Posterior Thigh and Knee SDL Flashcards
(84 cards)
What are the bones of the leg?
Tibia and fibula
Describe the location of the tibia
The tibia is much larger and lies medially
Describe the location of the fibula
The fibula is a thin bone that lies laterally
What forms the knee joint?
The proximal tibia articulates with the distal femur to form the knee joint - the fibula is not involved
What 3 articulations is the knee joint composed of?
- 2 femorotibial articulations (medial and lateral)
- Medial femorotibial
- Lateral femorotibial
- A femoropatellar articulation between the distal femur and patella

Bony landmarks of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the proximal tibia

What important muscle group inserts on the tibial tuberosity and how do these muscles move the knee?
The quads –> these are powerful extensors of the knee
What nerve winds around the neck of the fibula?
The common fibular nerve (also known as the common peroneal nerve). Here it is vulnerable to injury.

Which nerve courses through the posterior thigh?
The sciatic nerve
What is the sciatic nerve composed of?
2 separate nerves: the tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve which are bound together proximally but separate from each other in the posterior thigh and take different courses.
What muscles are found in the posterior thigh?
The hamstrings: semitendinosus, semimembranosus and long head of biceps femoris

Where do the hamstrings originate from?
The ischial tuberosity
What is the common nerve supply of the hamstrings?
The tibial division of the sciatic nerve
What are the actions of the hamstrings? What allows them to do this?
Because of their origin on the ischial tuberosity and their insertion on either the proximal tibia or fibula, they act in two ways: they extend the hip and flex the knee.
Distal insertion of semimembranosus?
It attaches to the medial tibial condyle

Distal insertion of semitendinosus?
the medial surface of the tibia.

Distal insertion of the long head of biceps femoris?
Together, the long head and short head form a tendon, which inserts into the head of the fibula.

Describe the long head of biceps femoris
The long head is a hamstring muscle, spanning the hip and knee joints and acting upon both.
Describe the short head of biceps femoris
The short head is technically not considered a hamstring muscle, as its origin is from the posterior aspect of the femoral shaft, not the ischial tuberosity; for this reason it cannot extend the hip
How does the short head of biceps femoris move the knee? What is its innervation?
Action: knee flexion
Innervation: common fibular part of sciatic nerve
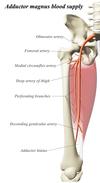
Where is adductor magnus found?
Adductor magnus is a large muscle of the medial compartment of the thigh.
What are the 2 parts of adductor magnus?
- Adductor part
- Hamstring part
Origin and insertion of adductor part of adductor magnus?
Origin: Inferior pubic ramus
Inserts: along the linea aspera

Action of adductor part of adductor magnus?
Adducts the hip