Gastrointestinal Flashcards
(29 cards)
What the two major vessels which supply the duodenum?
Gastroduodenal artery (proximal to the major duodenal papilla)
Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (distal to the major duodenal papilla)

What forms the rectus sheath?
The aponeurosis (deep fascia) of the transverse abdominal and external and internal oblique muscles

What are the anterior and posterior components of the rectus sheath above the costal margin?
Anterior - external oblique
Posterior - costal cartilages

What are the anterior and posterior components of the rectus sheath above the arcuate line?
Anterior - external oblique and the anterior portion of the internal oblique
Posterior - posterior portion of the internal oblique and the transverse abdominis

What are the anterior and posterior components of the rectus sheath below the arcuate line?
Anterior - tendinous expansions of all three oblique muscles
Posterior - transversalis fascia, peritoneum

Where is the arcuate line?
Midway between the umbilicus and pubis
Which four arteries supply the stomach?
- Right gastric
- Left gastric
- Right gastro-omental
- Left gastro-omental

What are the borders of Calot’s triangle?
Medial: common hepatic duct
Inferior: cystic duct
Superior: inferior surface of the liver
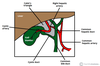
What are the borders of Hesselbach’s triangle?
Medial: lateral border of the rectus abdominus
Lateral: inferior epigastric vessels
Inferior: inguinal ligament

What are the boundaries of the femoral ring?
Medial: lacunar ligament
Anterior: medial part of the inguinal ligament
Lateral: femoral vein within the intermediate compartment of the femoral sheath
Posterior: pectineal ligament overlying the pectineus and its fascia covering the superior pubic ramus

What are the components of the portal triad?
Hepatic artery
Portal vein
Bile duct

What is the lesser sac (omental bursa)?
Potential peritoneal space formed by the greater and lesser omentum
Allows the stomach to move freely against the structures posterior and inferior to it

What is the lymphatic drainage of the anterior abdominal wall?
Above the umbilicus: axillary nodes
Below the umbilicus: superficial inguinal nodes
What is the lymphatic drainage of the anus?
Above the pectinate line: internal iliac
Below the pectinate line: superficial inguinal

What histological changes occur at the gastro-oesophageal junction?
Oesophagus: stratified squamous
Stomach: simple columnar
What is the notch on the lesser curvature, separating the body and pyloric antrum of the stomach, called?
The incisura angularis

What is biliverdin?
Product of heme catabolism
Responsible for the green colour seen in bruises
How does heme become bilirubin?
Heme → biliverdin (heme oxygenase) → bilirubin (biliverdin reductase)
What is urobilinogen?
Formed in the intestines from the bacterial breakdown of bilirubin
What are the three possible end points for urobilinogen?
- Urobilin (urine)
- Stercobilin (faeces)
- Hepatic reabsorption
Which liver enzyme conjugates bilirubin?
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
Defective in Crigler-Najjar syndrome
What is the ligament of Treitz?
Suspensory ligament of the duodenum
Landmark for discriminating upper and lower GI bleeding

What does the coeliac artery supply?
Liver, stomach, abdominal oesophagus, spleen, superior duodenum and superior pancreas
What does the superior mesenteric artery supply?
Distal duodenum, jejuno-ileum, ascending colon and part of the transverse colon





