Ultrasound of the Lower Limb Flashcards
(38 cards)
What frequency should be used for the patella tendon? Why?
10-15 MHz - relatively superficial
What frequency should be used for the suprapatellar pouch? Why?
7.5-12 MHz - slightly deeper structure so slightly lower frequency is required
What is the routine for a knee US?
- Patellar tendon
- Quadriceps tendon
- Supra-patella pouch
- Medial and lateral joint space
- Posterior knee
How is the probe held in an US of the proximal patella tendon? What position is the knee in?
- Knee in slightly flexed position
- Probe held in longitudinal position

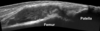
US image of a patella tendon
- Hoffa’s fat pad
- An area under the patella tendon
- Dermis and subcutaneous tissue above the patella tendon
- Above the patella is the prepatellar bursa (can’t see in this image)

What is an acoustic shadow?
Is characterised by a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves. It is a form of imaging artifact. This happens most frequently with solid structures, as sound conducts most rapidly in areas where molecules are closely packed, such as in bone or stones.

What is an ‘imaging artifact’?
An image artifact is any feature which appears in an image which is not present in the original imaged object.
i.e. seen here where the pointer is

What is an anisotropy?
An artefact encountered in ultrasound, notably in muscles and tendons during a musculoskeletal ultrasound. In musculoskeletal applications, the artefact may prompt an incorrect diagnosis of tendinosis or tendon tear.

What artifact are tendons susceptible to?
Anisotropy
Transverse US of proximal patella tendon


Longitudinal vs transverse view of the fibre bundles

Transverse view of fibres


What does this image show? (clue; patella tendinopathy)

- A thickened tendon
- Hypoechogenic tendon
- More dense or solid than usual
- Increased vascularity
Proximal patellar tendinopathy
Where does the quads tendon insert?
Proximal pole of the patella
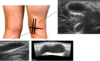
How should the probe be held durng quadds tendon US?
Longitudinal

Longitudinal quads tendon US image
N.B. should say femoral condyle instead of femoral head

US of quadriceps tendon ‘enthesitis’
Enthesitis is inflammation of the entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments insert into the bone.
- Tendon thicker and darker than normal (hypoechogenic)
- Common aspect of psoriatic arthritis

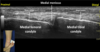
Position of knee during US of inter-trochlear groove and hyaline cartilage? Position of probe?
- Knee very flexed
- Probe transverse

US image of inter-trochlear groove and hyaline cartilage

A longitudinal view through the suprapatellar pouch - sonographic landmarks
The line represents the normal suprapatellar pouch. The full length of the pouch should be examined from the patella to most proximal aspect of the pouch.

Where does the suprapatellar pouch lie between?
Lies between the supra-patellar fat pad and the pre-femoral fat pad

Appearance of distended SPP - This is a longitudinal view through the suprapatellar pouch (SPP).
- The distended pouch can be seen as the fat plains of the supra-patella fat (SPF) and pre-femoral fat (PFF) are separated.
- The fluid (effusion) and synovial hypertrophy can be seen
- Thickened synovium with increased vascularity

Removal of fluid for analysis; different types of fluid
US can be used to help guide fluid removal


Normal synovial fluid
- Straw coloured
- Quite clear