Lower limb Flashcards
(143 cards)
1
Q

A
Iliacus
2
Q

A
Psoas major
3
Q

A
Gluteus maximus
4
Q

A
Gluteus medius
5
Q

A
Gluteus minimus
6
Q

A
Tensor fasciae latae
7
Q

A
Superior gemellus
8
Q

A
Inferior gemellus
9
Q

A
Quadratus femoris
10
Q

A
Piriformis
11
Q

A
Psoas minor
12
Q

A
Adductor magnus
13
Q

A
Adductor longus
14
Q

A
Adductor brevis
15
Q

A
Adductor minimus
16
Q

A
Pectineus
17
Q

A
Rectus femoris
18
Q

A
Vastus lateralis
19
Q

A
Vastus medialis
20
Q

A
Vastus intermedius
21
Q

A
Quadriceps femoris
22
Q

A
Sartorius
23
Q

A
Biceps femoris
24
Q

A
Semitendinosus
25

Semimembranosus
26

Gracilis
27

Tibialis posterior
28

Popliteus
29

Plantaris
30

Flexor digitorum longus
31

Flexor hallucis longus
32

Gastrocnemius
33

Soleus
34

Semimembranosus
35

Interosseous membrane
36

Extensor hallucis longus
37

Tibialis anterior
38

Semitendinosus
39

Extensor digitorum longus
40

Fibularis longus
41

Fibularis brevis
42

Lumbrical muscles
43
What are the superficial muscles of the gluteal region?
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus medius
Gluteus minimus
44
What are the deep muscles of the gluteal region?
Quadratus femoris
Piriformis
Gemellus superior and inferior
Obturator internus
45
What are the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Quadriceps femoris (vastus medialis and lateralis, rectus femoris)
Iliopsoas muscle
Sartorius
46
Which nerve innervates the anterior thigh?
Femoral nerve
47
What are the muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh?
Gracilis
Pectineus
Obturator externus
Adductor brevis
Adductor longus
Adductor magnus
48
What is the function of the muscles in the intermediate compartment of the thigh?
Hip adduction "hip adductors"
49
Which nerve innervates the muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh?
Obturator nerve
50
What are the muscles of the posterior component of the thigh?
Biceps femoris
Semitendiosus
Semimembranosus

51
What is the function of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh?
Extension at the hip and flexion of the knee
"hamstrings"
52
Which nerve innervates the muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh?
Sciatic nerve
53
What are the branches of the sciatic nerve?
Sciatic --\> tibial + common fibular
Common fibular --\> superficial fibular
54
What is the motor function of the femoral nerve?
Anterior thigh muscles
Hip flexors + knee extensors
55
What is the motor function of the obturator nerve?
Muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh
56
What is the motor function of the sciatic nerve?
Posterior compartment of the thigh
Tibial nerve - the muscles of the posterior leg (calf muscles), and some of the intrinsic muscles of the foot
Common fibular nerve - the muscles of the anterior leg, lateral leg, and the remaining intrinsic foot muscles
57
What is the motor function of the tibial nerve?
Muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg
58
What are the motor functions of the common fibular nerve?
Short head of the biceps femoris
Superficial fibular - lateral compartment of the leg (fibularis longus and brevis)
Deep fibular nerve - anterior compartment of the leg (tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus)
59
What are the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg?
Tibialis anterior
Extensor digitorum longus
Extensor hallucis longus
Fibularis tertius (not present in all individuals and often considered part of the extensor digitorum longus)

60
What are the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg?
Fibularis longus
Fibularis brevis
(eversion of the foot)

61
What are the superficial muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg?
Gastrocnemius
Plantaris
Soleus
(all insert into the calcaneus of the foot via the calcaneal tendon)

62
What are the deep muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg?
Popliteus
Tibialis posterior
Flexor digitorum longus
Flexor hallucis longus

63
What are the features of a femoral nerve compression?
Quadriceps weakness and sensory loss
64
What are the features of a sciatic nerve compression?
Leg pain and weakness affecting most lower leg muscles
Normal knee jerk, absent ankle jerk
65
What are the features of damage to the common fibular nerve?
Foot drop
Commonly caused by damage to the fibular
66
What are the features of a peroneal neuropathy?
Peroneal nerve = common fibular
Weakness on foot dorsiflexion and eversion, sensory loss on dorsum of foot, reflexes normal
67

Anterior cruciate ligament
68

Lateral collateral ligament
| (fibular collateral ligament)
69

Gerdy's tubercle
70

Head of the fibula
71

Intercondylar eminence
72

Lateral condyle of the tibia
73

Lateral malleolus
74

Lateral meniscus
75

Medial condyle of the tibia
76

Medial malleolus
77

Medial meniscus
78

Neck of the fibula
79

Oblique popliteal ligament

80

Patellar ligament
81

Posterior cruciate ligament
82

Medial collateral ligament
| (tibial collateral ligament)
83

Transverse ligament of the knee
84

Anterior lateral malleolar artery
85

Anterior medial malleolar artery
86

Anterior tibial artery
87

Common fibular nerve
88

Deep fibular nerve
89

Popliteal artery
90

Popliteal vein
91

Posterior tibial artery
92

Superficial fibular nerve
93

Superior medial genicular artery
94

Tibial nerves
95
Inside of which structure does the patella lie?
Quadriceps tendon

