(15) Respiratory Embryology (Keim) Flashcards
The respiratory system primarily comes from which germ layer?
ENDODERM
Specifically, the respiratory system’s endoderm comes from…
the 6th paryngeal arch
*technically this is the foregut endoderm
What gives rise to the larynx and trachea?
Laryngotracheal diverticulum/groove
aka
Respiratory diverticulum
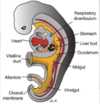
The inferior portion of the laryngotrachial diverticulum is also called:
The LUNG BUD
*Found on outside of embryo
What week does the respiratory system start to develop?
Week 4
What is occuring as the laryngotracheal diverticulum is forming during week 4?
The laryngotracheal diverticulum is forming the:
Esophagus
Stomach
The primitive trachea (laryngotracheal tube) and the esophagus are developing together in week 4. They need to be separated. How does this occur?
Tracheoesophageal folds meet the midline and form the tracheoesophageal septum.
This separates the esophagus from the laryngotracheal tube.

When is the tracheoesophageal septum complete?
Week 5

What type of structure is the tracheoesophageal septum?
Long structure longitudinally!!!

What does the larynx form from?
Foregut endoderm
6th Pharyngeal Arch

What are the structures you can identify to orient yourself to the 6th pharyngeal arch?
Bilateral arytenoid swellings
*remember! pharyngeal arch 6 is directly inferior to pharngeal arch 4

What are arytenoid swellings derived from?
Neural crest
covered with endoderm
What do the arytenoid swellings give rise to?
Cartilages in the larynx

What is the black wedge on top of the arytenoid swellings?

Glottis
What is the hypobranchial/hypopharyngeal eminence?
Region that develops the epiglottis

Which pharyngeal arches give rise to the hypobranchial/hypopharyngeal eminence?
Pharyngeal arches 3 and 4

When is epithelial occlusion w/ recanalization complete?
10th week
Congenital Abnormalities
What is:
Laryngeal Atresia?
Larynx is completly filled in as the result of failure of recanalization
Breathing is impossible; children present with asphyxia at time of birth
Requires an emergency tracheotomy

Congenital Abnormalities
What are:
Laryngeal Webs
Laryngeal webs are incomplete atresia, presenting as tissue between the vocal cords which blocks the glottis
Pts present with respiratory distress and stridor
Due to failure of recanalization (week 10)

Congenital Abnormalities
What is:
Laryngomalacia
Refers to a collapse of the supraglottic structures during inspiration
Most common congenital anomaly of the larynx

The tissue of the trachea comes from?
2 sources!!!
Pulmonary epithelium and glands = endoderm
Cartilage, connective tissue, smooth muscle = splanchnic mesoderm

What are tracheoesophageal (TE) fistulas?
Almost always associated with esophageal atresia = blind ended esophagus
Pts. struggle to feed

What is the cause of tracheoesophageal (TE) fistulas?
Failure of the tracheoesophageal folds to form in week 5

The lung bud forms out of the ____________ as the inferior portion of the ___________ at week ____.
The lung bud forms out of the foregut endoderm as the inferior portion of the laryngotracheal diverticulum at week 4