Upper limb Flashcards
1
Q

A
Biceps brachii
2
Q

A
Brachialis
3
Q

A
Triceps brachii
4
Q

A
Anconeus
5
Q

A
Teres major
6
Q

A
Subscapularis
7
Q

A
Deltoid
8
Q

A
Coracobrachialis
9
Q

A
Supraspinatus
10
Q

A
Infraspinatus
11
Q

A
Teres minor
12
Q

A
Proximal phalanges
13
Q

A
Middle phalanges
14
Q

A
Distal phalanges
15
Q

A
Palmaris brevis
Improves the palmar grip action by pulling on the skin over the hypothenar muscles, which deepens the hollow of the palm
16
Q

A
Dorsal interossei
Abduction at the MCP joint
17
Q

A
Palmar interossei
Adduction at the MCP joint
18
Q

A
Lumbrical muscles
Flex at MCP joint and extend at IP joint

19
Q

A
Flexor retinaculum
20
Q

A
Pisiform
21
Q

A
Hook of hamate
22
Q

A
Metacarpal bones
23
Q

A
Trapezium
24
Q

A
Trapezoid
25

Capitate
26

Lunate
27

Scaphoid
28

Hamate
29

Triquetral
30

Flexor digitorum profundus
31

Pronator quadratus
32

Pronator teres
33

Flexor carpi radialis
34

Palmaris longus
Absent in 15% of the population
Does not travel through the carpal tunnel so can see the tendon at the wrist when the thumb and pinky touch

35

Flexor digitorum superficialis
(there is a flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus. Profundus means deeper. The profundus flexes the distal interphalangeal joints)

36

Flexor carpi ulnaris

37

Flexor pollicis longus

38

Brachioradialis
39

Extensor digiti minimi
40

Extensor indicis
41

Supinator
42

Extensor carpi ulnaris
43

Extensor digitorum
44

Extensor pollicis longus
45

Extensor pollicis brevis
46

Abductor pollicis longus
47

Extensor carpi radialis brevis
48

Extensor carpi radialis longus
49
What are the muscles in the superficial compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Palmaris longus
Flexor carpi radialis
Pronator teres

50
What are the muscles in the intermediate compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor digitorum superficialis

51
What are the muscles in the deep compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor pollicis longus
Pronator quadratus
Allow you to clench your fist then pronate it like you're ready to punch someone.
Flexor digitorum profundus + flexor pollicis longus = clenching
Pronator quadratus = pronation

52
Which nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the upper arm?
**Musculocutaneous**
## Footnote
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Coracobrachialis
53
Which nerve innervates the posterior arm?
**Radial nerve**
## Footnote
(posterior extensors of the forearm and triceps)
54
What are the superficial muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm?

55
What are the deep muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm?

56
Which forearm muscles are innervated by the ulnar nerve?
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexor digitorum profundus (1/2 of it)
The ulnar nerve is sandwiched between these muscles
The rest of the anterior forearm is innervated by the medial nerve
57
Which hand muscles are innervated by the median nerve?
1/2 loaf
L - lateral **lumbricals** (1st and 2nd digit)
*+ the thenar muscles*
O - **opponens** **pollicis**
A - **abductor pollicis** **brevis**
F - **flexor pollicis** **brevis**

58
Which hand muscles are innervated by the median nerve?
Thenar muscles
Lateral two lumbricals
(the rest are innervated by the ulnar nerve)
59
What are the thenar muscles?
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
60
Which structures pass through the axilla?
Axillary artery
Axillary vein
Axillary lymph nodes
Brachial plexus
Biceps and coracobrachialis

61
What are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
Superior: imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus
Lateral: medial border of the brachioradialis
Medial: lateral border of the pronator teres

62
What are the contents of the cubital fossa? Medial to lateral
Median nerve
Brachial artery
Biceps tendon
Radial nerve (not always considered part of the cubital fossa)
(My Bulging Biceps Rock)

63
Label this diagram
| (deep veins of the upper limb)


64
Label this diagram
| (superficial veins of the upper limb)


65
What does an upper brachial plexus injury look like and what nerve roots are affected?
C5/6
The affected limb hangs limply, medially rotated by the unopposed action of pectoralis major. The forearm is pronated due to the loss of biceps brachii. This is position is known as ‘waiter’s tip’, and is characteristic of Erb’s palsy.

