Exam # 1 Flashcards
What is a muscle condition score?
measurement of muscling to determine if patient is adequate or has some muscle atrophy/ sarcopenia
What can cause iron losses in the body?
Chronic blood loss
- Internal parasites
- External parasites
- Tumors, Ulcers.
What is a Nutrient?
a substance that provides nourishment
essential for growth and the maintenance of life
What are the clinical signs of primary hyperlipidemia in dogs?
Does your course of treatment matter depending on the type of lipoproteins.
◦ Clinical signs:
‣ Pancreatitis
‣ Dystrophic changes
‣ Insulin resistance
‣ Hepatobiliary disease (mucocele)
‣ Seizures.
◦ There is no difference in clinical signs or approach to therapy according to the type of lipoproteins.
What dog breeds have more of a predisposition to zinc deficiency?
Northern breeds ( Husky/ Malamute)
Why is selenium important in canine and feline nutrition?
- Needed for testosterone and sperm function, as well as normal thyroid function.
What is the role of calcitriol?
- Calcitriol promotes elevation of plasma calcium and phosphate levels, which are required for mineralization of bone.
- Calcitriol stimulates intestinal
calcium absorption throughout the
entire length of the intestine - With PTH, calcitriol promotes mobilization of calcium from bone
- Increases reabsorption of calcium in the distal tubules in the kidneys
What is “sports anemia”?
Sports anemia is a type of non-
regenerative anemia in athletes where
protein intake is insufficient
What is the avian water requirement?
AVIAN: 2 ML/KG/HR
OR 48 ML/KG/DAY
What is vitamin E? What allows it to integrate into the cellular membrane?
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin but also has water solubility (amphipathic) which allows integration into cellular membranes
What are some clinical signs of an insulinoma?
Possible clinical signs:
• Lethargy
• pawing at the mouth
• weakness
• weight loss
• tremors/ seizures
• collapse
• abnormal behavior
In a cat on the 9 point BCS scale, what is the ideal body condition score?
5
Ionophores are toxic in which animals?
camelids and horses
Where can ruminants/ hindgut fermenters receive their cobalamin?
They can rely on their gastrointestinal microbiota for cobalamin if there is enough cobalt in diet.
What do vitamins differ in?
Solubility
What occurs in the stomach with non haem iron?
Some of the Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ in acid conditions of the stomach
What kind of fluids can be provided parentally to the patient
FLUIDS MAY BE ISOTONIC
(MOST COMMON),
HYPERTONIC OR
HYPOTONIC (SPECIFIC
INDICATIONS)
What can cause Heinz Body anemia?
Garlic/ Onion Ingestion
What is the normal specific gravity range for a goat?
1.015-1.045
What happens when minerals interact with each other?
Minerals may interact with each other, therefore the requirement for one mineral
may be impacted by the amounts of other minerals
- For example- divalent cation minerals may compete and decrease absorption of each
other (Zn2+; Ca2+; Mg2+ )
What is the Body condition score and what is it used for?
Body condition score (BCS): an indication of the energy status of an individual or a
group/herd
What can increase absorption of non haem iron?
Vitamin C
Why is energy required by animals?
– Basic metabolism
– Thermoregulation
– Activity
– Growth (young animals)
– Reproduction (females in reproduction)
What is failure to thrive?
Failure to thrive: a young (usually) animal that is in poor BCS and smaller size
What are the water soluble vitamins?
B vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, B12, biotin, choline), vitamin C
What would be indicated in test results with urine that has a low USG?
RENAL DISEASE, PYOMETRA, HYPERCALCEMIA, LIVER DISEASE, CUSHING’S DISEASE, ADDISON’S DISEASE, HYPERTHYROIDISM
Name two marine sources of common dietary fatty acids
◦ Eicosapentaenoic acid(EPA; 20:5) n-3
◦ Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 22:6) n-3
What product in excess can be detrimental to hindgut fermenters, why?
Excess simple sugars can be detrimental
in hindgut fermenters
• Starch and sugars not absorbed in the
small intestines reach the large intestines
• There it ferments and supports lactic
acid bacteria -> reduce pH
• This increases intestinal permeability and
is a risk for bacterial translocation,
enterotoxaemia, endotoxemia
• Can lead to gut stasis, laminitis in
horses, colic etc.
• In addition- excess sugars could lead
to obesity, increased blood insulin
and diabetes
What is released when an amino acid is deaminized?
• This releases ammonia
Give an example of essential fat synthesis
linoleic acid can be converted to arachidonic acid
◦ Cats have a slow enzymatic pathway for this, and so require arachidonic acid
How would a veterinarian diagnosis chylothorax?
includes physical exam findings (respiratory signs), radiographic changes and analysis of the fluid via thoracentesis
What does dietary protein provide?
Energy, essential amino acids, and nitrogen (to make non- essential amino acids)
Can you use/ is their benefit to using hydration drinks in veterinary medicine?
DEPENDS ON THE SPECIES
• HYDRATION DRINKS (W/ELECTROLYTES) ARE NOT USEFUL IN ANIMALS THAT
DO NOT SWEAT
Why would vitamin C increase absorption of haem iron?
acidic pH will cause the reduction of ferric (Fe3+) to ferrous (Fe2+) iron, which sees to be a requirement for the uptake of iron into mucosal cells.
What is the normal specific gravity range for a horse?
1.025-1.060
Which grains can cause rumen acidosis?
corn, wheat,
and barley
What do fat soluble vitamins require?
• These require dietary fat to be absorbed through the intestines
What is the function of lipoprotein lipase?
• Lipoprotein lipase breaks down the triglycerides and allows fat absorption in peripheral tissues
What other instance (in cats) may their be a deficiency of vitamin K?
Vitamin K deficiency has also been
described in cats fed a diet that contains
fish
- Mechanism is unclear
Therefore, fish diets in cats do require
vitamin K supplementation
What physiologic functions is protein important for?
- Enzyme activity/cellular function
- Barrier/skin function (deficient diet will cause skin to become brittle)
- Growth and reproduction
What occurs to blood volume with high sodium and increased plasma osmolarity?
• THIS INCREASES BLOOD VOLUME AS
FLUIDS SHIFTS EXTRA CELLULARLY • IT ALSO CONTRIBUTES TO THIRST AND
ACTIVATION OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS • CAN CAUSE INCREASED BLOOD
PRESSURE
What are probiotics? Prebiotics?
◦ Probiotics: beneficial microbial species
that can be provided to the organism and
support their health
◦ Prebiotics: compounds such as soluble
fibers that support a normal microbiome
What are the 3 types of vitamin K and where are they found?
Phylloquinone (K1) is present in
plants (leafy greens)
Menaquinone (K2) is produced by
the gut bacteria [this is why most
foods do not require added vitamin
K]
Menadione (K3) is a synthetic
supplement
What can the carbon skeleton of deaminized amino acids be used to make?
• The carbon skeleton can be used to make glucose or acetyl
CoA (fatty acid pathway)
What B vitamin is Pyridoxin?
B6
What is the equation for the metabolic energy requirements for the obese prone adult dog?
1.4X RER
What is the importance of linoleic acid?
◦ Immune function
◦ Skin barrier function
What is Isosthenuria?
USG of ~ 1.008- 1.012
TRUE OR FALSE: Visual inspection is not enough to make determination on BCS and you must palpate the patient.
