Cartilage and Bone Flashcards
3 types of cartilage and their locations
Hyaline cartilage: nose, articular joints, intercostal joints, rings of the trachea/lungs/larynx
Fibrocartilage: intervertebral discs & pubic symphysis
Elastic cartilage: external ear and epiglottis
What kind of cartilage is this?
Hyaline cartilage
What kind of cartilage is this?

Elastic cartilage
What kind of cartilage is this?

Fibrocartilage
How do chondrocytes receive nutrients?
By diffusion because cartilage is AVASCULAR
Components of cartilage

Chondrocytes
Collagen & elastic fibers
Ground substance (lots of GAGs, proteoglycans)
Matrix is the functional component
Ground substance is ___philic
Basophilic because of its high carbohydrate concentration (lots og GAGs, proteoglycans)
Chondrocytes have well developed ___ and have __.
rERs because they’re constantly secreting proteins
Also have lipids
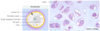
Describe the ring around chondrocytes
Lacunae: cavity in the ECM that chondrocytes sit in
The ring its territorial matrix is slightly darker, but the ones that are farther out between the cells that is barely stained is the interterritorial/interstitial matrix

Type __ collagen is in the territorial matrix

Type II collagen
There are also proteoglycans
Describe the main fibers in hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage.
Hyaline = type II collagen
Elastic = elastic fibers (requires special stain)
Fibrocartilage = type I collagen (network) as dense irregular connective tissue

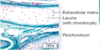
Explain the color differences between perichondrium and cartilage?

There’s a collagen (pink) in both, but there’s so much more ground substance (basophilic) in the cartilage
Two types of chondrogenesis
Appositional growth: at the surface of existing cartilage, perichondrial cells differentiate into chondroblasts
- Growth in girth of cartilage
Interstitial growth: within the cartilage plate, pre-existing chondrocytes are dividing mitotically
- Occurs in the early phases of cartilage formation to lengthen long bones
Describe the composition of the hyaline cartilage matrix
Capsular (pericellular) matrix
Territorial matrix
Interterritorial matrix
–
Collagen type II
Aggrecan (proteoglycan)
Chondronectin (glycoproein)
Describe the two layers of perichondrium
Outer fibrous layer: dense connective tissue = type I collagen + fibroblasts
Inner chondrogenic layer: chondroblasts; give rise to new cartilage
From top to bottom, you can see the progenitors > chondroblasts > chondrocytes

___ cartilage forms the fetal skeleton that will be replaced by bone through endochondral ossification
Hyaline cartilage

What kind of cartilage does not calcify with age?
Elastic cartilage
- Appositional growth
- type II collagen + elastic fibers
- Ears, epiglottis

What kind of cartilage does not have perichondrium? What is this cartilage type mostly made up of and how does it look ona lside?
Fibrocartilage
- Mostly type I collagen, some Type II collagen
- Cells align in an organized fashion to resist compression and shearing forces

What happens if you damage the perichondrium, which is responsible for supplying nutrition to the tissues via diffusion?
Fibroblasts in it will form scar tissue instead of chondrogenic cells
Lamellar/compact/mature bone vs Woven/primary/immature bone
Lamellar/compact/mature bone - regular alignment of collagen fiber
Woven/primary/immature bone - irregular alignment of collagen fiber
Osteon / Haversian system
the circular unit found within the compact portion of mature bone

Longitudinal Haversian Canal
Vertical blood vessel channels
Transverse / oblique / Volkmann’s canal
Horizontal blood vessel channels
Interstitial lamellae
Outer cicumferential lamellae
Inner circumferential lamellae
Lamellae between osteons
The most external layers of compact bone
The most internal layers of compact bone
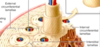
Outer vs Inner Periosteum
Outer periosteum: Type I collagen dense connective tissue called Sharpley’s fibers penetrate the bone matrix to bind the periosteum to the bone
Inner periosteum: composed of osteoprogenitor cells, which can differentiate into osteoblasts and help bone growth/repair

Endosteum
Lines internal cavities within the bone
Composed of osteo-progenitor cells with little connective tissue, so it’s thinner than periosteum.

