Reproductive Flashcards
(88 cards)
What is the lymphatic drainage of the scrotum?
Superficial inguinal nodes

What is the lymphatic drainage of the breast?
Axillary lymph nodes
Internal mammary chain

What happens to oestrogen, progesterone and prostaglandin levels during menstruation?
Decreased oestrogen and progesterone
Increased prostaglandin
What are the two layers of the endometrium?
Stratum basalis
Stratum functionalis
What stimulates a decrease in FSH in the preovulatory phase (days 6-13)?
Oestrogen and inhibin secreted by follicles
FSH declines and the follicle with the most FSH receptors becomes the dominant follicle
What is the name of the mature follicle?
Graafian
What is the role of oestrogen in stimulating ovulation?
Increased GnRH release
Increased LH release
Secreted by growing ovarian follicles
Which hormone surges during ovulation?
LH
Which hormones are secreted by the corpus luteum?
Progesterone - prepares the endometrium, inhibits GnRH + LH
Oestrogen - prepares the endometrium, inhibits GnRH + LH
Relaxin - inhibits uterine contractions
Inhibin - inhibits FSH release
What is the function of human chorionic gonadotropic hormone following fertilisation?
Inhibits degeneration of the corpus luteum
Which vessel supplies oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus?
Umbilical vein
Which vessel returns deoxygenated blood from the fetal internal iliac arteries to the placenta?
Umbilical arteries
What is the name of a mature sperm?
Spermatozoa
What is the name for sperm that are yet to develop/mature?
Spermatogonia
Which hormone triggers the production of thick cervical mucus which prevents sperm from entering the uterus?
Progesterone
Which nerve causes male ejaculation?
Pudendal
Which lymph nodes drain the distal vagina and vulva?
Superficial inguinal
Which lymph nodes drain the proximal vaginal and uterus?
Obturator, external iliac, hypogastric
Which ligament connects the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries to the side wall of the pelvis?
Broad ligament
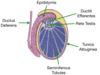
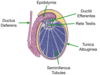
Which cells of the testes secrete testosterone?
Leydig cells
Which cells of the testes function to support and nourish developing spermatozoa?
Sertoli cells
Which cells of the follicle/ovary secrete oestrogen?
Granulosa cells
What type of epithelium is found at the vagina?
Non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
What type of epithelium is found at the uterus?
Simple columnar with long tubular glands