TRUE
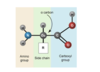
What is the structure of an amino acid?
Amino acids have an amine group and a carboxyl group
• The side chain determines which amino acid it is
What are the units of energy?
Calories and Joule
In anaerobic metabolism, what is pyruvate metabolized to? What is formed by this?
Lactic acid
- 2 ATPs
What ROS are produced by normal cellular respiration?
Superoxide radical
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydroxyl radical (OH-)
What is a body temperature that is concerning and potentially dangerous? What organs can be affected?
Body temperature > 104.
Intestines and kidneys are susceptible.
What is vitamin D? What are the roles of vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is involved in calcium, phosphorus and
bone metabolism.
Vitamin D has many additional roles and in fact has a nuclear vitamin D
receptor
- A transcription factor that regulates the expression of more than 900 genes
- Many animal species can use UVB light to synthesize vitamin D3
Why are some antibiotics lethal in rabbits?
This is because it changes their microbiome and the changes they are too sensitive too and cannot overcome.
What are signs of the patient being underweight in young animals?
- Higher susceptibility to disease
- Infectious > metabolic
- Poor response to medical treatments (unless nutritional status is corrected)
- Stunted growth, poor hair coat.
What causes fatty acid synthesis or lipogenesis? Why does this occur?
Acetyl CoA. Excess glucose and carbohydrates
Alpha linolenic acid can be transformed into?
In what species does this occur in?
◦ May be transformed to long chain omega-3 fatty acids in some species (not much in dogs and cats)
What is important to remember about taurine and cats?
Cats are very inefficient at converting methionine and cystine to taurine so we still have to supplement it in their diets.
Do carnivores easily convert Vitamin A? Why?
Carnivores have more trouble converting Vitamin A since they are eating herbivores who have already transferred it into Retinol
What are indicators of dehydration you can see on a physical exam?
- Change in body weight
- Mucus membrane character
- CRT
- Skin Turgor
- Heart Rate
- Respiratory Rate
- Pulse quality
- Urine output
- Blood pressure
What are poly unsaturated fatty acids? Where are they found?
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are a component in the phospholipids that
compose cell and organelle membranes
What are the two forms of MCTs?
Synthetic or purified
What determines cattle daily water requirements?
Age and production
In hindgut fermenters, where does bacterial fermentation occur?
In the cecum and colon
What is the normal specific gravity range for a pig?
1.010-1.050
What are the water soluable vitamins?
Vitamin B and C
What are the essential amino acids?
- Arginine
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
- Taurine (cats)
What are the three recognized types of diabetes mellitus?
• Type I (insulin-dependent): lack of insulin
production common form of DM in dogs
• Type II (noninsulin-dependent): peripheral
insulin resistance; found in cats (not dogs)
• Type III results from diabetogenic hormones
(progesterone, cortisol, epinephrine, growth
hormone, glucagon)
What are the consequences of iodine deficiency?
Iodine deficiency would result in an enlargement of the thyroid gland= goiter + decreased thyroid function. Can obstruct airways and be a life-threatening emergency!
What is important to remember about protein requirements of cats?
• Obligate carnivores such as the cat have
higher protein requirements than many
other species
• Cats cannot regulate deamination of
amino acids- even when protein intake
is low!
What is the treatment for a glucagonoma?
Treatment:
- Limited (surgery is treatment of choice)
- Risks for post-op pancreatitis
- SND: Skin lesions respond to supplementation with amino acids either enteral or parenteral

What forms urea?
Nitrogen and hydrogen
What are the clinical signs of Intestinal Lymphangiectasia?
‣ Chronic diarrhea
‣ Weight loss
‣ Protein loss (Protein losing enteropathy= PLE)
• Low albumin
• Ascites/pleural effusion
‣ Low calcium and vitamin D
• Seizures/tremors/ataxia/lethargy
• Face rubbing
Secondary hyperlipidemia affects what equine breeds?
◦ Ponies
◦ Miniature horses
◦ Donkeys
◦ Less common in standard adult horses
◦ Common in overweight ponies during negative energy balance
What is transported to the liver during fat digestion and absorption?
The remnants of chylomicrons.
What is primary reason for zinc deficiency?
Not enough zinc in diet.
What are DIP’s?
• This is called Degradable
intake protein (DIP) (usually
highly soluble protein) that is metabolized by microbial organisms.
What can BCS indicate?
Over-conditioned vs. Under-conditioned
Describe the chemical structure of MCTs
• These are triglycerides with a hydrocarbon tail chain of 6-12 unlike other fats carbons.
TRUE or FALSE: Many forages in the US are adequate at meeting copper requirements in live stock
FALSE:
Many forages in the US are inadequate to meet copper requirements in livestock
Copper supplementation is common in many feeds for production animals in the US, Australia, NZ
Where are VLDL and LDL formed? What happens after their formation?
• VLDL and LDL are formed in the liver from triglycerides and cholesterol and are transported from the liver to peripheral tissues LDL also returns to the liver and cleared from the blood stream
What are the metabolic costs?
digestion, gas, urine production
What is the treatment for chylothorax?
‣ Emergency: chest tube to relieve pressure on the lungs
‣ Surgical: such as thoracic duct ligation
‣ Non-surgical: low-fat diet may reduce the lipid content of the fluid and may help it reabsorb in the pleura
‣ Nutraceutical: Rutin is a medication that may stimulate macrophages and help break down the protein in the fluid.
What is the equation for the metabolic energy requirements for the obese prone adult cat?
1.2X RER
How is VLDL formed?
‣ assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins
What are dietary protein sources?
- animal protein (meat, dairy, egg)
- Plant protein (legume, grain)
- Microbial protein
What is Iron used for ?
Essential for hemoglobin
What is the equation for the metabolic energy requirements for the intact adult dog?
1.8X RER
Where is taurine found in the body? Where are they not found?
- Taurine is present in high amounts in muscle protein and heart tissue
- It is not present in high amounts in plants commonly used as ingredients in pet food such as legumes and grains
How is protein broken down? and where are these products absorbed?
• Protein is broken down to smaller
peptides, amino acids
• Amino acids are absorbed via
transporter
What can destroy carotenoids?
Storage heat or direct sunlight.
What are fat soluble vitamins at risk for? Explain why.
• Since these are fat soluble and not water soluble, there is higher risk for excess
What is the risks of using too much NPN’s
Encephalitis/ Neuro signs
Never feed raw whole soybeans and urea together! Soybeans contain an enzyme called urease which breaks down urea into ammonia
What are sources of carbohydrates for omnivores/ carnivores?
Fruits and veggies in dog food.
What are some other indications of dehydration in diagnostic testing?
- PVC/TS
- Decreased size of Vena cava on Radiographs ** Severe dehydration
- USG
- Lactate
- BUN/Creat
- Osmolality
What occurs with amino acids when no additonal protien is needed?
When no additional protein is required, or when some essential amino acids to build protein are missing, amino acids can be deaminized
Are lipids polar or non-polar? Therefore they are?
Non-polar and are therefore water insoluble.
When is there water loss in the body?
Normal physiologic activities.
What are the clinical signs of diabetes mellitus?
Clinical signs:
• PU/PD
• Weight loss
• Polyphagia
• Lethargy
• Cataracts (dogs)
What percentage of haem iron is absorbed?
Depending on the individuals iron stores 15-35% of haem iron is absorbed.
What is a primary reason dogs have zinc deficiency?