66
Which nerve roots form the musculocutaneous nerve?
C5-7
67
Which nerve roots form the axillary nerve?
C5-6
68
Which nerve roots form the radial nerve?
C5-8
69
Which nerve roots form the median nerve?
C6-T1
70
Which nerve roots form the ulnar nerve?
C8-T1
71
Which artery supplies the posterior compartment of the proximal arm?
Profunda brachii/deep brachial artery

72
Which artery supplies the anterior compartment of the proximal arm?
Brachial artery
73
Which nerve innervates the anconeus?
Radial
74
Which nerve root(s) is/are involved in the biceps reflex?
C5/6
75
Which nerve root(s) is/are involved in the triceps reflex?
C7/8
76
Around which structure does the deep artery of the arm (brachial artery) run?
Radial nerve around the humeral shaft
77
Which muscles does the axillary nerve innervate?
Deltoid
Teres minor
78
How do you perform Allen's test?
1. Compress the ulnar and radial arteries at the wrist with your fingers
2. Ask the patient to make a fist to blanch the palmar skin
3. Release the ulnar artery, ask the patient to relieve their fist and view reperfusion
4. Repeat with radial artery
Tests flow through anastomotic palmar arches composed of radial and ulnar artery blood
79
What is the blood supply of the humeral head?
Circumflex arteries (branches of the axillary artery)
80
What are the two proximal attachments of the biceps brachii?
Long head: superior glenoid tubercle
Short head: coracoid process

81
What is the distal attachment of the biceps brachii?
Radial tuberosity
82
Which nerve roots can be compressed by a pancoast tumour?
C8-T1
83
What might upper extremity findings from a pancoast tumour be?
Weakness and atrophy of the intrinsic muscles of the hand
Pain and paresthesia of the fourth and fifth digits and the medial aspect of the arm and forearm
84
Which muscles form the mobile wad of the arm?
1. Brachioradialis
2. Extensor carpi radialis brevis
3. Extensor carpi radialis longus
85
What are the 3 heads of the triceps brachii?
Lateral
Medial
Long

86
Where does the radial nerve become the posterior interosseous nerve?
As it pierces the supinator

87
Which muscles does the posterior interosseous nerve innervate?
Muscles of the posterior forearm EXCEPT for the extensor carpi radialis longus and brachioradialis (both radial nerve)
88
Which forearm muscles does the median nerve run between?
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor digitorum superficialis

89
Which muscle does the median nerve pierce?
Pronator teres

90
Which muscle does the ulnar nerve pierce in the forearm?
Flexor carpi ulnaris

91
What are the borders of the cubital tunnel?
Distal: cubital tunnel retinaculum (ligament or band of Osborne)
Lateral: olecranon process
Medial: medial epicondyle
Proximal: two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris

93
The deep palmar arch is predominantly supplied by which artery?
Radial

94
Which nerve provides sensation to the dorsal web space between the thumb and the index finger?
Radial nerve
95
What is the action of the lumbricals?
Flexion of the MCP, extension of the PIP and DIP joints

97
From which palmar arch do the digital arteries arise?
Superficial

98
Which muscles are supplied by the anterior interosseous nerve?
Flexor pollicis longus
Pronator quadratus
Flexor digitorum profundus (lateral half)
*Deep forearm muscles*

99
How is the function of the anterior interosseous nerve tested?
OK sign

100
How is the median nerve tested?
Thumb abduction against resistance

101
The superficial palmar arch is predominantly supplied by which artery?
Ulnar
103
What is the action of the palmar interossei?
Finger adduction
PAD - Palmars ADduct
104
What type of joint is the 1st carpometacarpal joint?
Saddle joint

105
What type of joint are the 2nd-5th carpometacarpal joints and the metacarpophalangeal joints?
Ellipsoid/condylar

106
List 2 factors that make the thumb more mobile than the other phalanges
1. Deep transverse metacarpal ligament does not connect to the thumb
2. It is a saddle joint

107
What type of joint are the interphalangeal joints?
Hinge

108
Which structures pass through the carpal tunnel?
Flexor digitorum profundus tendon x4
Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon x4
Flexor pollicis longus tendon
Median nerve (anterior to the tendons)

109
What are the borders of the anatomical snuffbox?
Lateral: abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendon
Medial: extensor pollicis longus tendon
Floor: scapoid and trapezium

110
What is the action of the dorsal interossei?
Finger abduction
DAB - Dorsals ABduct
112
Which landmark can be used to help find the radial pulse?
Tendon of the flexor carpi radialis
| (radial pulse lies laterally)

116
Which bones form the carpal arch?
Pisiform, hook of hamate, scaphoid, trapezium
117
Which muscle(s) contribute to extension at the IP joints?
Extensor digitorum (weak)

