Ch. 5-7 Hair Flashcards
epidermal derivatives
structures that originate from epidermis during development; hair follicles, sebaceous, sweat glands, and nails.
Hair
Non-living structures formed in organs called hair follicles
FUNCTIONS:
- Protects and insulates
- Guards against particles and insects
- Sensory receptors
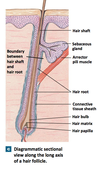
Hair follicle
- Organ
- Located in the dermis
- produces non-living hairs
- wrapped in dense connective tissue sheath
- base surrounded by sensory nerves (root hair plexus)

root hair plexus
sensory nerves that surround the base of each hair follcile
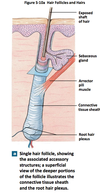
arrector pili
- involuntary smooth muscle
- extends from papillary layer of dermis to the connective tissue sheath surrounding the hair follicle
- Causes hair to stand up; goose bumps

hair root
- portion that anchors hair to skin
- begins at hair bulb and extends distally to the point at which the internal organization of the hair is complete (about halfway to skin surface)

hair shaft
portion that can be seen on the surface. Extends from hair root (halfway point) to exposed tip of the hair

club hair
- Term for hair at the end of the growth cycle
- Not growing
- Attached to inactive follicle
- The follicle gets smaller until the connections between the hair matrix and the club hair root break down.

Stages of the hair growth cycle
Anagen - growth (2-7 years)
Catagen - transition (2-3 weeks)
Telogen - restive (2-3 months). Bulb is gone.

alopecia
baldness
Many causes; senescecent hair follicle can be caused by telomer shortening.
hair bulb
- a mass of epitheleal cells that forms a cap that surrounds the hair papilla
- superficial cells are responsible for producing hair

hair papilla
- a peg of connective tissue containing capillaries and nerves
- contains melanocytes for hair pigment

hair matrix
- layer superficial cells of the hair bulb that are responsible for producing hair
- basal cells near the center divide, producing daughter cells pushed to the surface

medulla
- Core of hair; formed by daughter cells closest to the center of the hair matrix

cortex
middle layer of of the hair matrix

cuticle
cells at the edges of the hair matrix

Hair Follicle Structure
- Internal root sheath
- External root sheath
- Glassy membrane
- Connective tissue sheath

lanugo
hairs that first appear ~3 months of embryonic development. Fine and unpigmented.
vellus hairs
- Soft, fine
- covers body surface
terminal hairs
- heavy, pigmented
- head, eyebrows, lashes
- other parts converted from vellus hairs after puberty
- Organ
- Located in the dermis
- produces non-living hairs
- wrapped in dense connective tissue sheath
- base surrounded by sensory nerves (root hair plexus)

Hair follicle
sensory nerves that surround the base of each hair follcile

root hair plexus
- involuntary smooth muscle
- extends from papillary layer of dermis to the connective tissue sheath surrounding the hair follicle
- Causes hair to stand up; goose bumps

arrector pili