Diets that are unbalanced or poor quality
Where is there an issue with storage and carotenoids being destroyed?
In developing countries if hay is stored improperly.
What is vitamin A important for?
Epithelial health
What clinical signs would you see in a dog with zinc deficiency? Is this permenant?
Hyperkeratosis around the eyes, elbows and joints
Usually resolves when they receive the adequate amount of zinc (Ie diet change or supplementation)
EPA and DHA are sourced from?
Marine source
What is the formula for water requirements for cats?
Cat: 70 x Bw(kg)^0.75
Alternate: 80xBW(kg)^0.75
What can cause a protein to have a low biological value?
Protein with low biological value may provide amino acids that will be deaminated and form ammonia and then urea
What is biological value? What impacts it?
- Biological value is the ratio between the amount of protein absorbed from the GI tract and the amount of protein that is retained in the body
- This may be impacted by the relative concentrations of amino acids to form a complete protein
What are symptoms of energy deficiency?
- Weight loss
• Loss of internal organ mass
• Decline in healing, immune function
• Shift to use of protein and fat stores for energy
What is the result of high sodium on plasma osmolarity?
It results in high plasma osmolarity.
What are common forms of malnutrition?
- Overall energy and protein malnutrition-
Marasmus
◦ Protein malnutrition-Kwashiorkor (energy is
sufficient)
◦ Any nutritional deficiency is malnutrition
What is the importance of arachidonic acid?
◦ Important for immune function and primarily for reproductive success in queens
Why are milk replacers often used instead of whole milk, and what is the risk/ downside when doing that?
- Milk replacers are often used instead of whole milk for monetary reasons (cheaper) ($)
• But… vegetable protein is unlike casein - Therefore it does not curd with rennet
- The excess protein reaches the lower intestines, and can cause diarrhea and overall increased costs on veterinary treatments
What are vitamins?
Vitamins are organic compounds that
have various functions
Some vitamins are essential in certain
species and not others
Vitamins differ in their solubility:
water soluble vs. fat soluble
Are carbohydrates essential nutrients for cats/dogs?
No
Prolonged hypoxia can lead to what issue? What can this effect? What should you evaluate?
Prolonged hypoxia-> lactic
acidosis
• Can have negative effects on
cardiac function, enzyme
function
• Can be very serious and life
threatening
• What to evaluate: blood
pressure, respiratory function,
oxygenation
What can cause zinc deficiency in livestock and pets?
Zinc depleted soils
Define macronutrients. They are required in?
Macronutrients are carbohydrates, fats, and protiens.
Required in large amounts.
What is the most common reason for hyperlipidemia? Explain
Post prandial
- Increased chylomicrons causing hyperlipidemia
What is important about monitoring patients while they are receiving fluids?
• PATIENTS ON IV FLUIDS SHOULD
BE MONITORED TO ENSURE
THEIR REHYDRATION IS
PROGRESSING AT AN
ACCEPTABLE PACE.
What is diabetes mellitus? Is it common? What is a hallmark sign?
• Diabetes mellitus is characterized by
absolute or relative deficiency of insulin
• It has been reported in dogs and cats, and is
less common in horses and ruminants and
uncommon in rodents, lagomorphs and
birds
• The hallmark of DM is abnormal blood sugar
What is folate required for?
is required for nucleotide synthesis. Important for rapidly dividing
cells
What B vitamin is cobalamin?
B12
What occurs when oxygen is restored after anaerobic metabolism?
When oxygen is restored,
lactate can be metabolized
back to pyruvate in the
liver
What is the average heat of combustion for one gram of each of these: Lipid, Carbohydrate, Protein?
Lipid: 9.4 kcal/g
Carb: 4.2 Kcal/g
Protein: 5.65 kcal/g
Describe the stages of fat digestion:
◦ Stage 1: fat is emulsified with bile acids
‣ bile acids have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains
‣ the hydrophobic portions of bile acids interact with the lipid, and the hydrophilic domains remain at the surface
◦ Stage 2: hydrolysis of triglyceride into monoglyceride and free fatty acids by pancreatic lipase
‣ PL is water soluble, therefore stage 1 is required
◦ Stage 3: reformation of triglyceride molecules in the enterocytes in the small intestines
◦ Stage 4: the triglycerides are packaged with phospholipids, cholesterol, and protein (specifically, apoprotein B) to create chylomicrons
◦ Stage 5: chylomicrons are absorbed through the lymphatic vessels in the intestines which drain into the thoracic duct
◦ Stage 6: the thoracic duct is drained into the jugular vein
What do ionophores favor?
Ionophores favor propionate production
What are essential amino acids?
Essential amino acids are nutritionally required in amounts
the animal cannot synthesize on its own
What is the chain of events of cellular damage due to lipid peroxides?
- Phospholipid bilayers are excessively permeable which will disrupt normal cellular and organelle function. Excessive damage can lead to cellular death.
What will reactivate vitamin C?
Vitamin C, in turn, is reactivated by a selenium-containing enzyme, thioredoxin reductase
What is a balance diet?
a diet that provides all needed
nutrients in sufficient amounts and not in excess of
known safety limits
What is equation for resting energy requirements?
70 x BW(KG)^0.75
What is the function of ADH? What occurs in the absence of ADH? What is a condition that can cause Absence of ADH or resistance of ADH?
• ACTS TO INCREASE THE PERMEABILITY IN THE TUBULAR CELLS SO THAT
WATER IS ABSORBED AS THE INTERSTITIAL OSMOLALITY IS HIGHER THAN THE
FILTRATE • IN THE ABSENCE OF ADH (CENTRAL DIABETES INSIPIDUS) OR IF THE TUBULES
ARE RESISTANT TO ADH (NEPHROGENIC DI) URINE WILL BE DILUTE
What occurs with proteins of low digestibility?
Protein with low digestibility (regardless of its biological value) ferment in the large intestines and release ammonia that may be absorbed
• Excess low digestibility protein -> diarrhea, increased ammonia and urea
What factors can affect feed quality?
Graze:
Inadequate quantity
Overgrazing
Drought
Insufficient feed for physiological state or activity
Poor facilities- feeder space, cleanliness Extruded/pelleted/canned food:
Poor digestibility
Poor bioavailability
Unbalanced foods
What occurs in warfarin posioning and how would you treat it?
Vitamin K treatment is required in anticoagulant (warfarin) poisoning
- Inhibits vitamin K dependent clotting factors
What fatty acids are not attached to glycerol?
Free fatty acids or non-esterefied fatty acids (NFA)
What is one concern for a patient who is dehydrated?
Increased risk of overheating. Water loss in urine and evaporation is accelerated with exercise.
Why is supplementation of vitamin K not required in normal circumstances? What circumstances will you need supplementation? Why?
Since menaquinone is synthesized by the gastrointestinal microflora,
supplementation is only required in specific conditions
- Rodenticide toxicity (warfarin)
- Severe liver or intestinal disease
- In livestock- moldy sweet clover (contains dicumerol) ( fungal organisms can metabolize cumerin to dicumerol)
- These compounds interfere with the synthesis of the vitamin K dependent clotting
factors
What can occur with overhydration?
- OVERHYDRATION IS MOST OFTEN IATROGENIC
• CAUSED BY EXCESSIVE IV FLUID ADMINISTRATION
• CAN BE EVEN MORE DETRIMENTAL THAN DEHYDRATION
What increases the requirement for vitamin E? Why?
The requirement for vitamin E increases with dietary fat and PUFA
The requirement is also coupled to selenium (as it is needed to reduce the oxidized vitamin E)
More Polyunsaturated acids, more sites vulnerable to oxidation. So more vitamin E is needed to donate their hydrogen atom to neutralize the compounds that will oxidize.
Ionophores are safe in which animals?
Ionophores are safe in cattle, sheep, goats
What is the role of B vitamins and what is the consequence of thiamine deficiancy?
B vitamins are vital for cellular energy metabolism . The brain has a high demand for
energy. Cats with thiamin deficiency have
characteristic neurological signs (head drop) and cardiac signs. Diet change can resolve symptoms ( raw fish/shellfish diet can cause this)
Thiaminase can also be a problem in ruminants. Changes of rumen microflora as a result of diet change or intake pattern can cause an increase in growth of Bacillus thiaminolyticus This can cause neurological signs in ruminants:
aimless wondering, stargazing, blindness
ie. CCN: Cerebral-cortical necrosis /
polyencephalomalacia
What is zinc?
- Zinc is an essential mineral required
in the diet in micro amounts - Zinc is a cofactor for the enzyme
Super Oxide Dismutase (SOD) that is
important as it catalyzes the
dismutation of superoxide radicals
(O2−) to molecular oxygen (O2) and
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), providing
cellular defense against reactive
oxygen species
What combination can cause rumen acidosis?
Ionophores and Grain
List the types of fat soluble vitamins
A, D, E, K
What form is Vitamin A found in?
Vitamin A is found in the form of retinol (retinoic
acid) and beta carotene (provitamin A)
What is the absorption rate of non haem iron?
2-20%
Define hyperlipids/hyper lipoproteins/dyslipidemia
Increase in triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
What makes a lipoprotein smaller?
Density
What aids milk volume and where does it come from?
lactose aids milk volume, lactose comes from glucose.
In what situation can lipids be helpful (nutrition)?
Lipids could help animals with low appetite meet their nutritional requirements.
TRUE OR FALSE: Some minerals in excess can lead to adverse effects?
TRUE
What feed contains carbohydrates that bypass the rumen? Where are they digested instead?
Many carbohydrates in brewer’s and
distiller’s grains bypass the rumen
• They arrive in the small intestine,
where pancreatic amylase completes
digestion
- Any undigested carbohydrate and
fiber reaches the colon and the gut
microbes get a ‘second chance’ to
ferment it
In hindgut fermenters, where are sugars and starches ingested?
Sugars/ starches are ingested in the
small intestines
Where is retinol stored?
Retinol is stored in the liver and kidneys
What can be supplemented to help increase the production of clotting factors
Vitmain K3
What foods contain high amounts of arachidonic acid?
Animal fats such as Chicken and eggs
What can be metabolized from linoleic acid?
Arachidonic acid
What clinical signs can you see in patients with vitamin A deficiencies?
can cause brittle nails/ skin, higher incidence of ulcers.
What are drivers of palatability in omnivores and carnivores?
Protein and amino acids are also drivers for palatability in omnivores and carnivores
What do vitamins do in regards to enzyme activity? what other effects can they have within the body?
Many vitamins act as cofactors for enzyme activity, and some have effects such as being methyl donors, as well as gene translation and activation
What occurs to non haem iron / Fe3+ in the small intestines?
Some Fe3+ forms insoluble complexes at high pH of small intestine, lowering absorption rates and increasing excretion.
Name three plant sources of common dietary fatty acids
◦ Alpha linolenic acid (18:3)n-3
◦ Linoleic acid (18:2) n-6
◦ Oleic (18:1) n-9
Where is selenium deficiency in cattle/ livestock found most commonly? Why?
- cattle/livestock raised on selenium poor soil
ie: Soils formed from volcanic activity, soil that pre-dates cretaceous period
ex: Pacific
Northwest, Northern California
Northeastern United States and Eastern Canadian
provinces
What is important about leucine? What does it do? Where is it found?
Leucine is special among the BCAAs because it promotes muscle-protein synthesis
• Leucine is abundant in meat, and no evidence that supplementation beyond the requirement is helpful for muscle hypertrophy
What is important for management of renal and hepatic diseases?
Dietary:
- Reduced protein • Protein of high biological value and digestibility
• As a result- less protein reaches the large intestines, and less amino acids undergo deamination and less ammonia and urea are formed
Medications:
• Lactulose is often included in therapy of dogs with hepatic disease
What percent of moisture is found in dry food?
10% moisture
What are the Atwater factors for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates?
Standard Atwater Factors are:
– Protein (1 g)= 4 kcal ME
– Fat (1g)= 9 kcal ME
– Carbohydrate= 4 kcal ME
(Use this for human food)
Each point on the BCS scale is what percentage difference?
10% difference
What are the goals of therapy for DM? What is the therapy recommended?
The goals of therapy are:
• resolve clinical signs (pu/pd)
• Improve blood glucose
• Avoid complications (cataracts, pancreatitis)
Therapy:
• Insulin replacement (avoid hypoglycemia)
Dietary therapy:
• Dogs: high fiber, routine of food before insulin is provided, lower fat
• Cats: some respond to low carb diet. If overweight -> weight loss
What are fatty acids prone to?
Rancidity and oxidative damage.
What are morphometric measurements?
Measurements of various body parts to assess very overweight pets and monitor progress
What can be used as an alternate source of alanine? When does this occur?
- The muscle can be used as a source of alanine that is metabolized to glucose in the liver
- This occurs during starvation/inadequate energy intake
What is malnutrition?
poor diet/ poor nutrition
Define hypertriglyceridemia
increased blood triglycerides.
How do you calculate the water needed for a patient with a feeding tube?
1 ml/ 1 kcal consumed. Water should be added up to total per day and subtract what you are using to flush the tube and make the slurry.
What substances can be in parental fluids?
May provide water, electrolytes, glucose and sometimes, vitamins.
What, other than the body, can synthesize essential fats?
Gut microbes
E.g.
Where are UIP’s digested then?
• Much protein is then digested by abomasal acid and enzymes and the rest by pancreatic enzymes
- The amino acids are then absorbed in the small intestine as in monogastric species
What is copper? What can you see with copper deficiency?
Copper is a strong oxidant. In copper deficiency you can see anemia, decreased immune function.
Can also cause hypopigmentation ( since it is a cofactor for tyrosine which then cant convert to melanin)
Can also cause physitis, inflammation and abnormal maturation of the growth plates ( since it is a cofactor for lysyl oxidase, an enzyme important for collagen maturation)
What syndrome can be caused by a glucagonoma?
Can also cause a syndrome called superficial necrolytic dermatitis (SND)

List the different types of lipoproteins:
Chylomicrons
HDL
LDL
IDL
VLDL
What percent of the weight of amino acids accounts for nitrogen?
16%
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
What is intestinal lymphangiectasia?
What is the cause?
What species is it reported in?
- Pathologic dilation of intestinal lymph vessels
- May be the result or the cause of another enteropathy
- Reported in dogs, rare in cats and horses.
What is the calculation for metabolic body weight of an animal?
BW(kg)^0.75
Peroxidized PUFA’s can cause what?
Further oxidative damage
What can you see with vitamin D deficiency?
