Week 1 - J - Anatomy 5 - Meninges, SOLs, Herniations - Includes Subdural and extradural haematoma Flashcards
What are the 5 layers of the scalp and which layer contains the named arteries of the scalp?
S - skin
- C - connective tissue (dense)
- A - aponeurosis
- L - loose connective tissue
- P - pericranium
Which layer of the scalp is the highly vascular layer hence scalp incisions can continually bleed?
This would be the connective tissue layer of the scalp Loss subaponeurotic layer is the loss areolar connective tissue layer of the scalp

What is the layer of the scalp that runs from frontalis anteriorly to occipitalis posteriorly?
This would be the aponeurois layer - dense fibrous tissue
Why is it that scalp lacerations & incisions can bleed excessively?
This is due to the highly anastamotic network from the branches of the ECA and ICA that supply the scalp with blood
Sutures of skull (fibrous joints) help prevent skull fractures from spreading What are the main sutures of the skull and what do they separate?
Coronal suture - frontal and parietal bones Saggital suture - the right and left parietal bones Squamous suture - temporal bone from parietal bones Lamboid suture (black circle posteriorly) - occipital bone from the right and left parietal bones

What is the thinnest part of the skull known as and what bones form it? What shape is it?
This is the Pterion Formed by the frontal, parietal, temporal and sphenoid bones It is an H shaped structure

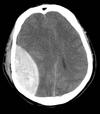
What artery courses over the deep aspect of the pterion? If a fracture occurs here and bleeding occurs, what is the bleed known as?
The middle meningeal artery runs along this apsect If a fracture occurs here, it causes an extradural (epidural) haemorrhage
What foramen in the skull is for the middle meningeal artery?
This would be the foramen spinosum - tiny hole situated next to the ovale shaped foramen ovale

What is the groove between the temporal and occipital bone caused by? What is the hole between the temporal and occipital bones known as? What cranial nerves pass here?
Caused by teh sigmoid sinus Hole is known as the jugular foramen Glossopharngeal, vagus and spinal accessory
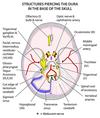
usually a bacterial or viral infection of the meninges What is this? What is the purpose of the meninges?
This is meningitis The meninges serve to protect the brain and spinal cord
the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three layers of membrane (“meninx” = membrane) What are the three layers of the meninges from superficial to deep? Which layers are usually joined to one another? Which layer is though to appear like a spiders web?
Dura mater Arachnoid mater Pia mater Dura and arachnoid are often joined to one another Arachnoid mater is often known as the spider web layer
What is the main nerve supply to the meninges?
This would be mainly a sensory nerve supply from CN V (TRIGEMNIAL NERVE)
The entire cranial cavity is lined by dura mater which is adherent to the bones of the skull What is the sheet of dura mater that forms a roof over the pituitary gland sitting in the pituitary fossa? What does the small hole in this sheet allow to pass through?
This is the diaphragm sellae Small hole to allow the pituitary stalk to pass through and attach to the hypothalamus

a tough sheet of dura mater “tenting” over the cerebellum What is this? and what does it attach to? What does the central gap in this sheet allow to pass throguh?
Tentorium cerebelli - attaches to the ridges of petrous temporal bone Central gap to allow brainstem to pas through
What is the opening in the tentorium cerebelli that allows passage of the brainstem known as? What is the midline structure of dura mater that separates the right and left hemispheres of the brain?
This is the tentorial notch Falx cerebri separates right and left hemispheres of the brain
What are the attachment points of the falx cerebri?
Attaches anteriorly to the crista galli Attaches to the internal aspect of the saggital suture Attaches to the internal occipital protuberance of occipital bone posteriorly
What is the crista galli a projection from?
It is a projection from the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone

The venous drainage of the brain drains into sinuses What are the veins that drain from the brain known as? What are the three sinuses that join to form the confluence of sinuses?
The cerebral veins drain the blood from the brain to sinuses The superior sagittal (dural venous) sinus, straight sinus and occipital sinus join to form the confluence of sinuses
Where is the confluence of sinuses located and how does this sinus become the internal jugular vein?
Confluence of sinuses is located at the internal occipital protuberance It drains into the transverse sinus which drains into the sigmoid sinus The sigmoid sinus exits the skull at the jugular foramen to become the internal jugular vein

Bacteria that enter a facial vein can travel directly back via the ophthalmic veins to the cavernous sinus The reason the bacteria can travel freely is due to the unique structure of the veins of the face, what is this unique structure?
The veins of the face are thick walled and therefore if punctured will not collapse and due to not having valves bacteria can flow freely into the ophthalmic veins to the cavernous isnus
What is the area of trauma of the face where if bacteria enters, then these veins can transport infection known as?
This is the danger triangle of the face

What do the vertebral arteries pass through to enter the cranial cavity? What do the right and left vertebral arteries become? What are the vertebral arteries a branch of?
They pass through the foramen magnum to become the basilar artery The vertebral arteries are branches of the right and left subclavian arteries

What do the cervical veretbraes posses to allow the vertebral arteries to pass through on their way to the skull?
They posses transverse foramina

The internal carotid artery also enters the cranial cavity to give off branches to supply the brain What foramen does it enter the cranial cavity via?
Via the carotid canal