4.2.2 animal tissues, organs, and systems (digestion, blood, heart, cancer) Flashcards
What is a meant by a specialised cell?
A cell that carries out a particular function (job).
What is meant by differentiation?
When a stem cell changes into a specialised cell.
What is a stem cell?
An undifferentiated cell that can change into any type of cell.
What is meant by an ‘undifferentiated cell’?
A cell that has not yet changed into a specialised cell (e.g. stem cells)
Many similar cells form a…
tissue
Many tissues form an…
organ
Many organs form an…
organ system
Many organ systems form an…
organism
When does differentiation occur in multicellular organisms?
During the development (in the uterus/womb)
What is meant by a multicellular organism?
An organism that is made from many different types of specialised cells.
Why do large multicellular organisms require organ systems?
To transport materials.
To exchange materials.
Name the 3 types of tissue that form the stomach (organ).
Epithelial tissue
Glandular tissue
Muscular tissue
What is the function of epithelial tissue in the stomach?
It covers the stomach like a skin.
What is the function of muscular tissue in the stomach?
It contracts to allow the stomach to churn food.
What is the function of glandular tissue in the stomach?
It secretes digestive enzymes that break down food.
What is the function of glandular tissue?
It secretes enzymes.
It secretes hormones.
Identify the organ system

Digestive System

Identify the organ.


Identify the organ.


Identify the organ.


Identify the organ.


Identify the organ.

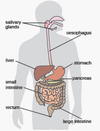
Identify the organ.












