- Abnormal growth plate closure
- Long bone deformity
- Lack of mineralization
List the oils that are high in Linoleic Acid
Corn oil, safflower oil, walnut oil, canola oil, cottonseeed oil.
What is B12 important for?
important for nucleotide synthesis, contains cobalt
Disturbance in chyle flow can be caused by:
heart disease, enlarged thyroid, vena caval obstruction/thrombosis, heartworm disease, diaphragmatic hernia, lung lobe torsion, and neoplasia
What can you rule out in primary hyperlipidemia?
◦ Rule outs:
‣ Post prandial sample (must be fasted!)
‣ Underlying metabolic disease
How would you diagnose primary hyperlipidemia
◦ Diagnosis:
‣ Elevated serum triglycerides
‣ Elevated cholesterol
‣ Moderate hypertriglyceridaemia (not hyperchoelsterolaemia) can be suspected based lactescent serum/plasma.
What is the formula for Water requirements for dogs?
Dog: 70 x Bw(kg)^0.75 Alternate formula ( 132 x Bw (kg)0.75 per 24 hours
What will likely cause the issues seen in this image?

Zinc hyperkeratosis, crusts, fissures and bleeding.
Zinc deficiency
What is the equation for the metabolic energy requirements for an adult neutered cat?
1.4X RER
What are colloid fluids?
Provide osmotic substance such as starch, albumin, gelatin
What percentage of the body is water? What can change the water percentage?
60% of the body is water ( may change with age, nutritional status, hydration)
What are the modified Atwater factors?
Modified Atwater Factors are:
– Protein (1 g)= 3.5 kcal ME
– Fat (1g)= 8.5 kcal ME
– Carbohydrate= 3.5 kcal ME
(use this for dog food)
What is density determined by?
• Density is determined by the relative concentrations of triacylglycerols (lighter= more TG) and proteins and by the diameters
What is energy?
the property of
matter and radiation which is
manifest as a capacity to perform work (such as causing motion or the interaction of molecules)
What is an Insulinoma? What does it cause? Is it common? Is it benign or malignant?
Beta islet cell tumor of the pancreas
• Has been reported in dogs, cats (rare),
ferrets, and have been rarely reported in
horses and cattle
• May be malignant (dogs), or benign
(sometimes in ferrets)
• Excess insulin -> hypoglycemia
In hindgut fermenters, where are VFA absorbed?
Through gut wall
What happens in rumen acidosis?
Rapid generation of volatile fatty acids which leads to a drop in rumen pH. Less chewing time and less saliva produced/ less salivary bicarb to buffer acids produced. This leads to acidosis (acid burn)
Primary hyperlipidemia in cats
Cats: (rare) inherited fasting hyperchylomicronaemia
‣ autosomal recessive disorder resulting from reduced LPL
What is required to activate vitamin D? How must dogs and cats receive vitamin D?
Vitamin D activation requires a functioning kidney. Reduced activation in kidney disease
Dogs and cats cannot synthesize vitamin D in the skin (no precursor), so it must be provided in the diet
What is Taurine?
- A unique sulfur amino acid
- It is a free amino acid (not part of a protein)
- Can be synthesized from other sulfur amino acids: methionine and cysteine
- Considered essential in cats and human infants
- Present in high concentrations in the retina and cardiac muscle
• Also conjugated to bile acids
What is the treatment for an insulinoma?
Treatment:
• Glucocorticoids (prednisone)
• Diet:
• Aim to reduce insulin secretion
• Small number of meals
• Low in simple carbs
• High fat
• High protein
In aerobic metabolism, how many ATP’s are made from 1 glucose?
38 ATPS
What hormones promote glycogenolysis?
epinephrine, glucagon, and cortisol
What lipoproteins made up of?
• Made up of droplets of fats surrounded by a single phospholipid layer
What occurs with Haem iron in the stomach?
Haem containing iron in Fe2+ form is hydrolyzed from protein ‘globin’ component
What can occur in patients with a taurine deficiency?
- Taurine deficiency can cause heart disease and blindness
• Should not occur in species where it is not an essential amino acid
(other than cats)
Define linoleic acid
◦ An essential omega-6 fatty acid (dogs and cats)
When would gluconeogenesis be needed?
• Normal state in some species
(cats)
• Stress
• Physical activity
• Lactation (milk production
requires much glucose)
• Gestation- fetus and placenta have
an obligate demand for glucose
What is non haem iron?
Non Haem Iron is from plants and is in the oxidized Fe3+ (ferric) form.
Where can medium chain triglycerides be found?
• MCTs can be found in palm kernel oil, and in small amounts in coconut oil
What are the important functions of vitamin A?
- Maintain normal epithelial function
- Maintain immune function
- Vision
What is an example of tests done for a workup of PU/PD?
WOULD INCLUDE A URINALYSIS (URINE TEST) AS A FIRST-TIER TEST
( Urine can be free catch unless, being also sent for culture.)
What is the equation for the metabolic energy requirements for the adult neutered dog?
1.6X RER
What can you see with excess of copper?
Copper excess stores in the liver, can
cause liver failure in some cases
Copper hepatopathy- Certain breeds are more predisposed to copper hepatopathy.
What can can cause dietary inhibition of zinc absorption?
- Gi Disease
- excess calcium, copper, or
phytates)
What are species can develop hyperlipidemia ?
Alpacas and llamas
What are sources of of vitamin E?
Vitamin E is synthesized by plants. High amounts in leafy greens, but also in seeds. Found in herbivore fat tissue (for carnivores) Many oils/ supplements would have tocopherols as preservatives.
Anemia caused by Iron deficiency is called?
Microcytic Anemia
Name two animal sources of common dietary fatty acids:
Palmatic acid (16:0) Stearic Acid (18:0)
Endogenous lipid abnormalities terminology?
Post-prandial: Most common reason for hyperlipidemia
• Increased chylomicrons causing hyperlipidemia
• Secondary hyperlipidemia:
• Renal disease
• Diabetes
• Cushing’s disease
• Hypothyroidism
• Negative energy balance in overweight animals (horses)
- Primary hyperlipidemia:
- Genetic/familial
What is ADH?
Antidiuretic hormone
What does normal cellular respiration generate?
Normal cellular respiration generates several oxidant compounds- reactive oxygen species (ROS)
What are clinical signs of Carotenoid deficiency?
- night blindness (nyctalopia) - visual
pigment deficiency - Xerophthalmia (dry eyes; corneal
opacity)
In aerobic metabolism, what does glycolysis produce? What does this product need to enter mitochondria?
Pyruvate
needs sufficient oxygen
What are some things you can see in patients who have eaten rodenticide?
Spontaneous bleeding
epistaxis
petichie
What can interfere with copper absorption?
High sulfur or high molybdenum soil may interfere with copper absorption
Also Thiomolybdate complexes with dietary copper ions
Where is Phytic acid high?
Phytic acid is high in beans that are often used as pig feed
What animal related factors would lead to animals becoming underweight?
Low social status
Illness
Dental/periodontal/oral disease
Foreign body- GI obstruction
Neurological disease
Musculoskeletal disease (ie inability to swallow)
GI disease
Liver disease
Kidney disease
cancer
Lameness
Young/timid
• Protein losing nephropathy (nephrotic syndrome)
◦ Hypercholesterolemia develops with hypoalbuminemia
◦ Metabolic pathways to synthesize cholesterol are stimulated when hepatic albumin synthesis increases.
