summary of veins
A
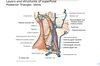
40
Q
- What are the branches off of the aortic arch?
A
- Right
- Brachiocephalic trunk
- Right common carotid a.
- Right subclavian a.
- Left
- Left common carotid a.
- Left subclavian a.
- Brachiocephalic trunk
41
Q
- Where is the 1st part of the subclavian a. located (anatomically speaking)
- Where is the 2nd part of the subclavian a. located
- Where is the 3rd part of the subclavian a. located
A
- Medial to the anterior scalene m.
- Behind the anterior scalene m.
- Lateral border of anterior scalene m. to first rib
42
Q
- What are the branches off of the first part of the subclavian
A
- Vertebral a.
- Thyrocervical trunk
- Suprascapular a. (supplies supraspinatus and infraspinatus m.)
- Transverse cervical a. (Supplies trapezius m.)
- Inferior thyroid a.
- Ascending cervical a.
- Internal thoracic a.
43
Q
- What are the branches off the second part of the subclavian
A
- Costocervical trunk
- Supreme intercostal a.
- Deep cervical a.
44
Q
- What are the branches off the third part of the subclavian
A
- Dorsal scapular a. (supplies rhomboid m. and levator scapulae m.)
45
Q
- Common carotid a. branches into what?
A
- External carotid a.
- Internal carotid a.
- Carotid sinus
- Superior to bifurcation on internal carotid a.
46
Q
- Baroreceptors on the carotid sinus are innervated by what cranial n.?
A
- Glossopharyngeal n (CN IX)
- Indirectly modulates activity of the sympathetic and paraympathetic response to blood pressure
47
Q
- Identify the branches of the external carotid a.

A
- Superior labial a.
- Superior thyroid a.
- Superficial temporal a.
- Transverse facial a.
- Maxillary a.
- Posterior auricular a.
- Ascending pharyngeal a.
- Occipital a.
- Facial a.
- Lingual a
- External carotid a.
48
Q
- What pneumonic can be used to remember the branches of the external carotid a.?
A
- Some anatomists like freaking out poor medical students
- S-superior thyroid a.
- A-Ascending pharyngeal a.
- L-Lingual a.
- F-Facial a.
- O-Occipital a.
- P-Posterior Auricular a.
- M-Maxillary a.
- S-Superficial temporal a.
49
Q
- Identify the following arteries

A
- Infrahyoid a.
- Superior laryngeal a.
- Sternocleidomastoid branch of the superior thyroid a.
- Superior thyroid a.
50
Q
- What vascular structure is shown in the following image

A
- Ascending pharyngeal a.
- Supplies pharynx musculature
51
Q
- _ travels obliquely upwards and medially to greater horns of hyoid bone
- Curves down and forward, passing beneath stylohyoid and digastric m.
- Travels medially to hyopoglossal n.
- Runs deep to hyoglossus m.
A
- Lingual a.
52
Q
- What are the terminal branches of the lingual a.?

A
-
Deep lingual a
- Goes to base of tongue
- Runs with lingual n
- Lingual n-superficial to hyoglossus m
- Lingual a-deep to hyoglossus m
-
Sublingual a
- Sublingual gland and oral floor
- Lingual a
53
Q
- What artery:
- Arises in carotid triangle
- Runs beneath digastric and stylohyoid m (superficial to hypoglossal n)
- Enters groove on posterior submandibular gland
- Curves over body of mandible
- Runs obliquely past the nose
A
- Facial a.
54
Q
- What are the branches of the facial a.?
A
- Cervical branches
- Ascending palatine a.-pharyngeal wall, soft palate, pharyngotympanic tube
- Tonsillar branch-palatine tonsils
- Submental a and glandular branches
- Facial branches
- Inferior labial a.
- Superior labial a.
- Lateral nasal branch
- Angular a. (terminal branch)

55
Q
- What is the relationship between the facial artery and vein?
A
- Facial artery sits anterior to the facial v and is more tortuous
56
Q
- What artery:
- Arises in carotid triangle from posterior aspect of external carotid
- Runs upward and posterior
- Terminal portion runs with greater occipital n.
A
- Occipital a
57
Q
- What artery:
- Arises above digastric and stylohyoid m.
- Ascends posteriorly beneath the parotid gland along lateral side of head behind the ear
- Runs with posterior auricular n.
- What are the branches of this artery?
A

58
Q
- What are the branches of the maxillary a.?
A
- Middle meningeal a.

59
Q
- What are the branches of the mandibular part of the maxillary a?
A

60
Q
- Epidural hematoma
A
- Tear in the middle meningeal a. external to the dura mater
61
Q
- Subdural hematoma
A
- Tear of middle meningeal a. deep to the dura mater
62
Q
- What are the portions of the pterygoid part of the maxillary a.?
A

63
Q
Pterygopalatine part of maxillary a
A
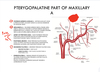
64
Q
- Which artery:
- Begins between TMJ and the ear
- Enters temporal fossa
- Terminates by dividing into frontal and parietal branches
- Branches run close to auriculotemporal n
A
- Superficial temporal a
65
Q
- What are the branches of the superficial temporal a.?
A
- Transverse facial a
- Middle temporal a
- Anterior auricular
- Terminal branches
- Frontal a
- Parietal a
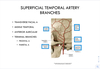
66
Q
- The internal carotid a. does not branch in the neck, but does enter cranial cavity thru _ part of temporal bone via _ canal
- It then courses anteriorly thru _ sinuses and runs in _ groove
- What are its branches?
A
- Petrous part of temporal bone via carotid canal
- Thru cavernous sinuses and runs in carotid groove
- Branches:
- Opthalmic a.
- Anterior cerebral a.
- Middle cerebral a.

67
Q
- Vertebral a. (branches off 1st part of subclavian a.)
- Runs thru _
- Takes a sharp turn between what two cervical vertebrae?
- This artery stretches with what movements?
A
- Vertebral foramen
- C1 and C2
- Rotation and extension
68
Q

A
- Posterior communicating artery
- Pontine arteries
- Anterior spinal a.
- Posterior cerebral a.
- Superior cerebellar a.
- Basilar a.
- Anterior inferior cerebellar a.
- Vertebral a.
- Posterior inferior cerebellar a.
69
Q
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
A
- Decreased posterior circulation due to intermittent vertebral a. occlusion
- From atherosclerosis
- During head rotation or extension
- Sx
- Syncope, vertigo, dizziness
- Double vision, loss of vision
- Numbness or weakness in hands/feet
- Slurred speech
- NV
- Loss of coordination or weakness
- Risk factors
- Smoking
- HTN
- Hyperlipidemia
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- > 50 years old
- Fam history
- Dx
- H&P
- CV and Neuro exam
- CT angiogram/MRA
- Tx
- Diet changes
- Cessation of smoking
- Lose weight
- Increase activity levels
- Bypass surg or endarterectomy
- Bloodthinners
- Meds for diabetes, HTN,etc
70
Q
- Subclavian Steal Syndrome
A
- Proximal stenosis or occlusion of subclavian a,
- Blockage causes reverse flow thru vertebral a of affected side to supply blood to upper extremity (decreases blood flow to brain)
- Sx
- Presyncope or syncope
- Different BPs in upper extremities
- Neurologic deficits or memory problems
- Causes
- Atherosclerosis
- Cervical rib
- Dx
- Doppler US
- CT Angiographt
- Tx
- Stent and Balloon angioplasty
- Endarterectomy


