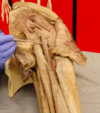
Posterior Thigh and Knee Anatomy Flashcards
What region is being pointed to?
Ischial tuberosity

What muscles originate from the ischial tuberosity?
The hamstrings
Is this a left or a righ femur?

Left - anterior aspect
What is being pointed to?

Medial and lateral lips of linea aspera
What muscles are attached to the linea aspera?
- Some of the quadriceps muscles (anterior)
- Some of the adductor muscles (medial)
- Short head of biceps femoris (posterior)
What is being pointed to? What does it articulate with?

Femoral condyles (medial and lateral) - articulate with tibial plateaus
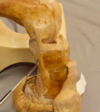
What structure is being pointed to? (anterior surface of distal femur)
Adductor tubercle
What attaches to the adductor tubercle?
Hamstring part of adductor magnus
What is being pointed to?

Tibial plateaus
What raised up area of bone is being pointed to?
Intercondylar eminence
What is found anterior and posterior to the intercondylar eminence on the tibia?
Attachment sites for cruciate ligaments
What is being pointed to? What is this an attachment site for?

Tibial tuberosity - attachment site for quads via the patella tendon
Which nerve wraps around the area being pointed to?

The common fibular nerve wraps around the fibular neck
Muscles of the posterior thigh generally act as…
- Hip extensors
- Knee flexors
What is the action of the short head of biceps femoris?
Flex the knee
What is the action of the hamstring part of adductor magnus?
Extends the hip
What nerves innervates the muscles of the posterior thigh?
Tibial nerve and common fibular (this innervates short head of biceps femoris)
What muscle is being pointed to?

Gluteus maximus
What is being pointed to?

Iliotibial tract (most laterally)
What muscle is this?

Gracilis (most medial)
What small triangular muscle in the gluteal region is being pointed to?

Piriformis
What bony landmark is being pointed to?

Ischial tuberosity
What nerve is being pointed to? How does it emerge in relation to piriformis?

Sciatic nerve - emerges inferiorly to piriformis
What ligament is being pointed to?

Sacrotuberous ligament
What 2 hamstring muscles are found on the medial side of the thigh?
- Semimembranosus
- Semitendinosus

What muscle is being pointed to? How does it lie in relation to the other medial hamstring muscle? Where does it inserts distally?

Semimembranosus - lies slightly deeper to semitendinosus - inserts distally onto the medial aspect of the proximal tibia
What muscle is being pointed to here? Where does it insert?

Semitendinosus - inserts on proximal aspect of tibia
What innervates semimembranosus and semitendinosus?
Tibial aspect of sciatic nerve
What muscle is being pointed to? Where does it lie in the posterior thigh?

Long head of biceps femoris - comes across laterally - inserts on the head of the fibula
Where does the tendon of biceps femoris insert?
Head of the fibula
What slip of muscle is being pointed to? Where does it originate? Where does it insert?

Short head of biceps femoris - originates from linea aspera (doesn’t act on hit) - joins common tendon with long head that inserts on the head of the fibula

What is the long and short head of biceps femoris innervated by?
Long head - tibial nerve
Short head - common fibular nerve
Actions of biceps femoris long vs short head?
Long - extends hip and flexes knee
Short - flexes knee only
What is the action of the hamstring part of adductor magnus?
Extends the hip (but cannot flex the knee as it doesn’t cross it)
What muscle is being pointed to?

Adductor magnus - large muscle in the medial thigh
What is being pointed to? Where does it insert?

Tendon of hamstring part of adductor magnus that inserts on the adductor tubercle
What is the hamstring part of adductor magnus innervated by?
The tibial nerve
What gap is being pointed to? What passes through here?
The adductor hiatus - the femoral vessels pass through here and become the popliteal vessels
What forms the adductor hiatus?
The hamstring and adductor part of adductor magnus
Where is the sciatic nerve located?
Deep in gluteal region - deep to gluteus maximus
Where should IM injections be placed in the buttock? Why?
Upper outer quadrant to avoid any danger of hitting the sciatic nerve

Danger of IM injection in:
- Upper medial quadrant
- Lower lateral quadrant
- Lower medial quadrant
- Upper medial –> danger of hitting gluteal arteries and nerves
- Lower medial –> danger of sciatic nerve
- Lower lateral –> danger of variations of sciatic nerve
What are possible variations of sciatic nerve?
- Emerges inferior to piriformis (most common)
- Can emerge superior to piriformis
- Can split and emerge both superior and inferior to piriformis
What are the nerve roots of sciatic nerve?
L4-S3
What does the sciatic nerve divide into in the mid posterior thigh?
Tibial nerve and common fibular nerve

Which nerve heads vertically down directly through the popliteal fossa and into the posterior compartment of the leg?
Tibial nerve

Where does the common fibular nerve head?
Heads out laterally along the edge of biceps femoris towards the lateral and anterior aspect of the leg. Wraps around the neck of the fibula.

