Cardiovascular Flashcards
Lymphatic vessels deliver lymph to what two veins?
internal jugular & subclavian
Systemic circulation sends blood from the __ side of the heart to the body
left
Layers of arteries & veins, outer to inner
Tunica adventitia (outer)
Tunica media
Tunica intima
Arteries & veins are made of similar components, but which has thicker walls? which has wider lumens?
Arteries have thicker walls
Veins have wider lumens
Which is the aorta and which is the vena cava? How can you tell?

The left one is the aorta, the right one is the vena cava.
The tunica media is much thicker in the aorta because it needs all those elastic fibers for its function; whereas, the tuncia adventitia is thicker in vena cava.
In arteries, the tunica intima is separated from the tunica media by ____. What is its purpose?
internal elastic lamina, full of elastin and fenestrae (gaps) that allow diffusion of substances to nourish cells deeps in teh vessel wall.

Tunica ___: one layer of endothelial cells supported by loose connective tissue and occasional smooth muscle cells.
Tunica ___: smooth muscle cells with variable amts of elastic fibers, reticular fibers (collagen type III), proteoglycans, and glycoproteins.
Tunica____: type I collagen & elastic fibers
Intima
Media
Adventitia
Elastic arteries
Composition, function, appearance, examples
- Composition: elastin
- Function: distention and recoil to stabilize blood flow
- Appearance:
- thicker intima than a muscular artery
- media has a lot of elastic fibers & elastic laminae (squiggles)
- Examples: aorta, carotids, subclavian arteries

Muscular arteries
Composition, function, appearance, examples
- Composition: much more smooth muscle
- Function: contracted state maintains blood pressure
- Appearance:
- prominent IEL
- A lot more smooth muscle cells in the media
- Examples: brachial, renal, ulnar, femoral arteries

What kind of artery is this?
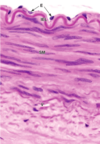
Prominent IEL and no squiggles –> muscular arteries
Arteriosclerosis
Deposits of calcium and elastin cause hardening of muscular arteries, which produge collagen, elastin, and gorund substance components
The amount of ___ material increases with age in the tunica media of muscular arteries.
Elastic fibers increases, while smooth muscle decreases
Thus, the arteries stiffen.
The smallest arteries are what? Describe apperance and function.
Arterioles
- Tunica intima consists of endothelium
- Tunica media has only 1-2 layers of SM
- Tunica adventitia is a very small layer of connective tissue
- Function: controls blood flow into capillaries, operating as control valves via vasodilation & vasoconstriction

Terminal arterioles brancha nd give rise to networks of ___
capillaries.
Without the pressure control of arterioles & metaarterioles, capillaries would rupture.
Vasa vasorum
Blood vessels that supply the cells of the tunica adventitia and tunica media of large vessels
the ___ in the wall of the aorta, an elastic artery, is responsible for distention
collagen

Which works w a higher blood pressure - arteries or veins?
Arteries - thats why their walls are larger w/ elastin
systolic vs diastolic number
Systolic: blood pressure when heart pushes blood thru arteries
Diastolic: pressure in arteris when the heart rests between beats and fills with oxygenated blood
High bp (htn stage 1)
130/80
An arteriole ends in a ___, where the smooth muscle of the tunica media becomes a _____.
Metarteriole
Smooth muscle of tunica media becomes precapillary sphincter
Precapillary sphincters
Vasoconstrict or vasodilate to control a pulsatile blood flow into the cpaillary bed for..
- body temp control
- nutrient, waste, gas exchange
Capillaries join with ___ to start returning blood to teh heart
Poscapillary venules
Edema
Postcapillary venules (thin, permeable walls) allow inappropriate amts of lymph fluid to leak out and accumulate

Some lymphatic organs have venules lined with cuboidal endothelial cells that allow…
lymphocytes to extravasate between blood & tissue
Capillaries are composed of a single layer of endothelial cells and are structurally supported by
Vimentin & Desmin
How do you know whats an artery vein and nerve here?