What diseases are secondary to diseases that affect lipid and energy metabolism?
◦ Cushing’s disease
◦ Hypothyroidism
◦ Diabetes mellitus
◦ Pancreatitis
◦ Obesity
◦ Hepatic Disease
◦ Treatment: treat underlying condition.
What is the goal when feeding dairy cows?
The goal when feeding dairy cows should always be to maximize microbial amino acid production as much as possible and then, supplement with additional amino acids which are expected to escape rumen fermentation.
Which has more bioavailability, Haem or non haem iron?
Haem iron
How much weight gain is needed to see 1 unit of change in horses?
16-20 kg bw gain
How many amino acids are there that are used as building blocks of proteins?
There are 20 amino acids that are used as building blocks
for protein or used as free amino acids
What is the other name of white muscle disease?
Zanker’s necrosis
What are the treatments for overhydration?
- D/C FLUIDS • DIURETICS • OXYGEN
What monitoring should be included when monitoring a patient on IVF?
• CLINICAL SIGNS OF DEHYDRATION
• TPR • BODYWEIGHT
• IF POSSIBLE- URINE PRODUCTION AND URINE
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
• AUSCULTATION
• MUCUS MEMBRANE COLOR
• PCV/TS
• BLOOD PRESSURE
How is crude dietary protien analyzed?
Kjeldahl method
• This method provides the weight of nitrogen out the entire amount of matter analyzed
How is protein digested and absorbed in hindgut fermentors?
- Highly digestible protein is absorbed similarly to omnivores in the small intestines
- Only limited microbial protein can be absorbed in the large intestines
- Therefore, hindgut fermenters require dietary protein and essential amino acids in their food (more so than foregut fermenters)
What are signs of protien deficiency in pateints?
Protein deficiency: hypoalbuminemia -> decreased oncotic pressure ->
ascites/effusion
How do mammalian neonates cause milk protein to clot in the stomach? What does this clot do?
- Mammalian neonates have rennet, an enzyme complex (pepsin, lipase, rennin) that causes milk protein (casein) to clot in the stomach
- The process also requires acid and calcium
- The clot stays in the stomach and gradually dissolves
What is the concern with increased drinking and urination?
- POLYURIA AND POLYDIPSIA (PU/PD) IS AN IMPORTANT CLINICAL SIGN IN SEVERAL DISEASES
- IT CAN ALSO INCREASE THE RISK FOR DEHYDRATION
- THIS CAN BE THE RESULT OF PRIMARY POLYDIPSIA OR A DECREASE IN THE RENAL ABILITY TO CONCENTRATE URINE (FOR A VARIETY OF REASONS) WHICH RESULTS IN INCREASED WATER INTAKE
What degree of dehydration will the patient begin to exhibit clinical signs of dehydration?
5%
What is the typical specific gravity of a cow?
1.030-1.045
What process is occuring when these PUFA are exposed to ROS?
Lipid peroxidation
Define a triglyceride.
A triglyceride is fatty acids linked together to a glycerol backbone.
What can be added to pig diets to enhance zinc availability?
Phytase can be added to pig diets to enhance zinc (and phosphorus) availability
In 2020 how much income was made from Pet food?
92.66 billion
What is the equation for the metabolic energy requirements for an intact adult cat?
1.6X RER
What is the main hormone responsible for shifting between gluconeogenesis and glycolysis?
Glucagon
Also: Cortisol and epinephrine (to provide glucose during stress)
Define arachadonic acid
◦ An essential omega-6 fatty acid in cats
What are the non essential amino acids?
- Alanine
- Asparagine
- Aspartate
- Cysteine
- Glutamate
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Hydroxyproline
- Proline
- Serine
- Tyrosine
What requires more nutrition per its body weight? A larger animal or a smaller one?
Smaller animal
Where is Haem Iron from?
Meats and fish
When may a taurine deficiency be problematic for patients who are not felines?
- Low methionine and cysteine intake
- Low methionine and cysteine bioavailability/ digestibility/ transformation
- High taurine loss
What are the steps to water intake regulation?
• INCREASED OSMOLARITY IN THE BLOOD -> OSMORECEPTORS THAT STIMULATE
THE HYPOTHALAMUS DIRECTLY OR THROUGH RELEASE OF ANGIOTENSIN II • THE RENIN–ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM INCREASES THIRST AS A WAY TO INCREASE
BLOOD VOLUME
• ACTIVATED BY HIGH PLASMA OSMOLARITY, LOW BLOOD VOLUME, LOW BLOOD
PRESSURE, AND STIMULATION OF THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
• THE ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE (ADH) IS IMPORTANT TO CONSERVE WATER IN
THE FACE OF DEHYDRATION
• A LACK OF RESPONSE TO ADH IN THE TUBULES, WOULD LEAD TO DILUTE URINE
AND DEHYDRATION
EPA and DHA are what type of fatty acid?
Long-chain omega-3 fatty acid
Primary hyperlipidemia is?
Genetic/familial
What varies in fatty acids?
Fatty acids vary in number of carbon double bonds that are not saturated with hydrogen (C=C)
What is vitamin E and selenium deficiency called?
vitamin E and selenium deficiencies are called
‘white muscle disease’
What increases lactose?
Propionate
What are the branch chain amino acids?
Valine, leucine and isoleucine
What is Pyridoxin required for?
important for protein synthesis
What is a glucagonoma? Is it common? And what is the cause?
Glucagonoma is a neoplasm of
alpha pancreatic islet cells
• Rare overall: reported in dogs
but not cats. One report exists in
a jaguar and in a horse
• Excess glucagon is antagonistic
to insulin, can cause clinical signs
similar to DM
Primary hyperlipidemia in dogs:
Hereditary
‣ Miniature Schnauzers
‣ Briard
‣ Beagle
‣ Sheltie
‣ Doberman
‣ Rottweiler
‣ Pyrenees Mountain Dog
• Primary Hyperlipidemia in dogs:
◦ The lipoprotein accumulation differs between breeds.
What factors would increase protein requirements?
• Protein requirements increase in
animals that do much physical activity.
- Sufficient protein is important to build
muscle
What determines an animals water requirements?
Species, Activity, and ambient temperature
What can happen with excess vitamin D? How can a patient be given excess vitamin? Why?
- Vitamin D excess can be lethal and it is even used in some rodenticides
- Vitamin D is of a narrow safety range so excess is not uncommon
- With excess of vitamin D you can see hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia
- This can cause soft tissue mineralization, kidney injury and hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia can also result in uroliths, neural signs and more.

Are all fats lipids?
Are all lipids fats?
All fats are lipids, but not all lipids are fats.
What is a provess involved with stabilization of free radicals?
Free radicals may reach the phospholipid bilayer, alpha tocopherol donates its own hydrogen atom and electron to the radical, stabilizing it
What water soluable vitamin is commonly deficient in dog and cat food? What animals food is it normally not deficient in? Why?
Thiamine (vitamin B1) is a vitamin that is commonly deficient in dogs
and cat food as well as swine
B vitamins are synthesized by the GI microbiota in foregut and hindgut
fermenters (horses, ruminants)
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) requires cobalt
It is relatively temperature sensitive and degrades easily
- Thiaminase- an enzyme that is found
in some raw fish /shellfish will also break down thiamine and is an antivitamin,
How would you treat Intestinal Lymphangiectasia?
