Week 1 - A - Neuroanatomy 1 - Paul Felts - mainly C.N.S Flashcards
What can the nervous system be divided into?
The central and peripheral nervous system (and the autonomic nervous system)
What forms the peripheral nervous system and what forms the central nervous system?
PNS - 12 cranial nerves and the 31 pairs of spinal nerves and their branches CNS - consists of the brain and spinal cord
What does the CNS begin as in the early stages of development - approx week 4?
Begins as the neural tube
At week 4, there are three primary besicles in the nueral tube, what are these primary vesicles known as? (forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain)
Prosencephalon (forebrain) Mesencephalon (midbrain) Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
The primary vesicles then form secondary vesicles by week 6-8 of development, what are the secondary vesicles known as?
Prosencephalon becomes - telencephalon and the diencephalon The mesenchephalon remains as the mesenchephalon The rhombencephalon becomes the metencephalon and the myelencephalon
What do the telencephalon and the diencephalon give rise to?
Telenchephalon - gives rise to the left and right cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon gives rise to thalalmus + hypothalamus
What do the mesencehphalon, metencephalon and myelencephalon give rise to?
Mesencephelon - midbrain Metencephalon - pons and cerebellum Myelencephalon - medulla oblonglata

Name the three primary vesicles What they divide into to become the secondary vesicles and The major derivatives from the secondary vesicles
Prosencephalon - Telencephalon: left and right cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon: thalamus + hypothalamus Mesenchephalon - Mesencephalon: Midbrain Rhombencephalon - Metencephalon: Pons and cerebellum Myelencephalon: medulla oblongata
What forms the brainstem?
The combination of the midbrain pons and medulla
Name the secondary vesicles which give rise to the derivatives of the mature brain - start with the outlined brain and work towards the spinal cord

Telencephalon - rise to the cerebral hemispheres Diencephalon - thalamus + hypothalamus Mesencephalon - gives rise to the midbrain Metencephalon - pons and cerebellum Myelencephalon - medulla oblongata
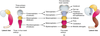
Neurones and glial cells are the two principle cells of the central nervous system What are the four parts of a typical neurone?
Have the dendrites, cell body, axon and nerve endings

What is the function of the dendrites and axons?
The dendrites are branched propagations from the cell body that recieve information from other neurons and carry it to the cell body Axons carry messages away from the cell body to the other neurons, muscles or glands
What are the 4 types of glial cell in the CNS?
Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Microglia Ependymal cells
What are the functions of the 4 types of glial cell?
Astrocytes - role in maintaining the blood brain barrier and environmental homeostasis Oligodendrocytes - produce myelin in the central nervous system Microglia - main immune surveillance cells and antigen presenting cell (APC) Ependymal cells - Ciliated cuboidal/columnar epithelium that line the ventricles
Oligodendrocytes produce myelin in the CNS, what produces myelin in the PNS? What is the function of myelin?
Schwann cells produce myelin the PNS The function of myelin is to increase the speed of nerve impulses
Throughout the brain, there are ‘bumps and valleys’ (indentations) What are these bumps and valleys properly known as?
Gyrus - bumps and sulcus - valley (indentation) (there are also fissures which are very deep indentations)

What is the functions of the gyri and sulci in the brain?
They increase the surface are of the brain increasing the amount of cerebral cortex able to fit in the skull
Which slice separates into right and left and which separates into front and back?
Coronal - front and back (anterior and posterior) Sagittal - right and left
What is the generalization for the arrangement of grey matter and white matter in the brain?
Generally grey matter on the outside with white matter on the inside - however there is a central cavity of grey matter in the brain

What do they grey and white matter in the brain contain?
The white matter contains mainly axons and their support cells The grey matter contains huge numbers of neuron cell bodies
What is the difference in arrangement of matter in the spinal cord compared to brain?
Brain White matter inside Grey matter outside with central cavity of grey matter also Spinal cord White matter outside Grey matter inside in a ‘H’ like fashion White matter - aons Grey matter- cell bodies

The grey matter in the spinal cord is arranged in horns What is the white matter arranged in?
The white matter is arranged in columns, anterior, posterior and lateral The columns are also known as funiculus - ie dorsal column = dorsal funiculus

Why can the white matter columns also be known as fascicles?
This is because the columns are groups of bundled axons which are also known as fascicles
What is the main sulcus in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe?
This is the central sulcus