118
What causes ape hand?
Medial nerve injury leading to weakness in the thenar muscles and unopposed action of the adductor pollicis

125
Which structures pass through the anatomical snuffbox?
1. Radial artery
2. Origin of the cephalic vein
3. Terminal parts of the superficial branch of the radial nerve
129
Which muscles abduct the wrist?
Flexor carpi radialis and extensor carpis radialis (longus and brevis)
130
Which muscles adduct the wrist?
Flexor carpi ulnaris and extensor carpi ulnaris
131
Which muscle(s) contribute to extension at the MCP joints?
Extensor digitorum (radial)
132
Which muscle(s) contribute to flexion at the MCP?
Lumbricals
134
Which muscle(s) contribute to flexion at the IP joints?
Flexor digitorum superficialis (PIP) and profundus (DIP)
135
Why do the digits take on a slightly flexed position at rest?
Flexion by the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus is stronger than extension by the extensor digitorum
136

Coronoid fossa of the humerus
Receives the coronoid process of the ulna during flexion of the forearm
Adjacent to the radial fossa of the humerus
137

Medial epicondyle of the humerus
138

Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
139

Medial supracondylar ridge
140

Coracoid process
141

Body of the humerus
142

Lesser tubercle
143

Greater tubercle
144

Surgical neck of the humerus
145

Anatomical neck of the humerus
146

Head of the humerus
147

Acromion
148

Supradeltoid bursa and subacromial bursa
149

Coracoclavicular ligament
150

Coracoacromial ligament
151

Glenohumeral ligaments
152

Supraglenoid tubercle
153

Infraglenoid tubercle
154

Medial border of the scapula
155

Subscapular fossa
156

Supraspinous fossa
157

Infraspinous fossa
158

Neck of the scapula
159

Glenoid cavity
160

Trochlea of the humerus
161

Capitulum of the humerus
162

Olecranon fossa
163

Radial fossa
164
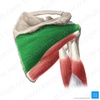
Infraspinatus
165

Teres minor
166

Teres major
167

Deltoid muscle
168

Biceps brachii muscle
169

Brachialis muscle
170

Triceps brachii muscle
171

Anconeus muscle
172
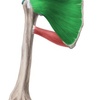
Subscapularis muscle
173

Supraspinatus muscle
174

Latissimus dorsi muscle
175

Pectoralis major muscle
176

Coracobrachialis muscle
177

Axillary artery
178

Brachial artery
179

Anterior humeral circumflex artery
180
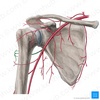
Posterior humeral circumflex artery
181

Circumflex scapular artery
182

Deep brachial artery
183

Subclavian artery
184

Thoracoacromial artery
185

Ulnar artery
186

Axillary vein
187
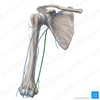
Basilic vein
188

Brachial veins
189

Cephalic vein
190

Subclavian vein
191
Which muscles attach to the greater tuberosity of the humerus?
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor

192
Which muscle(s) attach to the lesser tuberosity of the humerus?
Subscapularis

195
What is the innervation of the subscapularis?
Upper and lower subscapular nerves
(from the posterior chord of the brachial plexus)

196
What are the borders of the quadrangular space?
Superior: teres minor
Inferior: teres major
Medial: long head of triceps
Lateral: humeral shaft

197
What are the borders of the triangular space?
Inferior: teres major
Lateral: long head of triceps
Superior: lower border of teres minor

199
What are the borders of the triangular interval?
Superior: teres major
Lateral: lateral head of the triceps or the humerus
Medial: long head of the triceps

201
Draw the brachial plexus

202
What are the contents of the quadrangular space?

Axillary nerve
Posterior humeral circumflex artery
203
What are the contents of the triangular space?

Scapular circumflex artery
204
What are the contents of the triangular interval?

Profunda brachii artery
Radial nerve
259
What is the main function of the supraspinatus?
Arm abduction (particularly initiation of abduction)
260
What is the major function of the infraspinatus?
External rotation of the shoulder
261
What is the major function of the subscapularis?
Internal rotation of the shoulder
262
What is the innervation of the supraspinatus?
Suprascapular nerve
263
What is the innervation of the infraspinatus?
Suprascapular nerve
267
What are the contents of the triangular space?
Scapular circumflex artery
269
What are the contents of the triangular interval?
Profunda brachii artery
Radial nerve
270
What type of joint is the humeroulnar joint?
Hinge
271
What type of joint is the wrist?
Condyloid/ellipsoid

272
Damage to which nerve causes a winged scapula?

Long thoracic
## Footnote
*Serratus anterior*