What does the tibial nerve innervate in the lower leg?
Posterior muscles and muscles in sole of foot
What does the common fibular innervate in the lower leg?
Lateral and anterior compartment
What muscle is being hovered over?

Soleus
What ligament is being pointed to?

Patella ligament
What structure is being hovered over?
Medial femoral condyle
What ligament is being pointed to?
PCL
What muscle is mainly being hovered over?

Popliteus
What structure is being pointed to?

Lateral meniscus - sat between the tibial plateau and the femoral condyle
What are the contents of the popliteal fossa?
Popliteal artery and vein, tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve runs along superolateral boundary alongside biceps femoris
How can the popliteal artery be palpated?
In the popliteal fossa - gently press the popliteal artery onto the posterior aspect of femur. This can be difficult as it is deep.
What is the patella embedded within?
The quadriceps tendon

Anterior view of knee (patella has been reflected)

In flexion, what can you see the femoral condyles covered by?

Articular cartilage
What is being pointed to? Where does it lie?

Lying between the femoral condyel and the tibial plateau –> an important area of fibrocartilage –> the lateral miniscus
Where are the menisci thicker?
At the external margins (wedge shape)
How can a torn meniscus affect the knee?
Can lock the knee when debris from meniscus gets trapped inside the joint.
Locking implies that the torn part of the meniscus has displaced into a part of the knee where it doesn’t belong or fit.
What ligament is being pointed to?

Fibular / lateral collateral ligament –> this is found outside the joint capsule
Is the fibular collateral ligament attached to the lateral meniscus?
No –> therefore not commonly injured together

What ligament is being pointed to? What is it attached to?
Medial/tibial collateral ligament - attached to the medial meniscus
Knee in extension
Larger region of articulation –> more stable

Knee in flexion
Less articulation

What ligament is being pointed to?
ACL

Arises from the anterior intercondylar area, and travels to medial aspect of lateral femoral condyle
Function of the ACL?
- Prevents hyperextension of the knee
- Preventing anterior movement of the tibia relative to the femur
What is being pointed to?

PCL
Where does the PCL arise from? Where does it travel?
Posterior part of intercondylar area on the tibia and travels up towards medial femoral condyle
Function of PCL?
- Helps to prevent posterior movement of the tibia relative to the femur
- Keeps knee stable when the knee is flexed but weight bearing (e.g. walking downhill)
What muscle can be seen here?

Popliteus
How does the femur rotate during knee extension?
As full extension of the knee is approached, the femur undergoes a small amount of medial rotation on the tibia –> this locks the knee.
What is the purpose of this ‘locking’ during full extension?
Gives stability to the knee (muscles can temp relax)
How is the knee ‘unlocked’? What muscle allows this?
Small degree of lateral rotation as knee goes back towards flexion –> popliteus contracts to allow this
What movements do lateral/medial collateral ligaments prohibit?
- Limit sideways movement of joint (medial and lateral dislocation)
- Strong stabilisers
What movements do the cruciate ligaments prohibit?
Forwards and backwards
What movement often ruptures an ACL?
Twisting a flexed knee
What is osteoscarcoma?
- Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer that begins in the cells that form bones.
- Often prevents with problems around knees –> affects young people
What is muscle 6? What are its actions? What is it innervated by?

Long head of biceps femoris: extends hip and flexes knee, innervated by tibial nerve
What bony landmark is 3?

Ischial tuberosity
What is muscle 5?

Semitendinosus
Identify the nerve indicated by the number 8.

Common fibular nerve
Action of short head of biceps femoris?
Flexor of knee
Which muscle(s) form the superomedial boundary of the popliteal fossa?
Semimembranosus and semitendinosus
Action of the hamstring part of adductor magnus?
Extends the hip joint
Is this a right or left popliteal fossa? Identify nerve 6.

Right
Tibial nerve
What is muscle 4? Where does muscle 6 insert?

Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris inserts on proximal fibula
Which muscle(s) form the superolateral boundary of the popliteal fossa?
Biceps femoris
If a patient had a thombus in the popliteal vein, which signs would be expected in the affected limb?
Warmth, redness, swelling of the leg, tenderness
What is structure A?

Tibial collateral ligament
Muscle D is involved with which movement at the knee joint?

Lateral rotation of the femur
An injury to structure A is often associated with injury to the medial collateral ligament. Is this statement true or false?

False
If there is a normal response to the examination shown below, which of the following spinal segments are intact?

L2-L4
What is A?

PCL
What are A and B?

Menisci
What inserts on A?

Patella tendon (quads)
What is A?

PCL
Muscle D is innervated by which nerve?

Tibial
When the patella dislocates, it almost always dislocates…?
Laterally


