Uterus, Cervix, Vagina Flashcards
Functions of uterus
- Proper environment for implantation
- Proper environment for fetal development
- Expels fetus
Define endometrium, myometrium, and perimetrium.
What kind of cell lines the endometrium?
-
Endometrium = mucosa
- lined by simple columnar epithelium
- Myometrium = muscularis
- Perimetrium = Serosa/adventitia

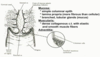
Label


Myometrium
Huge bundles of smooth muscle interlaced with collagen fibers
3 layers, but middle circular layer is the thickest and contains arcuate arteries
Estrogen, progesterone, relaxin, and oxytocin on the myometrium
-
Estrogen:
- proliferates
- maintains/increases contractility
- formation of gap jxns
- Progesterone: decrease contractility
- Relaxin: increase uterine contractions
- Oxytocin: stimulates uterine contractions
Layers of endometrium
Stratum functionale: this is what gets lost in mesnes

Stratum basale
Menstrual phase
- Shedding of the funcitonal layer
- Glands: short, collapsed
- Stroma: leukocytes and red blood cells
- Due to breakdown of vasculature
- Columnar epithelium

What phase is this endometrium in?

Menstrual phase (days 1-5)
Disrupted stratum functionale; red blood cells

Proliferative phase (days 5-14)
- Thickness goes from 1 –> 4mm
- Narrow & straight glands, but no secretions
- Proliferating stroma, w/ no leukocytes
- Columnar epithelium
- Lots of mitoses
What phase is this endometrium in?

Proliferative (days 5-14)
- straight & narrow glands w simple columnar epithelium
- columnar epithelium at top
- stroma in between

Secretory phase (days 15-26)
- Thickness: 4-6mm
-
Glands: wide, sacculated, secretory
- Glycogen rich secretions essentials for survival and development of the embryo
- Stroma: edematous, no leukocytes
- Tall columnar epithelium
- Mitoses only in coiled / helical arteries

What phase is this endometrium in?

Secretory phase (days 15-26)
wide, sacculated, curvy glands
What phase is this endometrium in?

Secretory phase ( days 15- 26 )
wide, sacculated glands
Premenstrual phase (days 27-28)
- Thickness: 4-5mm
- Glands: wide, irregular in outline
- Stroma: dense, leukocytes, RBCs
- Columnar epithelium
- Absent mitoses

What phases of the endometrium are these?


Functions of cervix
- At ovulation: Secretes watery mucus to help sperm into uterus
- Other times & during pregnancy: Secretes viscous mucus to prevent sperm and microorganisms entering the tuerus
When would cervical mucous be the most abundant and watery?
At ovulation (mid-cycle) to promote survival and transport of sperm through cervical canal.
Note: this is under the control of estrogen

Components of cervix wall
-
Mucosa:
-
Simple columnar epithelium
- Transitions to stratified squamous outside the external os
- Lamina propria (more fibrous than cellular)
- Branched, tubular glands lined by simple columnar epithelium
- Nabothian cysts: mucus retention in gland
-
Simple columnar epithelium
- Muscularis - dense collagenous c.t. w elastic & smooth muscle fibers
- Adventitia
In the cervix, the mucosa transitions from __ to __ epithelium at the __

Simple columnar to stratified squamous at the external os

What is this

Cervix’s nabothian cyst: mucus got stuck in the gland
What is this?

Stratified squamous epithelium of cervix outside the external os
Cervical glands are lined with __ epithelium

Pap smear
Swabbing the stratified squamous epithelium in the cervix to check for cervical carcinoma (frequently observed, but low mortality due to early detection)
cervical cancer most often caused by hpv 16
Hormonal regulation of the cervix
- Estradiol -> produce watery mucous (lysozyme)
- Progesterone -> viscous mucous
-
Relaxin: softening of the cervix by lysis of collagen during parturition
- Produced by corpus luteum & placenta
Vagina funcitons
excretory duct for uterus
organ of copulation
birth canal
Structure of vagina

What is this

Vagina
- stratified squamous epithelium of mucosa
- blood & vasculature in the lamina propria and muscularis
- outer, thick adventitia
What hormone stimulates the basal cells to produce that stratified squamous epithelium?

estradiol

Hormonal regulation of vagina

E & P on oviducts, uterus, vagina

Carcinoma of the cervix originates from
Stratified squamous NONkeratinized epithelial cells.
Can be contained in the epithelium and not invade the underlying stroma OR penetrate the basal lamina and metastasize to toher parts of the body (invasive)
Usu caught by pap smear –> surgery
Endometriosis
Endomterial tissu eexists in the pelvic peritoneal cavity
- ASsociated w hormone-induced changes -> pain, cysts, adhesions
- May lead to sterility bc deformed ovaries & oviducts
*


