Week 3 - A - Neuroradiology 1and2 (CT v MRI and aneurysms) - Subarachnoid haemorrhage included Flashcards
CT scan is basically a very intricate Xray What type of atoms does the contrast of a CT scan depend on? Protons, electrons, neutrons?
Contrast is determined by the electron density
What colour is bone on xray? What colour is gas? In terms of a CT scan, rate these in order from white to black Fat, bone, gas, brain, haematoma
White to black Bone - haematoma - brain - fat - gas Bone is white, gas is black
The denser something is on CT, is it more black or white? Is grey or white matter denser?
Increasing density increase the whiteness on CT scan (low density is black, high density is white) White matter is less dense than CT as it is mainly myelinated axons (fatty) therefore is darker Grey matter is more dense due to cell bodies and therefore is lighter

How are CT scans actually made?
They are made by rotating an Xray beam around a patient taking multiple images that a computer stitches together

What colour is the CSF on CT scan? Blockage of what part of the CSF pathway can cause hydrocephalus of one ventricle?
The CSF in the ventricles is a very dark colour Blockage to the interventricular foramen (of monroe)
Which part of the brain usually calciifes so on CT appears white? Helps to tell if their is raised ICP as it should sit in the midline and not be deviated?
The pineal gland Can also see the very dark CSF filled ventricles here Can see the calcified pineal gland
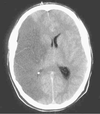
Does the dura mater peel off the skull in epi(extra)dural or subdural haematoma? Where is fracture likely to occur in extradural and what artery?
Dura mater peels of the skull in extradural haematoma Likely to be a fracture at the pterion - thinnest part of temporal bone damaging the middle meningeal artery
What is given for artifical contrast in a CT scan? After the bolus is pumped, when is it a CT angiogram? How long till it becomes a CT venogram?
Idoine is given as artificial contrast CT angiogram immediatedly during and after bolus is pumped CT venogram 30 seconds after bolus is pumped
Can iodine normally cross the blood brain barrier? If not when can it?
It cannot normally Iodinated contrast does not normally pass into the brain because of the ‘blood brain barrier’ however this can be disrupted by tumours or inflammation and a CT scan 5mins after contrast injection will show ‘enhancement’ ( whiteness) where BBB is disrupted
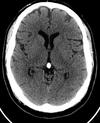
How long after the iodine bolus was pumped must this image have been taken? Nb - iodine only crosses the BBB if it has been interrupted

The scan must have been taken 5 minutes after bolus was pumped in order to enhance the lesion
MRI tells a bit more than CT scans when it comes to soft tissue injury What does it use instead of electron density to determine the contrast?
Contrast determined by: Proton density T1 and T2 weighted images T1 and T2 are measurements of the chemical and molecular movements of protons
Is it in T1 or T2 weighted images that the fluid is bright? Ie are the lateral ventricles (contain fluid) bright on T1 or T2?
Lateral ventricles are bright on T2 weighted images

T1 vs T2 - black white or grey are the options Fat? CSF? White matter? Grey matter? Air? Bone or calcification?
T1 Fat - White, CSF - Black White matter - White(has more meyelin therefore more fat making it white), Grey matter - Dark grey
T2 Fat - black, CSF - White White matter - dark grey (contains more fat), grey matter - light grey

Basically fat is white on T1 and black on T2 Water (CSF) is black on T1 and white on T2 What does this mean for white and grey mtter?
Fat is white on T1 therefore so is white matter as myelin contains lipid Fat is black on T2 therefore white matter is dark as it contains fat (opposite for grey matter) Water is black on T1 so ventricles are black Water is white on T2 so ventricles are white

What is this patients growth known as? What nerves could be affected?

This is an acoustic neuroma Could affect CN VI, VII, CN VIII (all arise at the pontomedullary junction) (also maybe CN V) And can affect cerebellum as the growth arises at the cerebellopontine angle

Does MRI cause ionising radiation?
MRI does not cause ionising radiation
What is the main contraindication to MRI?
Unable to have the scan if you have a metal device Also claustrophobics may have difficulty with MRI scan
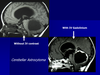
What substance is used as artifical contrast in MRI making images whiter in the T1 weighted section of the scan?
Galadonium is used as artifical contrast in MRI scans - enhances the image on T1 weighted section (whiter) Can see the cystic type cerebellar astroctyoma
State which is which between CT and MRI Fast vs Slow Good bone detail vs good soft tissue detail Acute haematoma hard to see vs easy to see More expensive vs less expensive Ionising vs non ionising Uses gadolinium vs uses iodine
CT Fast, good bone detail, acute haematoma easy to see, less expensive, ionising, uses iodine for artificial contrast MRI Slow, good soft tissue detail, acute haematoma hard to see, more expensive, non-ionising, uses gadolinium
What is the commonest cause of spontanoeus subarachnoid haemorrhage? What is another cause?
Ruptured aneurysm - 85% AVM (arteriovenous malformation) - 10% undetermined - 5%
What type of aneursym is the most common cause of subarachnoid haemorrhages? Where do these aneursyms occur?
Most common cause are saccular (aka berry) aneurysms These aneurysms occur at vessel bifurcations ie basilar artery into posterior cerebral arteries
saccular aneursyms are generally assymptomatic until rupture, uncommonly produce cranial nerve palsies,particularly giant aneurysms (>2.5cm). WHat are the symtpoms of rupture?
Sudden severe headache (like being hit in the head with a bat) Can get nausea and vomiting and double vision Stroke like symptoms
What imaging technique is first line in the diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhae? If the subarachnoid haemorrhage isn present on this scan but the symptoms strongly suggest it, what is carried out?
CT scan is first line Lumbar puncture if not seen on CT scan but symtpoms suggest haemorrhage
What technique is used to identify the artery causing the haemorrhage in subarachnoid haemorrhage?
After spontaneous SAH is confirmed, the aim of investigation is to identify a causative pathology that needs urgent treatment:
- CT intracranial angiogram (to identify a vascular lesion e.g. aneurysm or AVM)
- +/- digital subtraction angiogram (catheter angiogram)
Image shows DSA - digital subtraction angiography