Cervical Endocrine, Pulmonology and Gastroenterology Flashcards
1
Q

A
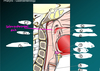
- Left lobe of the thyroid gland
- Right lobe of the thyroid gland
- Isthmus of the thyroid gland
2
Q

A
- Right lobe of thyroid gland
- Isthmus of thyroid gland
3
Q
Posterior view

A
- Left superior parathyroid gland
- Right superior parathyroid gland
- Left inferior parathyroid gland
- Right inferior parathyroid gland
4
Q
- Which cervical triangle contains the thyroid and parathyroid glands?
A
- Muscular triangle
5
Q
- Isthmus crosses below _ cartilage, much lower than thyroid cartilage
A
- Cricoid
6
Q
- Abberant thyroid gland can be seen anywhere along the _ duct
A
- Embryonic thyroglossal
7
Q
- Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
A
- Cyst forming across the thyroglossal duct as it descends into the neck
- May cause issues with the hyoid bone and need to be surgically removed
8
Q
- Accessory thyroid gland
A
- Additional thyroid glandular tissue forms in thyroglossal duct
9
Q
- Pyramidal Lobe of the Thyroid Gland
A
- Not always present
- May extend to hyoid
- Some exist in absence of thyroid isthmus

10
Q
- Thyroid Ima Artery
A
- 10% of people
- Unparied
- Can come off of
- Brachiocephalic trunk (most common)
- Arch of the aorta
- Right Common carotid
- Subclavian
- Internal thoracic
- Ascends on anterior surface of trachea and continues to thyroid isthmus
- Consider if this is present before doing tracheotomy
11
Q
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland is called _
A
- Goiter
12
Q
- Steps of a total thyroidectomy
A

13
Q
- Troubles of thyroidectomy
A
- Thyroid is in close proximity to recurrent laryngeal nerves
- Also usually dont take out parathyroids with it

14
Q

A
- Nasopharynx
- Fauces
- Oropharynx
- Laryngeal Inlet
- Laryngopharynx
- Esophagus
15
Q

A
- Soft Palate
- Uvula
- Fauces
- Isthmus of Fauces
- Fauces
- Palatopharyngeal arch
- Epiglottis
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Piriform recess
16
Q

A
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
17
Q

A
- Pharyngeal recess
- Choanae
- Nasopharynx
- Fauces
- Oropharynx
- Laryngeal inlet
- Laryngopharynx
18
Q

A
- Lingual tonsil
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Torus Tubarius
- Opening of the Pharyngotympanic tube
- Soft Palate
- Uvula
- Epiglottic Vallecula
- Epiglottis
19
Q

A
- Epiglottis
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Laryngeal vestibule
- Vestibular fold (aka false volcal cords)
- Laryngeal ventricle
- Vocal fold
- Infraglottic cavity
20
Q

A
- Epiglottis
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Laryngeal vestibule
- Vestibular fold
- Laryngeal ventricle
- Vocal fold
- Vocalis m.
- Conus Elasticus
- Infraglottic cavity
21
Q

A
- Epiglottis
- Rima glottidis
- Vocal fold
- Vestibular fold
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Cuneiform tubercle
- Corniculate tubercle
22
Q
- Aspiration of Foreign Bodies
A
- Involves any foreign body entering airway thru laryngeal inlet and trapped in vestibular folds
- Laryngeal muscles will spasm and prevent air from reaching the lungs
- Heimlich maneuver-forces air out of lungs and removes foreign body
23
Q
- Cricothyrotomy
A
- Typically emergent procedure
- Needle passes thru cricothyroid membrane
24
Q
- Tracheostomy
A
- Involves an incision thru skin, separation of infrahyoid muscles and removal of isthmus of thyroid gland
- Insert tube in trachea to establish airway
- performed on 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings
25
* ***How does puberty change the larynx?***
* ***How does aging change the larynx?***
Males at puberty-laryngeal cartilages will enlarge and grow anteriorly
Aging-ossification of laryngeal cartilages (seen on x rays)
26
* ***Laryngeal Cancer***
* Common among smokers
* Laryngectomy and tracheostomy performed during malignant cases
* Changes in vocalization (ie: esophageal speech)
27
1. Soft Palate
2. Uvula
3. Isthmus of Fauces
4. Palatoglossal Arch
5. Palatine Tonsil
6. Palatopharyngeal Arch
7. Epiglottic Vallecula
8. Epiglottis
9. Aryepiglottic Fold
10. Esophagus
11. Trachea
28
* ***Branchial fistula***
* Abnormal patency of remnants of the 2nd Pharyngeal Pouch and 2nd Pharyngeal Groove
* Results in a canal between the Tonsillar Cleft and side of the Neck.
* Food leak out of yo neck (ewie)

29
* ***Branchial Sinus***
* Persistance of embryonic cervical sinus
* Communicates externally but not internally
* May exist anywhere on the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid m.

30
* ***Branchial Cyst***
* Similar to a Branchial Sinus
* if the embryonic cervical sinus does not communicate externally it exists as a cyst
* These cysts may result in complicatoins due to their proximity to important structures of the Neck such as the Hypoglossal, Glossopharyngeal and Spinal Accessory nerves

31
* ***Tracheoesophageal Fistula***
* Esophagus is blind ended pouch
* Stomach communicates with trachea
* Blind ended pouch with no tracheal communication
* Esophagus with communication with trachea distal to epiglottis
32
* What is deglutination?
* Swallowing
33
* ***What are the stages of deglutination***
Stage 0: Eat and Chew
Stage 1 (Voluntary): Food bolus pushed to back of mouth by pushing tongue against palate
Stage 2 (Involuntary and Rapid): Nasopharynx is sealed off from oropharynx when soft palate is elevated; the pharynx shortens and widens when suprahyoid and longitudinal pharyngeal muscles elevate the larynx
Stage 3 (Involuntary): Pharyngeal constrictor muscles contract sequentially (creating peristaltic ridge forcing food bolus inferiorly); epiglottis deflects bolus but does not completely seal off the larynx and trachea