Mechanisms of capillary exchange
Diffusion: lipid-soluble gases
Transcytosis: endocytosis & exocytosis for large molecules
Leaks: between tight junctions; caused by signaling molecules (e.g.histamine)
Carrier-mediated transport
Types of cpaillaries & examples

Continuous capillaries
- Most common
-
Brain, muscle, nervous tissue, glands, and connective tissue
- Important to BBB
- Forms a continuous tube joined by tight junctions
- Vesicles from pinocytosis transport bidirecitonally via transcytosis
- Pericytes

Pericytes
cells of mesenchymal origin that surround capillaries. Functions:
- Differentiate into SM cells after injury
- Contains tropomyosin & isiomyosin for contraction to regulate blood flow into capillaries
- More pericytes -> fewer leaks
Fenestrated capillaries
- Fenestrae betwen cells; endothelium covered by a thin diaphragm
- Continuous and thicker basal lamina
-
Kidney, choroid plexus, endocrine organs, gut
- Needs rapid interchange of substances

Adrenal medulla uses what kind of capillaries?
Fenestrated capillaries
Secretory granules secreted via excoytosis contain catecholamine hormones

Discontinuous capillaries/sinusoids
- Has even larger openings beetween endothelium because discontinuous basal lamina
- Liver, bone marrow, spleen, gallbladder

Lymphatic capillaries
Thin endothelial lining with openings between cells
Valves prevent backflow
Converge at the thoracic duct & right lymphatic duct

Differentiating between a, v, and n in a neurovascular bundle
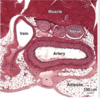
Vein has larger lumen and usually has more RBCs than arteries
Nerve fascicles are covered in perineurial sheath

Veins are capacitance vessels - they contain 70% of the body’s blood volume, but don’t allow blood to pool because they have
one-way valves that assist blood return and prevent backward flow
Valves can lose elasticity –>
Gnarled, incompetent varicose veins
Hemorrhoids
Esophageal varices
Deep vein thrombosis
Large veins are distinguishable by…
Very thick tunica adventitia containing bundles of SM, collagen, and elastin
Vena cava, portal, splenic, renal veins

Medium veins
Deep veins; Tunica media is thinner than the tunica adventitia, which contains smooth muscle cells interspersed between type I collagen
Popliteal, radial, tibial, great saphenous vein
Deep vein thrombosis
- Blood clot in deep veins
- Usually in the leg following long periods of not moving.
- Can cause pulmonary embolism
- Pain, swelling
- Causes: age, genetics, blood viscosity
- Treatment: anticoagulants
- Prevention: exercise, aspirin, stocking
Purkinje fibers

- Specialized myocardial cells containing scant, poorly organized myofibrils in the subendocardial region of ventricles
- Abundant glycogen
- Contact normal cardiac muscle via gap junctions to pass the signal and thus initiate contractions in those cells –> expel blood from ventricles
- Does not contract itself
- Rapidly conducts impulses to the apex of the heart –> contraction starts at the apex and squeezes blood toward the base to blood leaves from the “top” of the heart

Ischemic heart disease- caused by _, causes _
Often caused by atherosclerosis as the tunica intima narrows due to accumulation of lipids as an atheromatous plaque
Can cause myocardial infarct (heart attack) -> sudden death of muscle tissue
Which is a muscular artery?

The middle one. It has those undulations/wiggly lines and IEL
The left is the trachea; the right is a gland
Which components of the AVN are illustrated here?

Wall is too thick to be a vein.

Each vessel seen here will narrow and become a

Metarterioles
A capillary has continuous endothelium, lacking fenestrations but with many pinocytotic vesicles. Based on this, the tissue is most likely
- muscle
- liver
- spleen
- adrenal medulla
Muscle*-continuous
Liver & spleen- discontinuous
Adnreal medulla - fenestrated

The arrow is pointing to a vasa vasorum (a bv to a bv); similarly, the coronary artery is also a blood vessel that provides blood to a blood vessel (the heart)

C is false - it’s not a vein
The vessel on the left has IEL & SM layers –> muscular artery
The vessel on the right has a thick tunica media & lots of elastic layers –> elastic artery, like an aorta
Key feature of capillaries
Only one RBC can pass through at a time
Arterioles have __ layer(s) of endothelial cells, but 1-2 smooth muscl elayers
1
If you see a capillary surrounded by muscle w intercalated disks, what type of capillary is it?
Continuous capillary.
because that’s the type of capillary in hearts.
In a continuous capillary, the ___ is continuous with ___
endothelial cells is continuous with basal lamina
In a discontinuous capillary/sinusoid, the endothelial cell layer and the basal lamina
are both discontinuous