‣ Anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive
‣ Diet:
• Low-fat: absorption of long-chain triglycerides is a stimulus for lymph flow
• Supplementation of fat-soluble vitamins (carefully)
• Novel protein diet (?)
What would be indicated in test results with urine that is concentrated and has glucose?
POSSIBLE DIABETES MELLITUS (EARLY) OR PRIMARY RENAL GLYCOSURIA (RARE)
What is produced by glycolysis and becomes acetyl CoA
Pyruvates
How would a veterinarian diagnose Intestinal Lymphangiectasia?
‣ Clinical signs
‣ Lab results- low albumin, low cholesterol, low lymphocytes, hypocalcemia
‣ Endoscopy: abnormal appearance of the intestinal mucosa
‣ Intestinal biopsies (full thickness)
What does it mean when a fatty acid has high fluidity?
That means there is a higher number of un-saturated bonds.
What else can cause decrease in uptake of vitamin E?
Excess vitamin A may antagonize other fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins E, K, D)
What is transamination?
Transamination: the transference of an amine group from one amino acid to form another amino acid
What clinical signs can be seen with over hydration?
- RESPIRATORY DIFFICULTIES
- LUNG EDEMA
- PITTING EDEMA
- CONFUSION/SEIZURES
- HIGH BP, TACHYCARDIA
- EXCESSIVE MUCUS MEMBRANE MOISTURE
What are Ionophores?
Ionophores are compounds that alter the rumen microfloral
population such that propionate production is favored
What B vitamin is Folate?
B9
Define chylothorax
◦ Chylothorax is the accumulation of lymphatic fluid (chyle) in the pleural space
What is the issue with BCS’s?
Variability due to objectiveness.
What is oxidation?
Oxidation is a process by which a substance loses one or more electrons; the substance that gains the electron(s) is called an oxidant
What is the proper way to administer fluids?
ALL NEED TO BE STERILE, AND ADMINISTERED ASEPTICALLY.
In a dog, on the 9 point BCS scale, what is the ideal body condition score?
4-5
List the different types of lipids.
- Fats
- Cholesterol
- Phospholipids
- Waxes
- Steroids
What forms LDL?
‣ formed when triglycerides are removed from VLDL by lipoprotein lipase enzyme (LPL) and become smaller and denser.
Herbivores are very efficient at doing what (in regards to vitamin A)?
Herbivores are efficient in the transformation of beta
carotene to retinol
What is the water requirement for a horse?
HORSE:0.3-0.8 GALLONS/100LB/DAY OR 25-70 ml kg/day
What is the reptile daily water requirement?
~2.5–3.5% OF BODY WEIGHT ON A DAILY BASIS
If protien requirements are increased, will that also increase essential amino acid requirements?
No
Why is it important to keep track of BCS?
Allows us to monitor progress over time, evaluate different sizes/ life stages. No equipment needed. Gives owners measurable goals.
What is the treatment for primary hyperlipidemia in dogs?
◦ Treatment:
‣ Low fat
‣ Long-chain polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids (PUFA)
• EPA & DHA 200 to 300 mg/kg/day PO
‣ Fibrates
• Impact lipid metabolism.
‣ Niacin
• Vitamin B3
• Reduces triglycerides biosynthesis.
‣ Statins (HMG-CoA reductive inhibitors)
• Reversible inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductive (cholesterol biosynthesis)
• In dogs, hypertriglyceridemia is of clinical importance.
• Possible hepatotoxicity.
What is important to remember about patients protein requirements?
Protein requirements differ between species
What is the consequence of water deficiency? What is it called?
Can be fatal much sooner than any other nutritional deficiency. It is called dehydration
What are can cause secondary hyperlipidemia in horses?
Stress
Gestation
Disease
Overproduction of lipids in the liver —> hepatic lipidosis
Define hypercholesterolemia
increased cholesterol in the blood
What ways can water be provided to the patient?
- ORALLY (PO)
- INTRAVENOUSLY (IV)
- SUBCUTANEOUSLY (SQ)
- INTRAOSSEOUS (IO)
What are the steps of hydroxylation of vitamin D?
The first- in the liver, converts vitamin
D to 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D],
also known as calcdiol
The second is in the kidney which
results in the active form of vitamin D
[1,25 (OH)2D] or calcitriol
What is Gross energy?
Energy in food if you were to burn it in a bomb calorimeter
What are symptoms of excess energy?
- Weight gain
• Hyperlipidemia
• Hepatic disease
• Pancreatitis
• Lipoma/xanthoma
When is high ammonia or urea problematic?
Liver disease -> Excess ammonia is not transfered to urea -> Hepatic encephalopathy
Kidney disease-> Excess urea -> Causes vomiting, diarrhea, nauesea, inappetence.
More urea excreted -> Grass burn
What is the diagnostic indications for a glucagonoma?
Diagnosis:
• High blood glucose, liver enzymes
• Plasma glucagon levels
• Honeycomb liver on ultrasound
• Skin lesions:
• Biopsy (‘red white and blue’)

What are NPN’s?
Non-protein nitrogen (NPN)
• NPN can be provided in the form of urea as a substitute for protein
($) • This nitrogen is metabolized to ammonia in the rumen and can be
used by bacteria for amino acid synthesis
Who was the first requirement of iodine documented about in veterinay medicine?
Budgies
What are the examples of protein malnutrition and what symptoms would you see in each?
Kwashiorkor: protein malnutrition
• Abdomen appears swollen due to effusion
• Loss of muscle mass
• May be overall sufficient energy intake
Marasmus
• Overall emaciation
• Both protein and energy intake is insufficient
What does glucose become polymerized to and where is it stored afterwards?
Glycogen
Mostly in liver and muscle
What are symptoms/ consequences of ruminal acidosis?
- Anorexia (indigestion)
• Bloat, from rapid build-up of gases in a rumen
• Bacteria can invade and pass through the acid-burned rumen wall ->
bacteremia
What do cats do with the amino acids from protein?
They are constantly converted them to glucose.
What occurs to Fe2+ as it enters the small intestines?
Fe2+ remains soluble as it is bound to proteins and absorbed through enterocytes.
What are some important glucogenic precursors used to generate glucose?
• Some important glucogenic
precursors used to generate
glucose include:
• Pyruvate / pyruvic acid from
glycolysis (CHO)
• Oxaloacetate / oxaloacetic
acid (Anaerobic respiration)
• Lactate / lactic acid
• Almost all of the amino acids (protein)
• Glycerol: the 3-carbon
backbone of triglycerides (fat)
• Propionic acid: a 3-carbon
volatile (short chain) fatty
acid produced by microbial
fermentation
What is the function of HDL?
delivers lipids from peripheral tissue to the liver
What is gluconeogenesis?
To make new glucose
What are signs of the patient being underweight in older animals?
Chronic disease: Cancer, Metabolic disease.
- Decreased appetite when aging
- Can decrease sense acuity
- Rapid decline without medical and nutritional intervention.
What are minerals?
There are multiple essential minerals
are required in the diet
Minerals may interact between them
to affect absorption and/or
metabolism
Some minerals can be provided in
excess and cause negative effects on
health or nutrient absorption
What Factor is the one that requires the highest nutritional requirement?
Reproductive state/ lactation
What are the diagnostic indications for an insulinoma?
Dagnosis
• Lab results:
• Hypoglycemia
- Elevated insulin
- Ultrasound/CT/MRI
Where can zinc be found in high quantities?
