1.1 Amino acids and peptides Flashcards
What is the simple definition of Gibbs free energy?
It is the energy of the reaction available to do work
What is the equation relating the change in gibbs free energy to heat and entropy?

How are spontaneous reactions defined in terms of delta G?
Spontaneous reactions have a negative delta G
What is the difference between exergonic and endergonic?

What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic?

whats up
What does the sign of delta S indicate in terms of the change in entropy?
Delta S is negative: less disorder
Delta S is positive: more disorder
What is the equation linking delta G and delta G*?

How does the position of equilibrium relate to the change in Gibbs free energy?
The further away from equilibrium you start, the more work is done before you get there.

What are some ways through which a negative delta G can be achieved?
- Negative delta H (exothermic)
- Positive delta S (increase in entropy)
- Any combination that leaves delta G negative
What are the standard conditions in chemistry?
- 298 K
- Gases at a partial pressure of 101.3 kPa (1 atm)
- Reactants and products at 1 M concentrations
What are the standard conditions in biochemistry?
Same as those of chemistry but the reaction occurs in a well buffered aqueous solution at pH 7 with [H+] ion concentration 10-7 and Mg2+ = 1mM
If you look at the free energy equation and set all initial concentrations to 1, what happens?
Shows delta G is equal to delta Go when everything is at standard conditions

How does the free energy equation change when all concentrations are at equilibrium?
At equilibrium delta G=0 this means the reaction can do no more work.
This shows that delta G0 is a constant
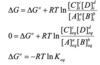
What is used to predict where a reaction will be spontaneous?
The measure of whether a reaction will proceed spontaneously is delta G not delta Go.
How can the initial conditions of a reaction be altered in order to get a spontaneous reaction?

What are three ways of making unfavourable reactions go?
- Remove one or more of the products at a rate much faster than it is produced so that the reaction is now kinetically driven
- Replenish one or more of the reactants at a much faster rate than it is removed
- Couple the unfavourable reaction with a highly favourable reaction (in the active site of an enzyme)
Label the blanks on this ATP molecules


What is the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside?
Nucleotide = base + sugar + phosphate
Nucleoside = base + sugar
What causes the release of energy via ATP?
Energy is released upon the hydrolysis of phosphoanhydride bonds
Show the equation for the release of energy via ATP including delta G

How is bond energy related to bond breakage/forming?
Energy is required to break any bond
Energy is released when any bond forms
Why is energy required to break any bond?
The bonded state is a more stable state that’s why it required energy to break
Why is the ATP reaction highly exergonic?
- ATP has a higher negative charge density than ADP (ATP less stable)
- Pi is very stable: multiple resonance states exist
- ATP phosphoanhydride bonds are relatively weak
- ADP phosphoanhydride bonds and Pi bonds are relatively strong
Why is tri phosphtate less stable than di phosphate?
Due to charge density, are there is a great accumualtion of negative charges and more strain and repulsion