Development L7 - oral development biology Odontogenesis Flashcards
epithelium (ectoderm) gives rise to what parts of the developing tooth
enamel
hyaline layer of the root
the innermost layer of cells or tissues of an embryo in early development that go on to form the primitive gut
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
endoderm
refers to cells that develop into connective tissue, blood vessels and lymphatic tissue
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
mesenchymal
third stage in tooth development, in which the germ grows in to a cap shape
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
cap stage
what does the dental papilla form

forms odontoblasts (dentine) and pulp
the 1st pharyngeal arch gives rise to which two process
mandibular and maxillary process
a loosely organised, mainly mesodermal embryonic tissue which develops into connective and skeletal tissue, including blood and lymph
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
mesenchyme
what is the name of the 1st pharyngeal arch
mandibular arch
second stage simple, spherical to ovid, epithelial condensation poorly morphodifferentiated and histodifferentiated
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
bud stage
the enamel organ consists what four features in the picture

inner enamel epithelium
stratum intermedium
stellate reticulum
outer enamel epithelium
from weeks 6 to 12 the vestibular lamina grows and undergoes cell death to form what?
formation of the sulcus (vestibule)
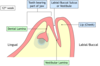
mesenchyme (ectomesenchyme) gives rise to what part of the developing tooth?
dentine
pulp
cementum
periodontium - pdl and bone
a thickening of the ectodermal epithelium (outer most layer) the primary band then later differentiates into the vestibular band, which eventually forms the lips and cheeks and the dental lamina from which the tooth germ develops
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
primary epithelial band
condensation of the ectomesenchyme, results in the formation of the primary epithelial band.
the proliferation of the primary epithelial band forms what?

denal lamina and vestibular lamina

which of the four enamel organ components is responsible for the formation of ameloblasts
inner enamel epithelium
stratum intermedium
stellate reticulum
outer enamel epithelium
inner enamel epithelium
ameloblast forms enamel
contributes to the vestibule of the mouth, delineating (bordering) the lips and cheeks from the teeth formation sulcus
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
vestibular lamina
at which week does the sulcus form
week 12
fully developed tooth
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
crown stage
the middle layer of cells of an embryo , which go on to develop cartilage, muscles and bones.
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
mesoderm
the outermost layer of the cells or tissue of a embryo in early development which go on to make the epidermis and nerve tissue.
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
ectoderm
fourth stage, in which differentiation occurs to furthest extent and starts to resemble a bell
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
bell stage
tooth development is 3 overlapping phases - initiation, morphogenesis and histogenesis. and requires the interaction between what?
epithelium and mesenchyme
of epithelial orgin but behave like mesenchymal cells, synthesis of collagen 1,2,3
the above statement matches which of the below:
Histogenesis
Mineralised dental tissues
Dental lamina
Vestibular lamina
Initiation stage
Bud stage
Cap stage
Bell stage
Crown stage
External Enamel Epithelium
Stellate reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
Ectomesenchyme
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
mesenchyme
mesenchymal
stellate reticulum



