Ch. 5.2 Strata of the Epidermis Flashcards
Epidermis
AVASCULAR STRATIFIED SQUAMEOUS EPITHELIA
Nutrients diffuse from capillaries in dermis

Keratinocytes
- Dominant cell of epidermis
- Body’s most abundant epithelial cell
Thin Skin
- Covers most of the body surface
- Contains four layers of keratinocytes
- ~thick as a sandwhich bag (0.08mm)

Thick Skin
- Palms of the hands
- Soles of the feet
- Additional 5th layer: stratum lucidum
- Thicker stratum corneum layer
- 0.5mm

What are the layers of thick skin?
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum lucideum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum basale

Stratum basale
- Innermost epidermal layer
- Hemidesmosomes attach to basement membrane
stratum germinativum
stratum basale
epidermal ridges
- Ridges formed by the stratum basale that project into the epidermis
- Adjacent to dermal papillae
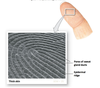
dermal papillae
dermal projections that project into the epidermis. The strength of attachment is proportions to SA of basement membrane.
These ridges form fingerprints.

Basal cells (germinative cells)
dominate the stratum basale. Stem cells whose divisions replace the superficial keratinocytes.
Tactile cells (Merkel cells)
- Found on skin surfaces that lack hair, in stratum basale.
- Sensitive to touch
Melanocytes
Found in stratum basale. Produce brown skin tones (melanin). Cell processes extend into superficial layers.
stratum spinosum
- “Spiny layer” - chemicals shrunk the cytoplasm of keratinocyte, leaving cytoskeletal elements
- Superficial to stratum basale.
- 8-10 layers of keratinocytes bound together by desmosomes.
- Generated from one of the daugher cells of dividing stem cells in stratum basale
- Cells continue divide, increasing thickness

Cells of the stratum basale
- Merkel cells (hairless skin)
- Melanocytes
Cells of stratum spinosum
dendritic (langerhans) cells
- Defense against microorganisms that penetrate superficial layers
- Defend against superficial skin cancers
stratum granulosum
- “grainy layer”
- 3-5 layers of keratinocytes derived from stratum spinosum
- Most stop dividing at this layer
- Begin making large amounts of kertain and keratohyalin
- Makes cells thinner and flatter, less permeable

keratin
- a fibrous protein in stratum granulosum
- basic component of skin and nails
keratohyalin
Found in stratum granulosum. Forms dense cytoplasmic granules that promotes:
- dehydration of cells
- aggregation/cross-linking of keratin fibers to lock cells together
- organelles disintegrate, cells die
stratum lucidum
- “clear layer”
- Covers stratum granulosum
- Cells are flattened, densely packed, devoid of organells, filled with keratin

stratum corneum
- 15-30 layers of keratinized cells
- 7-10 days for cells to move from stratum basale to stratum corneum

kertainization (cornification)
- the formation of protective superficial layers of cells filled with keratin
- Occurs on all exposed skin surfaces except anterior to eyes
- Dead cells tightly linked by desmosomes
Insensible perspiration
- Water from interstitial fluid slowly penetrates to surface, evaporates into surrounding air
- Unable to see or feel this water loss
- ~500 mL (1 pint)/ day
Sensible perspiration
- Produced by active sweat glands
- If stratum corneum is damaged, insensible perspiration skyrockets. Complication of bruns and xerosis
blisters
Fluid accumulation. Damage breaks connection between superficial and deeper layers of epidermis, or between epidermis and derms if the basement membrane is damged.


