(16) Heart Development (Keim) Flashcards
When does the circulation and heartbeat begin in development?
4th week (day 22)
Nearly all of the heart comes from ____________
Though some comes from _________
Splanchnic mesoderm
Neural crest cells
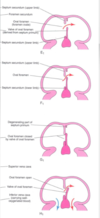
Label the diagram


Mesenchyme is derived from:
Neural Crest
Heart Fields are derived from….
Splanchinc Mesoderm

What do primary heart fields develop into?
Left/Right Atria
Left Ventricle
What do secondary heart fields develop into?
Right Ventricle
Outflow tract (eventually becomes aorta and pulmonary trunk)
What is another name for primary heart fields?
Cardiogenic cords
Heart Primordia
Describe the basic mechanism of heart development
Start with two endocardial heart tubes, one on each side.
They come together in the chest and fuse.

What is a mesentery?
Double layer of splanchnic mesoderm that provides a route for blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves to get to and from organs
The ____ _______ is a mesentary that exists at the heart primordia stage
Dorsal Mesocardium

All of the heart is ___________
Splanchnic mesoderm
What is the dorsal mesocardium?
Mesentery that disintegrates and becomes the transverse pericardial sinus.
This is the sinus that separates the outflow tract from the venous tract.

Mesenchyme:
State what it is and what it’s derived from:
Endocardium
Internal endothelial lining
Splanchnic Mesoderm
Mesenchyme:
State what it is and what it’s derived from:
Myocardium
Muscular Wall
Splanchnic mesoderm
Mesenchyme:
State what it is and what it’s derived from:
Epicardium
(Visceral pericardium)
Outer covering of the heart
Splanchnic mesoderm
Where do the neural crest cells that contribute to heart development come from?
Myelencephalon
Where do the neural crest cells that contribute to heart formation mirgrate from?
Migrate through pharyngeal arches 3,4,6
What do neural crest cells to help with the development of the heart?
Help with the formation of the bulbus cordis and truncus arteriosus
*These structures form the aorticopulmonary septum that separates the aorta and pulmonary trunk
Movement of neural crest cells is mediated by…
VITAMIN A (retinoic acid)
Hox Genes
Nf-1
Pax 3
What is the problem with too much vitamin A during pregnancy?
Can lead to heart defects
What are the primitive divisions in heart formation? (5)
- Truncus arteriosus
- Bulbus cordis
- Ventricle
- Atrium
- Sinus Venosus
What day do we have the sinus venosus?
Why do we care?
Day 23
When blood is being brought to the heart

How does blood travel through the heart with the primitive divisions?
Sinus venosus –> Atrium –> Ventricle –> Bulbus cordis –> Truncus arteriosus