Immune System & Lymphoid Organs Flashcards
(65 cards)
Innate immunity
Immediate, nonspecific actions.
Skin, mucus, neutrophils, NK cells, macrophages, and other leukocytes producing antimicrobial chemicals (HCl, defensins, lysozymes, complements, interferons)
How do macrophages in the innate immune system know when a bacterium is out there?
toll-like receptors recognize common invader patterns (structurally conserved molecules from microbes)
What are the 3 funcitons of macrophages in general again?
PIcks up debris
Eats invaders and presents antigens to the B cell
Non-specific phagocytosis to kill
Cell lineage of macrophages
Hematopoietic stem cells
> Common myeloid progenitor
> Progenitor cells
> Monoblasts
> Monocytes
> Macrophage
Neutrophils in the innate immune system
are ready in the blood, waiting to kill
(don’t present antigens)
How do natural killer cells kill?
Produce cytokines
Force infected cells into apoptosis
(Like neutrophils, they’re also just waiting in the blood to kill)
Adaptive/acquired immunity
Acquired gradually by exposure; more specific; slower
- B & T lymphocytes activated against specific invaders when they are presented with specific molecules by antigen-presenting cells (APC)
- Produces memory lymphocytes so a similar response can be mounted rapidly if the invader appears again
B cells make antibodies. Which part of an antibody binds to antigens?
Which part binds the cell receptor?
Fab binds antigen
Fc binds cell receptor (and determines Ab’s class)

What are the 5 types of antibodies B cells make?
IgG
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgM

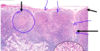
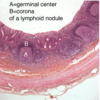
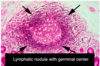
Clonal selection
- Stem cells differentiate into antigenically committed B cells in the bone marrow
- B-cells move to peripheral lymph tissue and contact their antigen
-
Rapid proliferation into memory cells & plasma cells (forms germinal center)
- Plasma cells create antibodies for greater immune response
- Memory cells circulate and allow an even faster immune response if the antigen is encountered again

2 main mechanisms antibodies work by
*Opsonization: receptors on leukocytes bind antibodies that are already attached to the antigens of microorganisms, thus increasing the efficiency of phagocytosis.
*Neutralization: antibody covers viruses outside the cell so it can’t enter one

B cells differentiated in bone marrow; T cells differentiate ____
B cells secrete its receptors for antibodies; T cells’ receptors ____
B cells can recognize an antigen by itself; T cells recognize antigens if ____
T cells mature in the thymus
T cell receptors remain on its surface
T cells recognize antigens if properly presented
3 types of T cells: CTLs, Helper, and Regulatory
-
Killer T cells/Cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTL): they attach to cell sources of antigens on foreign or virus-infected cells and trigger apoptosis.
- Has CD8 coreceptors for MHC class I molecules
- Similar to NK cells
-
Helper T cells (Th cells):
- Has CD4 coreceptors for MHC class II molecules
- Produces cytokines that promote differentiation of B cells into plasma cells
- Activates macrophages & CTLs
- Induce inflammation
- Can become memory helper T cells
- Regulatory/Suppressor T cells inhibit immune response & maintain unresponsiveness to self-antigens
-
T cell diversity is generated by
gene segment recombination
Major histocompatibility complex proteins (MHCs)
- MHC I proteins are displayed as “non-self” peptides on infected or mutated cells to alert killer T cells that they need assisted suicide
-
MHC II proteins displayed on the cell surface w/antigens by APCs to inform helper T cells to activate immmune response
- these MHCs display peptides from whatever the cell ingested
Adaptive immune response
- Antigen-presenting cell ingests antigen and displays on its MHC II
-
Helper T cell (Th) bind MHC II and becomes activated to secrete interleukins that promote both Tc & Th cell proliferation & differentiation
- “MHCII-restricted”
Cellular Immunity: Tc cells are activated by antigen-MHC I complex (“MHC I restricted”) expressed on infected cells to differentiate into memory & CTL cells.
Humoral immunity: Th cell activate B cells to proliferate into plasma & B memory cells

Humoral immunity purpose
antibody production

cellular immunity purpose
killing virally infected cells

Lymphocytes vs Accessory cells
- lymphocytes
- B cells
- T cells
- NK cells
- Accessory cells (antigen-presenting cells)
- Macrophages
- Dendritic cells
- Follicular dendritic cells
Both T & B cells are derived from the ___, but differentiate in different places.
bone marrow
Macrophages & dendritic cells are both derived from ____ and both present antigens, but which one is phagocytic?
Both are from monocytes
Macrophages are phagocytic
Follicular dendritic cells are derived where?
Lymph nodes
(mesenchymal origin, not bone marrow)
What are the two supporting cells of lymphoid organs?
- Reticular cells: create a meshwork of reticular fibers (collagen type III)
-
Thymic epithelial cells (TECs)/ Epithelioreticular cells support the thymus
- Note: no reticular fibers in the thymus!
- Origin is epithelial.
The primary lymphatic organs are ____
The secondary lymphatic organs are ___
Primary: bone marrow & thymus
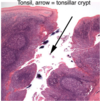
Secondary: tonsil, spleen, lymph nodes, lymphatic nodules