2.8 Epigenetics Flashcards
(33 cards)


What is epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that occur without changes in DNA sequence.
Epigenetic changes are mitotically heritable
In what way can epigenetic modifications be reset?
- Some epigenetic marks around implantation will persist for the entire lifetime
- Germ cell and early embryonic development is where epigenetic marks are removed (break in the cycle)

Name the five epigenetic alterations
- DNA methylation
- Post translational histone modification
- Non coding RNAs
- Histone Variants
- Nucleosome remodelling/chromatin remodelling
Where does DNA methylation occur
- At CpG dinucleotides in mammals, regions where C is followed by G base
- A 5-methyl group is added

How does DNA methylation occur?
- DNA methylation is laid down by de novo methyltransferases, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in mammals

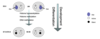
How is DNA methylation symmetrical?
- The new daughter strand of DNA (green) is not methylated
- Because it is semi conservative you still have one strand with methylation
- Maintenance DNMT1 lays down methylation on the other strand, recognising hemi methylated DNA

Apart from CpG islands where else does DNA methylation occur?

What is ICF syndrome?
- Immunodeficiency, Chromosomal instability and Facial Anomolies syndrome
- Very rare, autosomal recessive disorder with variable phenotypes
What causes ICF syndrome?
- Mutation in DNA methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B)
- Hypomethylation of a small amount of the gemone in patients - not enough methylation
- Pericentromeric repeats at centromeres of chromosome 1, 9, 16 related to chromosomal instability
- Hypomethylation of CpG islands on inactive X chromosome in females, Y chromosome in males
- Some other genes, related neurogenesis, immune funciton, craniofacial patterning, which all relate to phenotypes in patients
When does DNA demethylation happen?
- It is mitotically heritable, due to action of maintenance methyltransferase DNMT1
- DNA demethylation is shown to occur in early development, in primordial germ cell development and at later specific stages of differentiation
How is DNA demethylation achieved?

In what ways can DNA methylation cause silencing?
- It can interfere with transcription factor binding
- Result in the binding of methyl-CpG binding proteins which recruit other factors that alter chromatin state
Where do histone tail modifications occur?

What is histone acetylation?
- Acetylation is correlated with gene activity, partly due to reduced positive charge of histone.
- Not mitotically heritablem not strictly epigenetic, chromatin mark

What is histone methylation?
- Histone methylation does not alter the charge of the histone
- It can correlate either with transcriptional activity or inactivity, depending on which histone tail residue is methylated
- Mono, di and tri methylation exist

Why do histone tail modifications correlate with different chromatin states?
- Histone tail modifications are “read” by other chromatin proteins
- The interacting chromatin proteins may alter chromatin packaging or bring about other histone modifications
- They don’t cause altered gene expression but instead mark euchromatin or heterochromatin to be bound by other factors that themselves can alter accessibiility
What is the role of histone tails and chromatin proteins?
- Modified histone tails act as docking sites for other chromatin proteins
- Proteins that bind Me or Ac at specific residues alter chromatin packaging or bring about additional epigenetic charges

What are 3 examples of chromodomain proteins?
- CHD1 - ATP dependent chromatin remodeller
- HP1 - essential heterochromatin protein, can recruit DNA methyltransferase 1
- CBX2 - part of polycomb repressive complex that lays down H2AK119ub, another epigenetic mark



What are two examples of long non coding RNAs?
- X inactivation (e.g. Xist)
- Genomic imprinting (e.g. Kcnq1OT1, Snrpn, Airn)
What are some of the possible mechanisms for long non coding RNAs?
The common feature is that there is the formation of RNA - protein complexes that influence the regulation of gene expression

How do long non coding RNAs guide epigenetic complexes of proteins?
- Sequence complementarity allows the lncRNA to guide the epigenetic modifier complex to a specific location in the DNA

What is X Chromosome inactivation?
- X inactivation is an epigenetic dosage compensation mechanism in mammals, so that males and females have the same dose of genes on the X chromosome.
- Random X inactivation occurs at gastrulation in the embryo, then this epigenetic state is mitotically inherited by each daughter cell