96
What is the blood supply of the knee?
Genicular anastomoses
(from the femoral and popliteal arteries)
97
What are the four major bursae of the knee?
1. Suprapatella
2. Prepatella
3. Infrapatella
4. Semimembranous

98
Damage to the tibial collateral ligament is likely to also affect which structure?
Medial meniscus
99
What is the common insertion for the superficial muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg?
Calcaneus of the foot via the calcaneal tendon
100
Which three muscles insert into the pes anserine?
1. Sartorius
2. Gracilis
3. Semitendinosus
101
What inserts into Gerdy's tubercle?
ITB

102
What structures pass through the popliteal fossa?
Popliteal artery
Popliteal vein
Tibial nerve
Common fibular nerve
103
What forms the superior margin of the popliteal fossa?
Hamstring muscles (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris)

104
What forms the medial margin of the popliteal fossa?
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus

105
What forms the lateral margin of the popliteal fossa?
Biceps femoris

106
What forms the inferior margin of the popliteal fossa?
Gastrocnemius

107
What are the attachments for the ACL?
Anterior intercondylar tibia
Lateral femoral condyle (medial aspect)

108
What are the attachments for the PCL?
Posterior intercondylar tibia
Medial femoral condyle (lateral aspect)

109
Which part of the knee menisci are vascularised?
Peripheral (central tears do not cause haematoma formation)
The inner 2/3 are nourished by synovial fluid
110
When does the femoral artery become the popliteal artery?
As it passes through the adductor hiatus

111
What are the 3 branches of the deep femoral artery?
1. Perforating branches - perforates the adductor magnus, supplying muscles in the medial and posterior thigh
2. Lateral femoral circumflex
3. Medial femoral circumflex

112
The femoral artery is a branch of which major vessel?
External iliac
113
The obturator artery is a branch of which major vessel?
Internal iliac
114
The gluteal arteries arise from which major artery?
Internal iliac
115
Which muscle separates the superior and inferior gluteal arteries?
Piriformis divides the arteries as they pass through the **greater sciatic foramen**

116
What are the borders of the femoral triangle?
Superior: inguinal ligament
Lateral: sartorius
Medial: adductor longus

117
Where does the small saphenous vein empty?
Popliteal vein

118
Which nerve supplies the muscles of the anterior leg?
Deep fibular
119
Which nerve supplies the muscles of the lateral leg?
Superficial fibular
120
Which nerve supplies the muscles of the posterior leg?
Tibial
121
What are the actions of the sartorius?
Hip flexion, abduction and lateral rotation
Knee flexion

122
What action does the long head of the biceps femoris do that the short head does not?
Extension and lateral rotation of the hip
(both do knee flexion)
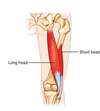
123
What is the innervation of the long and short heads of the biceps femoris?
Long: tibial division of the sciatic nerve
Short: common fibular division of the sciatic nerve

124
Which muscle is not in the posterior compartment of the thigh but has a hamstring component?
Adductor magnus
Can also extend the thigh
125
What is the innervation of the hamstring part of the abductor magnus?
Tibial part of sciatic nerve
126
When does the femoral artery become the popliteal artery?
Adductor canal
127
What is the blood supply to the ACL/PCL?
Middle geniculate artery

128
Which two muscles in the lower limb run counterintuitively and cross over?
Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor digitorum longus

129
What is the most commonly fractured tarsal bone?
Talus

130
What are the five tarsal bones?
1. Calcaneus
2. Talus
3. Navicular
4. Cuboid
5. Cuneiformis

131
What landmark can be used to help find the dorsalis pedis pulse?
Externsor hallucis longus tendon
Lateral

132
Which structures pass through the tarsal tunnel?
1. Tendon of the tibialis posterior
2. Tendons of the flexor digitorum longus
3. Posterior tibial artery
4. Associated veins
5. Tibial nerve
6. Tendon of the flexor hallucis longus
Tom, Dick And Very Naughty Harry

133
What makes the navicular prone to stress fractures?
Central navicular is in a watershed zone between the dorsalis pedis artery and the tibialis posterior artery

134
What is the clinical term for bunions?
Hallux valgus
135
Which muscles are involved in foot eversion?
Fibularis longus and brevis (lateral - superficial fibular nerve)
Fibularis tertius (anterior - deep fibular nerve)
136
Which muscles are involved in foot inversion?
Tibialis anterior and posterior
137
What are the two major superficial veins of the lower limb?
Great saphenous
Small saphenous
138
Which veins form the great saphenous vein?
Dorsal venous arch of the foot
Dorsal vein of the great toe
(runs medially)
139
Which veins form the small saphenous vein?
Dorsal venous arch
Dorsal vein of the little toe
140
What is the venous drainage of the plantar arch?
Posterior tibial and fibular veins
141
Which arteries supply the knee?
Genicular (from the femoral artery)
142
What are the borders of the adductor canal?
Anteromedial: sartorius
Lateral: vastus medialis
Posterior: adductor longus and adductor magnus

143
What are the contents of the adductor canal?
Femoral artery
Femoral vein
Saphenous nerve (largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve)
Nerve to the vastus medialis



