1.3 Protein function Flashcards
(54 cards)
Label these proteins




What term would you use to describe the relationship between myoglobin and hemoglobin?
They are homologues or paralogues, as they exist in the same organism
What is a protomer?
The structural unit of a protein with quaternary structure - the smallest unit that can be replicated by symmetry


What is the structure of immunoglobin Gs (IgG)?
Consist of four subunits
2 heave chains
2 light chains
Both involved in binding to the antigen ligand



Why have antibodies evolved to be multivalent?
Multi valent binding is more efficient than binding through a single fold. More effective due to avidity


What are the two functions of Mb?
- Storage of oxygen in muscles
- Release of oxygen when rapidly contracting muscle needs energy
Where does oxygen bind?
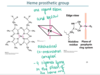
Oxygen binds to the Fe2+ of the Heme group.
In what animals is Mb abundant in?
The muscle of diving animals - seals, otters and whales


What is the prostheic group of hemoglobin?
It is where O2 bind reversibly to the Fe2+ of the heme prothetic group.
It is a prosthetic group as it is separate to the protein itself


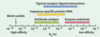
What is the equilibrium constant for association and dissociation?

What does thetha mean?

What happens when half the binding sites are occupied?

What is the relationship between Kd and affinity?
If there is a high Kd then there is low affinity and vice versa
What is biotin and what is it needed for?
- Biotin is a vitamin essential in the diet
- Needed for carboxylations
- It binds the protein avidin found in raw egg white
Explain the binding interaction of biotin and avidin with reference to the Kd
- Avidin in egg whites bind biotin
- The Kd of 10-15 is so small that the binding can be considered irreversible
- Biotin deficiency in humans is associated with long term consumption of raw eggs rich diets but when eggs are cooked the avidin unfolds and does not bind biotin
What can be deduced about Mb and oygen binding from the shape of this curve?

- Curve is very steep
- Demonstrates tight binding
- Half the ligand binding sites will be occupied at a very low partial pressure
With reference to kPa values of pO2, could myoglobin transport oxygen?
pO2 in the lungs is about 13 kPa so myoglobin will bind it.
pO2 in the tissues is about 4 kPa so it will not release it!

What is the T state of hemoglobin?
T = tense state
– more interactions, more stable
– lower affinity for O2






