Zinc is high in plants grown on zinc replete soil (especially beans, legumes)
Zinc is high in internal viscera (kidneys, liver), and in red meat
What is an essential nutrient?
a nutrient that the animal cannot
synthesize in sufficient quantities and should be
provided in the diet.
What is an iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency can occur as a result of either low intake or increased losses
What are the other forms of Vitamin D and where are they found?
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is a plant/fungal derived form
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is animal derived (milk, meat egg)
In what species is chylothorax most reported? Rare in?
Dogs and cats, rare in horses.
Lipoproteins allow the transport of?
hydrophobic lipid molecules in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids
What are clinical signs of white muscle disease?
- Muscle degeneration/ necrosis
- Acute extreme weakness
- The condition may affect the glottis and pharynx resulting in
secondary aspiration pneumonia
-Can cause cardiac failure and death

What is selenium?
Selenium is an essential mineral in all animals
It has several important functions but is primarily functions as a cofactor for
enzymes with antioxidant function
What factors are taken into consideration when determining the protein quality?
Protein quality takes into consideration the biological value and protein digestibility
What is the source of alpha linolenic acid?
◦ plant-based (flaxseed, chia, soybean…)
In hindgut fermenters, where do fibers reach?
Large intestines
What increases milkfat?
Acetate
Which is more absorbable. Haem or Non haem Iron?
Haem Iron is more absorbable ( Already in Ferrous form)
What are some consequences of dehydration?
- Poor perfusion
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Acid base disturbance
- endothelial injury
- inflammation
- coagulapathy
What requires more nutrition? A larger animal or a smaller one?
Larger animal
What is the most important nutrient?
H2O
What is the specific amino acid that has a strong odor and could drive palatability?
Specific amino acids such as methionine have a stronger flavor and odor that can drive palatability
Why does PTH and calcitriol regulate the mobilization of calcium from bone?
Narrow range of safety for calcium so it helps us to regulate it/ calcitriol + PTH
Why can grain free diets lead to taurine deficiencies in dogs?
- Potential for loss of methionine loss or taurine loss thus potential cardiomyopathies.
Where does protein digestion occur?
Enzymatic digestion in the stomach and intestines
What is a protein with a biological value of near 100%?
Eggs “ the ideal protein” (High digestibility, High biological value)
What is an enzyme that reduces lipid hydroperoxides to alcohols? Does it contain selenium?
Glutathione peroxidase (yes it contains selenium)
What is UIP?
Undegradable intake protein (UIP)
or “rumen bypass protein”
• This protein is usually heat-treated
protein that is not digestible by the microbial enzymes.
Ex: Brewers grains, distillers grains.
What are most succeptible to damage by ROS?
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
TRUE OR FALSE: Fiber is digestable by mammalian enzymes
FALSE:
Fiber is not digestible by mammalian enzymes
What is the results of the stabilization of free radicals?
This results in a non-reactive, oxidized alpha tocopherol form that can be reduced by vitamin C
What is vitamin K important for?
Vitamin K: important for coagulation
Vitamin K is an important cofactor for the synthesis of blood clotting factors
II, VII, IX, and X in the liver
How are MCTs absorbed?
What about in dogs and cats?
- MCTs are largely absorbed through the portal vein system unlike other fats.
- (in dogs and cats, likely portal absorption is in addition to lymphatic absorption)
What is the function of EPA and DHA?
◦ Neural function and development
◦ Immunomodulation
What is the normal specific gravity of sheeps urine?
1.015-1.045
What flavor can cats not taste?
Sweet
What would be indicated in test results with urine that is adequately concentrated and has no glucose?
LIKELY BEHAVIORAL, CYSTITIS, BLADDER MASS, UROLITHIASIS, ANATOMIC/
NEUROLOGIC
TRUE or FALSE: All species can cleave beta carotene?
Not all species can cleave beta carotene
What are the fat soluble vitamins?
Fat soluble vitamins: A, D, E and K (KADE)
What is Haem Iron?
Haem iron is from haemoglobin in meat and fish and is in the reduced ferrous form.
What is equation for the daily digestible energy requirement in a horse?
A nonworking adult horse in good body condition is estimated to
be on average 33.3 kcal/BW (kg)
• Range: (30.3 kcal/kg-36.3 kcal/kg)
Unsaturated fats can provide?
Give an example
Health benefits
E.g. omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Secondary hyperlipidemia
- Renal disease
- Diabetes
- Cushing’s disease
- Hypothyroidism
- Negative energy balance in overweight animals (horses)
What essential nutrients are required for normal red cell production?
- Iron
- Folate (Vitamin B9 )
- Pyridoxin (Vitamin B6)
- Cobalamin (B12)
What is a metabolome?
totality of metabolites in a certain environment
What are the tests that can be done for overhydration?
Radiographs
What are crystalloid fluids?
Clear fluids
- No lipids/ protein
- Saline (0.9% NaCl)
- LRS Solution
What is the main clinical intervention that could be provided for a patient who is dehydrated?
Rehydration
What are some pathological lesions of patients with white muscle disease?
White muscle disease causes muscles to be swollen and
edematous
White streaks in the muscle are highly characteristic of this
pathology
The result of oxidation
What can cause taurine deficiency in dogs?
- Conjugated taurine is recycled with enterohepatic recirculation
- Shifts in the normal GI microbiota may cause increased taurine loss Taurine
- Taurine deficiency has been found in dogs, and can occur as a result of diets with low methionine and cysteine
- Diets with low digestibility
- Diets with high fiber that change the GI microflora
What is the typical specific gravity range for cats?
1.030-1.050 (as per Stockman)
Book says 1.020-1.040
How is lactulose effective in decreasing issues for dogs with hepatic disease?
- Bacterial degradation in colon reduces colon pH -> retention of ammonia in colon as ammonium
- migration of ammonia in blood into colon to form ammonium ion
What percent of moisture is found in canned food?
80% moisture
What is Metabolized energy?
Energy that is available for use after
the metabolic ‘costs’ are subtracte
What are vitamins?
Vitamins are organic substances, present in small amounts in natural
foodstuffs, which are essential to normal metabolism and lack of which cause deficiency diseases
How are proteins digested in forestomach fermenters?
Some nitrogenous compounds passing through the forestomach may be metabolized by microbial organisms
• Urea may be metabolized to ammonia and incorporated into bacterial protein
Describe the structure and function of Alpha linolenic acid.
◦ essential omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
◦ Ensures adequate neuronal function
What is the most concentrated source of energy?
Lipids
What is the function of VLDL?
VLDL transports endogenous products to the peripheral tissues
What occurs to undigested amino acids in the large intestine?
• Large intestine: undigested amino acids
are converted by microbes into
ammonia
• which is captured by the liver and
catabolized to urea
What is the role of iodine?
Iodine is key micromineral for the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)
Iodine deficiency would result in an enlargement of the thyroid gland= goiter + decreased thyroid function
It is reversible with iodine supplementation
What is Hyposthenuria?
USG Lower than 1.008
What factors change nutritional requirements?
Reproductive state, lactation, age, diseases, spay/ neuter status, activity, growth/ life stage.
Anemia caused by B12 deficiency is called?
Macrocytic Anemia
What do PUFA’s posess in terms of bonds?
PUFA possess unsaturated carbon or double bonds (C=C-)