Components of bone
- Cells: osteoprogenitor, osteoblast, osteocyte, osteoclast
- Fibers: type I collagen
- Ground substance: mineralized, so it stains (unlike cartilage)
-
Extracellular matrix- mostly inorganic
- Calcium phosphate w/ hydroxyapatite
- type I collagen, proteoglycans, non-collagenous proteins
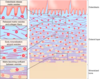
Specailized fibroblasts derived from mesenchyme desitned to become osteoblasts
Osteoprogenitor cells
Ostoeblasts
Large cells that enable bone production by releasing
- Matrix proteins (osteo calcin & RANK),
- Type I collagen
- Matrix vesicles (e.g. alkaline phsophatase) that help mineralize bone

Osteocyte
Mature cells of mature bones; highly branched and allows cell-cell communication via gap jxns
Formed when osteoblasts and their secretions get trapped in teh osteoid and ground substance

Osteoclasts
Large, multinucleated eosinophilic cells derived from bone marrow (monocytes); reabsorbs bone (forms howship’s lacuna when doing so)
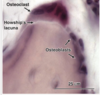
Bone mineralization
- Osteoblasts secrete osteocalcium, which recruits more calcium
- Positive feedback of calcium secretion increases seretion of matrix vesicles containing proteins
- Calcium & phosphate reach their needed concentrations –> mineralize and calcify into calcium-phosphate
Most of osteogenesis occurs when?

as a fetus
Intermembranous ossification - where and steps
- Osteoblasts start secreting osteoid into mesenchymal connective tissue
- Primary bone patches within the connective tissue form and grow by appositional growth
- Growth slows as patches on the outer surface merge into compact bone and patches in the marrow cavity become spongy bone
- Connective tissue is replaced with adipose or hematopoietic tissue
Where: most of skull, diaphyseal shafts of long bones
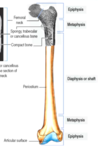
Endochondral ossification in long & short bones
- Chondroblasts in the condensed mesenchyme grow the cartilage, then start being replaced w bone
-
Bone collar formation in the perichondrium along the middle of the diaphysis
- Chondrocytes hypertrophy, deposit calcium phosphate into the matrix, and die
-
Primary ossification center formation
- Blood vessels penetrate the bone collar through channels created by osteoclasts
- Osteoprogenitor cells enter and produce osteoblasts that deposit primary bone on the cartilage matrix
- Diaphysis expands via intramembranous ossification while marrow cavity enlarges by osteoclasts
- Secondary ossification center formation: after birth, blood vessels invade the epiphyses
- Epiphyseal growth plate (band of hyaline cartilage) remains between the primary and secondary centers; expands and supplies matrix for ossification
- Bone increases in length until the growth plate disappears in your 20s
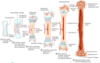
From epiphyseal to metaphyseal, whats the order of the zones of epiphyseal plate?
Resting > Proliferation > Maturation & hypertrophy > Calcifcation & cell death > Ossification

Zone of resting/reserve cartilage
Chondrocytes here serve as a reservoir of cells to supply the rest of the zones
Zone of proliferaiton
Chondrocytes are actively dividing, creating columns of cells parallel to the long axis of the bone
Secretes type II collagen and other matrix components for hyaline cartilage
Zone of maturation/hypertrophy
Cells stop dividing, swell up, and secrete collagen & proteins to promote calcification
Zone of calcification & cell death
Chondrocytes die as the matrix accumulates hydroxyapatite
Zone of ossification
Osteoprogenitor cells invade teh matrix and produce osteoblasts that begin creating woven bone on teh calcified matrix
Endochondral ossificiation is built on ___ plates
cartilage plates
What cell/type of growth is responsible for the bone growing in length?
Chondrocytes - the CARTILAGE- grows as they divide (interstitial growth) –> bone grows in length
Th bone grows in girth thanks to __ cells in the ___.
Osteoprogenitor cells in the periosteum
Name these


Identify




