Week 1 - G - Neuroanatomy 4 - Cranial nerve nuclei Flashcards
What are the twelve cranial nerves and where do they exit the central nervous system?
Olfactory nerve - forebrain Optic nerve - forebrain Oculomotor nerve - midbrain Trochlear nerve - midbrain Trigeminal nerve - pons Abducent, Facial, Vestibulocochlear nerve - pontomedullary junction Glossopharyngeal, Vagus nerve - medulla Spinal accessory nerve - arises in the cervical vertebrae Hypoglossal nerve - medulla
What nerves are only sensory and no motor control?
Olfactory Optic Vestibulocochlear nerve
Nerves exit the brainstem anteriorly apart from which cranial nerves? how do they exit?
Cranial nerve 4 - trochlear nerve exits the brainstem posteriorly Cranial nerve 8 - vestibulocochlear nerve exits the brainstem laterally

As we have seen, some CN are purely motor, some purely sensory and some mixed. Motor components will be associated with motor nuclei, groups of efferent nerve cells that send their axons into the cranial nerve. Sensory components will be associated with sensory nuclei, groups of nerve cells upon which the sensory neurons of the cranial nerves synapse. Where is the soma of the sensory nerves found?
The soma of the sensory nerve cells will be found outside the CNS and axons will project into the CNS where they will synaspe
What is the only sensory system that does not synapse in the thalamus before reaching the brain cortex
This would be olfaction
What type of neurones are the oflactory neurones that project down into the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone? (it has two neurites)
The olfactory neurones are bipolar neurones - the cell body gives off two neurites (dendrite + axon)
The olfactory tracts travel from the olfactory bulbs to the primary olfactory area which is located where?
The primary olfactory cortex is located in the medial aspect of the temporal lobe known as the uncus

The primary olfactory cortex is located in the medial aspect of the temporal lobe known as the uncus Where is the primary auditory cortex located?
The primary auditory cortex is located in the superior temporal gyrus

What is the nucleus of the olfactory nerve then?
The nucleus of the olfactory nerve is known as the olfactory bulb located in the forebrain
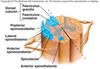
Label the diagram

Orange circle - superior colliculus Black circle -inferior colliculus Green circle - floor of the 4th ventricle Blue circle - Middle cerebellar peduncle

What are the different modalities of the oculomotor nerve? What is the function of the oculomtor nerve?
Oculomtor nerve provides somatic motor supply and parasympathetic supply Somatic motor to levator palpebrae superioris, medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus and inferior oblique Parasympathetic to the sphincter pupillae (constriction of the pupil) and the ciliary muscles of the ciliary body
What are the oculomotor nerve nuclei? What level is the nuclei located?
Oculomotor nucleus - at the level of the superior colliculus is for the somatic motor control Edinger Westphal nucleus supplies the parasympathetics
If there is damage to the oculomotor nucleus, what will happen to the eye?
Pupil will be dilated The eye will be facing down and out
What nerve nuclei arises at the level of the inferior colliculus?
This would be the trochlear nucleus
What is the modality of the trochlear nerve? Where does it exit the central nervous system? (ie where does the nerve arise on the brain) What does the trochlear nerve supply?
Somatic motor axons to the superior oblique muscle - moves eye down and out Trochlear nerve is the only nerve to exit the brainstem posteriorly (posterior aspect of midbrain)
Which part of the brainstem are the oculomotor and trochlear nucleus located?
Oculomotor and trochlear nucleus are both located in the midbrain at the levels of the superior and inferior colliculus respectively
What is the abducent nerve nucleus known as? What does the abducent nerve supply? and what action does this bring about? What are its modalities?
Known as abducens nucleus Supplies the lateral rectus - brings about abduction of the eye It is a somatic motor nerve
Where is the abducent nerve nucleus located?
The abudcent nerve nucleus is located in the caudal aspect of the pons
What is the final motor cranial nerve? (not a mixed one) What muscles does it supply? WHat extrinsic muscle of the tongue does it not supply and what supplies this? What modality is this nerve?
The hypoglossal nerve Supplies the intrinsic muscles of the tongue and the genioglossus, styloglossus, hyoglossus Doesnt supply the palatoglossus which is supplied by the vagus nerve hypoglossal nerve is somatic motor
Hypoglossal nucleus extends over a very long distance as it a long column of cells What part of the brainstem does it extend through?
Extends over most of the medulla of the brainstem

Note how III, IV, VI and XII emerge close to the midline: reflects the location of their nuclei Run through again the nucleus and where the nucleus are located (which part of brainstem) and what muscles/modalities the nerves are
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/picture1jpggifjpg-15E4DC4E6614B533D3F.png

Spinal accessory nerve has two components - the cranial accessory and spinal accessory components Were do nuclei for both the components arise?
Spinal accessory nuclei - anterior horns of the spinal cord segments C1-C5 Cranial accessory nuclei - the nucleus ambiguus located in the medulla
How does the spinal root of the accessory nerve exit and enter the cranial cavity? Where is it that the cranial and spinal roots come into contact?
Spinal root comes up through the foramen magnum and curves round to exit the cranial cavity via the jugular foramen The cranial and spinal roots only come into contact as they exit via the jugular foramen and then the cranial accessory root joins with the vagus nerve

What modality is the spinal accessory nerve and what muscles are supplied?
It is somatic motor Supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles