Spotter Qs Flashcards
Which congenital heart defect can be identified in this image?
Patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot

Which congenital heart defect can be identified in this image?
Patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
which muscles move the arm into this position? [2]

deltoid
supraspinatous
which cranial nerve is affected in this patient?

trigeminal
which segmental level is being assessed here?

S1
structure E is WHAT? [1]

white ramus
In this cross section of a peripheral nerve, what type of fibre has a morphology as illustrated by C?
- C axon
- A-beta axon
- A-gamma axon
- A-alpha axon
- A-delta axon

In this cross section of a peripheral nerve, what type of fibre has a morphology as illustrated by C?
- C axon
- A-beta axon
- A-gamma axon
- A-alpha axon
* *5. A-delta axon**

Which pathway runs through the region indicated by the asterisk?
- Lateral lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
- Corticospinal tractt
- Spinocerebellar tract

Which pathway runs through the region indicated by the asterisk?
- Lateral lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
* *4. Corticospinal tractt** - Spinocerebellar tract

In order to perform a lumbar puncture, the needle should inserted at position
A
B
C
D
E

In order to perform a lumbar puncture, the needle should inserted at position
A
B
C
D
E
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow that helps stablise the hip joint
- long head of biceps tendon
- articular capsule
- acetabular labrum
- acetabular ligament
- ligamentum teres

Identify the structure indicated by the arrow that helps stablise the hip joint
- long head of biceps tendon
- articular capsule
- acetabular labrum
- acetabular ligament
* *5. ligamentum teres**
The muscles that produce this movement are innervated by which nerve?
- sciatic
- common peroneal
- femoral
- tibial
- obturator

The muscles that produce this movement are innervated by which nerve?
- sciatic
* *2. common peroneal** - femoral
- tibial
- obturator
The functions of area B include:
- Control of mastication and facial expression
- Processing discriminative touch sensation from the limbs
- Control of visual and auditory reflexes and conjugate eye movements
- Control of tongue movements, swallowing, coughing and vomiting
- Regulating cortical arousal and sleep wake cycles
The functions of area B include:
- Control of mastication and facial expression
- Processing discriminative touch sensation from the limbs
- Control of visual and auditory reflexes and conjugate eye movements
4. Control of tongue movements, swallowing, coughing and vomiting
5. Regulating cortical arousal and sleep wake cycles

- CT
- MRI
- Myelogram
- Angiogram
- Ventriculogram

- CT
- MRI
3. Myelogram - Angiogram
5. Ventriculogram
what type of tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
2. dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
3 compact bone
4. cancellous bone
5. hyaline cartilage

what type of tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
2. dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
3 compact bone
4. cancellous bone
5. hyaline cartilage
The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in this section.
A
B
C
D

The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in this section.
A
B
C
D
sympathetic action of this would cause pupil dilation
A
B
C
D
E
F

sympathetic action of this would cause pupil dilation
A
B
C
D
E
F
what is A?
- ciliary
ganglion - Edinger
Westphal
nucleus - pretectal
nucleus - sympathetic
ganglion - medial
vestibular
nucleus - oculomotor
nucleus

what is A?
- ciliary
ganglion
2. Edinger
Westphal
nucleus
- pretectal
nucleus - sympathetic
ganglion - medial
vestibular
nucleus - oculomotor
nucleus
which is the highlighted nerve?
- Optic
- Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
- Troclear
- Abducens
- Oculomotor

which is the highlighted nerve?
- Optic
2. Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
3. Troclear - Abducens
- Oculomotor

ID B
- F wave
- Stimulus
artefact - H wave
- M wave

ID B
1. F wave
2. Stimulus
artefact
3. H wave
4. M wave

damge to the blue arrow causes:
- Agraphia
- Expressive aphasia
- Loss of musical appreciation
- Alexia
- Conduction aphasia
- Receptive aphasia
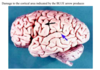
damge to the blue arrow causes:
1. Agraphia
- Expressive aphasia
- Loss of musical appreciation
- Alexia
- Conduction aphasia
* *6. Receptive aphasia**
ID H
- Basal ganglion
- Midbrain
- Thalamus
- Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Fornix
- Pons

ID H
- Basal ganglion
- Midbrain
* *3. Thalamus** - Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Fornix
- Pons
what is A?
- extensor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicis longus
- flexor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicic brevis
- extensor pollicis brevis

what is A?
- extensor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicis longus
- flexor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicic brevis
- extensor pollicis brevis
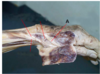
Which spinal curve is exaggerated in this woman?
- lumbar lordosis
- sacral kyphosis
- thoracic kyphosis
- cervical lordosis

Which spinal curve is exaggerated in this woman?
- *1. lumbar lordosis**
2. sacral kyphosis
3. thoracic kyphosis
4. cervical lordosis
what is 10?
- Tibiotalar ligament
- tendon of tibialis anterior
- spring ligament
- Deltoid ligaments of the ankle
- calcaneal tendon

what is 10?
- Tibiotalar ligament
- tendon of tibialis anterior
3. spring ligament - Deltoid ligaments of the ankle
- calcaneal tendon
what is a
- synovial fluid
- nucleus pulposus
- bone
- epiphyseal growth plate
- annulus fibrosus

what is a
- synovial fluid
* *2. nucleus pulposus** - bone
- epiphyseal growth plate
- annulus fibrosus
Identify the structure which prevents adduction of the leg
- A
- G
- B
- D
- F
- C
- E

Identify the structure which prevents adduction of the leg
- A
- G
- B
- D
- F
* *6. C** - E

What muscle group is being tested in this image?
- hip extensors
- knee extensors
- hip adductors
- hip abductors
- knee flexors
- hip flexors

The image below depicts the process of?
Activation of complement
Agglutination
Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Neutralisation
Opsonisation

The image below depicts the process of?
Activation of complement
Agglutination
Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Neutralisation
Opsonisation

Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is the process by which antibodies assist immune cells to identify and destroy infected cells by apoptosis.
What is A?

what is A?
bulobspongiosus
crus of penis
urogenital diaphragm
corpus caveronsum
corpus spongiosum
ischiocavernosus

what is A?
bulobspongiosus
crus of penis
urogenital diaphragm
corpus caveronsum
corpus spongiosum
ischiocavernosus
what is the cell indicated?
- mesothelial cell
- syncytiotrophoblast
- mesenchymal cell
- cytotrophoblast
- endothelial cell
- decidual cell

what is the cell indicated?
- mesothelial cell
2. syncytiotrophoblast - mesenchymal cell
- cytotrophoblast
- endothelial cell
6. decidual cell
which cells are indicated by the }
- pellucidal cells
- theca externa cells
- fibroblasts
- theca interna cells
- granulosa cells
- granulosa lutein cells 7. theca l

which cells are indicated by the }
- pellucidal cells
- theca externa cells
- fibroblasts
4. theca interna cells - granulosa cells
6. granulosa lutein cells - theca lutein cells
In the ovary, the first layer of stromal cells that organise around the growing follicle is called the Feedback: theca interna. These theca interna cells help to synthesise estrogens.
This is an organ of the male reproductive system. The structures cut in cross section here are lined by
acinar glandular epithelium
- germinal epithelium
- simple cuboidal epithelium
- stratified columnar epithelium
- stratified cuboidal epithelium
- pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- stratified squamous epithelium

This is an organ of the male reproductive system. The structures cut in cross section here are lined by
acinar glandular epithelium
2. germinal epithelium
3. simple cuboidal epithelium
4. stratified columnar epithelium
5. stratified cuboidal epithelium
6. pseudostratified columnar epithelium
7. stratified squamous epithelium
This is a diagram of the mature placenta and associated maternal structures. What is indicated by A?
- chorion
- amnion
- stratum basalis of the endometrium
- decidua capsularis
- myometrium
- decidua basalis
This is a diagram of the mature placenta and associated maternal structures. What is indicated by A?
- chorion
- amnion
- stratum basalis of the endometrium
- decidua capsularis
- myometrium
* *6. decidua basalis
The decidua basalis is the maternal part of the placenta derived from the endometrial tissue where the embryo implanted.**

Which cranial nerve innervates the structures that form in the arrowed pharyngeal arch?
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, recurrent laryngeal branch)
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, superior laryngeal branch)
- cranial nerve VII (facial)
- cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal)
- cranial nerve V (maxillary branch)
- cranial nerve V (mandibu

Which cranial nerve innervates the structures that form in the arrowed pharyngeal arch?
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, recurrent laryngeal branch)
- Cranial nerve X (vagus, superior laryngeal branch)
- cranial nerve VII (facial)
- cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal)
- cranial nerve V (maxillary branch)
* *6. cranial nerve V (mandibur branch)**
Identify the type of ovarian follicle.
- primordial 2. secondary (antral) 3. Graafian 4. primary 5. atretic 6. growing

Identify the type of ovarian follicle.
1. primordial 2. secondary (antral) 3. Graafian 4. primary 5. atretic **6. growing
A growing follicle has several layers of granulosa cells associated with the large central oocyte.**
This is a cross section through a female pelvis. A is the ischium, B is the pubic body and c is obturator internus. Identify d.
A iliococcygeus
B. coccygeus
C. puborectalis
D. deep transverse perineal muscle
E. internal anal sphincter

This is a cross section through a female pelvis. A is the ischium, B is the pubic body and c is obturator internus. Identify d.
A iliococcygeus
B. coccygeus
C. puborectalis
D. deep transverse perineal muscle
E. internal anal sphincter
What is the name of the fetal shunt shown in the diagram?
- umbilical vein
- foramen ovale
- ductus venosus
- ductus ateriosus
- ligamentum teres

What is the name of the fetal shunt shown in the diagram?
- umbilical vein
2. foramen ovale - ductus venosus
- ductus ateriosus
5. ligamentum teres
The peripheral blood cell that is most involved in the defence against viral pathogens is indicated by which letter?
A
B
C
D
E
The peripheral blood cell that is most involved in the defence against viral pathogens is indicated by which letter?
A
B
C
D
E
This patient was diagnosed with autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. The cells indicated by the arrows are
- nucleated erythrocytes 2. neutrophils 3. sickle cells 4. reticulocytes 5. spherocytes 6. target cells 7. lymphocytes

This patient was diagnosed with autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. The cells indicated by the arrows are
- nucleated erythrocytes 2. neutrophils 3. sickle cells 4. reticulocytes 5. spherocytes 6. target cells 7. lymphocytes
A characteristic of haemolytic anaemia is the increased production of red blood cells to compensate for increased destruction. As a result, increased numbers of immature erythrocytes are seen on a blood film. Reticulocytes are such immature red blood cells. They still possess mRNA and so stain slightly bluish and are larger than mature erythrocytes. Also they do not have the mature cell’s bi-concave form yet so don’t have a pale centre.
what is nerve supply to the pleura indicated?
- phrenic nerve
- vagus nerve and greater splanchnic nerve fibres
- pulmonary plexus
- intercostal nerves
- internal thoracic nerve

what is nerve supply to the pleura indicated?
- phrenic nerve
- vagus nerve and greater splanchnic nerve fibres
3. pulmonary plexus - intercostal nerves
5. internal thoracic nerve
the image of the bronchus from an asthma patient, the arrow indicates
- dense fibrocollagenous tissue
- hyaline cartilage
- basement membrane thickening
- hyperplasia of mucous glands
- bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
- elastic cartilage
- hypertrophied smooth muscle

the image of the bronchus from an asthma patient, the arrow indicates
- dense fibrocollagenous tissue
- hyaline cartilage
- basement membrane thickening
- hyperplasia of mucous glands
- bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
- elastic cartilage
* *7. hypertrophied smooth muscle**
this a pohotmicrogrpah taken of the small intestine, the arrow indicates
- basement membrane
- muscularis mucosae
- lamina propria
- submucosa
- epithelium

this a pohotmicrogrpah taken of the small intestine, the arrow indicates
- basement membrane
- muscularis mucosae
3. lamina propria - submucosa
5. epithelium
Identify the organ of the alimentary system shown in the high power magnification photomicrograph of part of its mucosa.
- stomach 2. large intestine 3. small intestine 4. oesophagus

Identify the organ of the alimentary system shown in the high power magnification photomicrograph of part of its mucosa.
1. stomach 2. large intestine 3. small intestine 4. oesophagus
what is A?
- conjoint tendon
- internal oblique muscle
- inguinal ligament
- spermatic cord
- superficial inguinal ring
- rectus sheath

what is A?
1. conjoint tendon
2. internal oblique muscle
3. inguinal ligament
4. spermatic cord
5. superficial inguinal ring
6. rectus sheath
sheath of connective tissue formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle, joining the muscle to the pelvis
what is A
- left gastric artery
- splenic artery
- left renal artery
- inferior phrenic artery
- pancreatic artery

what is A
- left gastric artery
2. splenic artery - left renal artery
- inferior phrenic artery
5. pancreatic artery
what type of hernia is shown here?
Indirect inguinal hernia
- Direct inguinal hernia
- Femoral hernia
- Incisional hernia
- Congenital inguinal hernia

what type of hernia is shown here?
- Indirect inguinal hernia
2. Direct inguinal hernia - Femoral hernia
- Incisional hernia
5. Congenital inguinal hernia
ID the structure identified
- cochlear
- vestibule
- incus
- semicircular canals
- stapes

ID the structure identified
1. cochlear
- vestibule
- incus
* *4. semicircular canals** - stapes
what is structure C?
- Anterior Commisure
- Fornix
- Corpus callosum
- Posterior commisure
- Internal capsule

what is structure C?
1. Anterior Commisure
- Fornix
- Corpus callosum
- Posterior commisure
* *5. Internal capsule**
Identify the cranial nerve indicated on this diagram of the dorsal aspect of the brain stem
- trochlear
- abducens
- oculomotor
- trigeminal
- facial
- opthalmic

Identify the cranial nerve indicated on this diagram of the dorsal aspect of the brain stem
1. trochlear
- *2. abducens**
3. oculomotor
4. trigeminal
5. facial
6. opthalmic
What is the function of the nerve indicated?
- motor to the muscles of facial
expression - motor to most of the
extraoccular muscles of the
eye - sensory for hearing and
balance - sensory to the pharynx and
the posterior 1/3 of the tongue - sensory nerve of the face and
motor to muscles of
mastication

What is the function of the nerve indicated?
1. motor to the muscles of facial
expression
2. motor to most of the
extraoccular muscles of the
eye
3. sensory for hearing and
balance
4. sensory to the pharynx and
the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
5. sensory nerve of the face and
motor to muscles of
mastication
In the diagram of the pupillary eye reflex shown, what is A?
- oculomotor nucleus
- sympathetic ganglion
- pretectal nucleus
- Edinger Westphal nucleus
- medial vestibular nucleus
- ciliary ganglion

In the diagram of the pupillary eye reflex shown, what is A?
- oculomotor nucleus
- sympathetic ganglion
- pretectal nucleus
- Edinger Westphal nucleus
- medial vestibular nucleus
* *6. ciliary ganglion**
In this anterior dissection of the neck region, identify D
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Sympathetic trunk
- Accessory nerve
- Vagus nerve

In this anterior dissection of the neck region, identify D
1. Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
* *3. Sympathetic trunk** - Accessory nerve
- Vagus nerve
A lesion in the optic tracts will result in which visual field defect
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G

A lesion in the optic tracts will result in which visual field defect
- A
- B
- C
* *4. D** - E
- F
- G
What is A
- Caudate nucleus
- Putamen
- Hypothalamus
- Globus pallidus
- Thalamus
What is A
1. Caudate nucleus
- Putamen
- Hypothalamus
- Globus pallidus
* *5. Thalamus**
What region/zone of the epiphyseal growth plate is indicated by the double headed arrows?
- dying
- calcifying
- hypertrophying
- resting
- proliferating

What region/zone of the epiphyseal growth plate is indicated by the double headed arrows?
1. dying
- calcifying
- hypertrophying
- resting
* *5. proliferating**
which muscle attaches here?
- deltoid
- supraspinatus
- teres minor
- infraspinatus
- long head of biceps
- subscapularis

which muscle attaches here?
1. deltoid
- supraspinatus
- teres minor
- infraspinatus
- long head of biceps
* *6. subscapularis**
Identify the muscle indicated
- subscapularis
- infraspinatus
- pectoralis major
- deltoid
- supraspinatus
- pectoralis minor

Identify the muscle indicated
- subscapularis
- infraspinatus
- pectoralis major
- deltoid
* *5. supraspinatus** - pectoralis minor
which muscles would normally prevent this positive sign
- gluteus medius and minimus
- iliopsoas
- gluteus maximus
- adductor longus and brevis
- quadriceps femoris

which muscles would normally prevent this positive sign
- *1. gluteus medius and minimus**
2. iliopsoas
3. gluteus maximus
4. adductor longus and brevis
5. quadriceps femoris
What is A?
- lateral collateral ligament
- lateral meniscus
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- medial collateral ligament
- medial meniscus

What is A?
1. lateral collateral ligament
- lateral meniscus
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- medial collateral ligament
* *6. medial meniscus**
ID the muscle indicated
- vastus medialis
- adductor longus
- adductor magnus
- pectineus
- sartorius

ID the muscle indicated
- vastus medialis
2. adductor longus - adductor magnus
- pectineus
5. sartorius
MCP is the middle cerebellar peduncle in this section.
The fibre tract indicated by the arrow is the
- medial
longitudinal
fasciculus - spinocerebellar
tract - corticospinal
tract - medial
lemniscus - spinothalamic
tract

MCP is the middle cerebellar peduncle in this section.
The fibre tract indicated by the arrow is the
1. medial
longitudinal
fasciculus
2. spinocerebellar
tract
3. corticospinal
tract
4. medial
lemniscus
5. spinothalamic
tract
what is A?
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior communicating artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- inferior sagital sinus
- superior sagital sinus

what is A?
- middle cerebral artery
- anterior communicating artery
* *3. anterior cerebral artery** - inferior sagital sinus
- superior sagital sinus
What is the primary function of the nerve indicated?
- lateral eye
movement - facial sensation
- tongue
movement - hearing
- facial expression
- parasympathetic
innervation of
thoracic and
abdominal
organs

What is the primary function of the nerve indicated?
1. lateral eye
movement
2. facial sensation
3. tongue
movement
4. hearing
5. facial expression
6. parasympathetic
innervation of
thoracic and
abdominal
organs
In this highly simplified diagram of the corneal blink reflex, identify the nucleus labelled A that receives the afferent information.
- facial
- supraoptic
- optic
- vestibulocochlear
- trigeminal
- oculomotor

In this highly simplified diagram of the corneal blink reflex, identify the nucleus labelled A that receives the afferent information.
1. facial
- supraoptic
- optic
- vestibulocochlear
* *5. trigeminal** - oculomotor
Identify the sulcus indicated by the arrow.
1. Post central sulcus
- Central sulcus
- Cingulate sulcus
- Precentral sulcus
- Parietoccipital sulcus
- Calacrine sulcus

Identify the sulcus indicated by the arrow.
1. Post central sulcus
- Central sulcus
* *3. Cingulate sulcus** - Precentral sulcus
- Parietoccipital sulcus
- Calacrine sulcus
Match the letters to the appropriate tracts.


In this sagittal section of the female pelvis, which of the labelled structures is mainly supplied by the gonadal artery?
C
D
E
F
H

In this sagittal section of the female pelvis, which of the labelled structures is mainly supplied by the gonadal artery?
C
D
E
F
H
**In this sagittal section of the female pelvis, the structure labelled F is an ovary and is mainly supplied by the gonadal artery.
The ovarian artery is the main arterial supply to the gonads in females.**

What is the structure labelled B?
Vas deferens
Prostate
Internal urethral orifice
Ureter
Seminal vesicle

What is the structure labelled B?
Vas deferens
Prostate
Internal urethral orifice
Ureter
Seminal vesicle

Which of the following relaxes pubic symphysis during labour?
Oxytocin
Oestrogen
Progesterone
Androstenedione
Vasopressin
Which of the following relaxes pubic symphysis during labour?
Oxytocin
Oestrogen
Progesterone
Androstenedione
Vasopressin
Venous blood from which structure is drained into A?
Right ovary
Right testicle
Left testicle
Right kidney
Spleen

Venous blood from which structure is drained into A?
Right ovary
Right testicle
Left testicle
Right kidney
Spleen
Venous blood from the left testicle is drained via the left testicular vein into the left renal vein.
However, the right testicular vein drains directly into the IVC, whereas the left testicular vein drains into the left renal vein, before the IVC is reached. Compression of the left renal vein can thus impede venous blood drainage from the left testicle, possibly resulting in a varicocoele.

In this prosection of a female in the lithotomy position, identify A
A. perineal body
B. bulbospongiosus
C. greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) gland
D. Cowper’s gland
E. crus of clitoris

A. perineal body
B. bulbospongiosus
C. greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) gland
D. Cowper’s gland
E. crus of clitoris
Ovary: What type of follicle is labelled A?
- Secondary
(antral) - Primordial
- Growing
- Atretic
- Primary
- Graafian

Ovary: What type of follicle is labelled A?
- Secondary
(antral) - Primordial
3. Growing - Atretic
- Primary
- Graafian
Having several layers of granulosa cells, this is a growing follicle. There
is no antrum.
What is A?
A. vas deferens
B. ejaculatory duct
C. testicular artery
D. spermatic cord
E. ilioinguinal nerve
F. genitofemoral nerve

What is A?
A. vas deferens
B. ejaculatory duct
C. testicular artery
D. spermatic cord
E. ilioinguinal nerve
F. genitofemoral nerve
Which chamber of the heart will A become?
- left
atrium - right
atrium - right
ventricle - left
ventricle

Which chamber of the heart will A become?
- left
atrium - right
atrium - right
ventricle - left
ventricle
Identify A on this lateral view of the penis and testes
A. epididymis
B. external spermatic fascia
C. Buck’s fascia
D. tunica vaginalis
E. pampiniform (venous) plexus
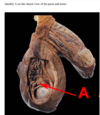
Identify A on this lateral view of the penis and testes
A. epididymis
B. external spermatic fascia
C. Buck’s fascia
D. tunica vaginalis
E. pampiniform (venous) plexus
In this diagram of a growing placenta (~21 days), the large black arrow indicates the
- Extraembryonic mesoderm
- Stratum basalis of the endometrium
- Decidua basalis
- Syncytiotrophoblast
- Trophoblastic lacuna
- Cytotrophoblast shell

In this diagram of a growing placenta (~21 days), the large black arrow indicates the
- Extraembryonic mesoderm
- Stratum basalis of the endometrium
- Decidua basalis
- Syncytiotrophoblast
- Trophoblastic lacuna
* *6. Cytotrophoblast shell**
What type of cell is indicated in this growing placental villus?
- Simple cuboidal epithelial cell
- Syncytiotrophoblast
- Erythrocyte
- Mesenchymal cell
- Cytotrophoblast
- Decidual cell

What type of cell is indicated in this growing placental villus?
- Simple cuboidal epithelial cell
- Syncytiotrophoblast
- Erythrocyte
- Mesenchymal cell
* *5. Cytotrophoblast** - Decidual cell
Cytotrophoblast cells extend out of the villus to form branches in the
lacunae and also when invading into the endometrium. The
cytotrophoblast cells are stained brown in this preparation. If in contact
with maternal blood, the surface becomes covered by
syncytiotrophoblast.
Testis: What cell is indicated by the arrows?
- Spermatocyte
- Spermatid
(late) - Spermatid
(early) - Spermatogonia

Testis: What cell is indicated by the arrows?
1. Spermatocyte
2. Spermatid
(late)
3. Spermatid
(early)
4. Spermatogonia
Primary spermatocytes are cells with large nuclei fairly close to the
bottom of the seminiferous tubule but above the spermatogonia (which
have more condensed nuclei).
Identify A
A. rectovesical pouch
B. seminal vesicles
C. epididymis
D. prostate gland
E. Cowper’s gland
F. urethra

Identify A
A. rectovesical pouch
B. seminal vesicles
C. epididymis
D. prostate gland
E. Cowper’s gland
F. urethra
Identify A on this PA xray of the chest
- lung hilum
- left atrium
- auricle of left atrium
- superior vena cava
- arch of aorta

Identify A on this PA xray of the chest
1. lung hilum
2. left atrium
3. auricle of left atrium
4. superior vena cava
5. arch of aorta
This image shows a ‘fatty streak’ in a coronary artery. ‘Foam’ cells at the arrows
can be derived from
macrophages and what other cell type?
- Endothelial
cells - Adipocytes
- Mesothelial
cells - Lymphocytes
- Neutrophils
- Smooth
muscle cells

This image shows a ‘fatty streak’ in a coronary artery. ‘Foam’ cells at the arrows
can be derived from
macrophages and what other cell type?
1. Endothelial
cells
2. Adipocytes
3. Mesothelial
cells
4. Lymphocytes
5. Neutrophils
6. Smooth
muscle cells
The fatty streak forms in the intima of a blood vessel and is comprised of
foam cells which sequester lipid. These cells are macrophages and
smooth muscle cells that have migrated there (smooth muscle cells come
in part from the underlying tunica media).
The cell indicate in this peripheral blood film is a/an
- Reticulocyte
- Eosinophil
- Spherocyte
- Target cell
- Sickle cell

The cell indicate in this peripheral blood film is a/an
- *1. Reticulocyte**
2. Eosinophil
3. Spherocyte
4. Target cell
5. Sickle cell
A reticulocyte is an immature erythrocyte and stains slightly blue in a
blood film due to its content of RNA.
Identify A in the sagitally sectioned head
- superior nasal meatus
- superior nasal conchae
- nasal septum
- middle nasal concha
- middle nasal meatus

Identify A in the sagitally sectioned head
- superior nasal meatus
- superior nasal conchae
- nasal septum
* *4. middle nasal concha** - middle nasal meatus
In this blood film, erythrocytes are
- microcytic
- hypochromic
- macrocytic
- spherocytic
- sickled

In this blood film, erythrocytes are
- microcytic
- hypochromic
* *3. macrocytic** - spherocytic
- sickled
Here the erythrocytes are larger than those in the normal (macrocytic).
They show differing shapes as well (poikilocytosis). The neutrophil
shows hypersegmentation.
Respiratory tract: The arrow indicates
- Bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
- Smooth muscle
- Internal elastic lamina
- Hyaline cartilage
- Elastic cartilage
- Fibrocollagenous tissue

Respiratory tract: The arrow indicates
1. Bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
- *2. Smooth muscle**
3. Internal elastic lamina
4. Hyaline cartilage
5. Elastic cartilage
6. Fibrocollagenous tissue
This is a bronchiole with alveoli surrounding it. The bronchiole has
prominent smooth muscle obvious from its elongated nuclei and dark
pink staining cytoplasm.
In which area can the right middle lobe be ascultated
- b
- d
- a
- e
- c

In which area can the right middle lobe be ascultated
- b
* *2. d** - a
- e
- c
The right middle lobe of the lung can be listened to in the axilla (lateral
to the normal position of the right nipple in the non-obese male)
Alimentary system: What does the arrow indicate?
- Smooth muscle
- Congregated fibroblasts
- Gastric glands
- Goblet cells
- Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue

Alimentary system: What does the arrow indicate?
- Smooth muscle
- Congregated fibroblasts
- Gastric glands
- Goblet cells
* *5. Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue**
Identify A
- common hepatic duct
- cystic duct
- common bile duct
- right hepatic duct
- pancreatic duct

Identify A
- *1. common hepatic duct**
2. cystic duct
3. common bile duct
4. right hepatic duct
5. pancreatic duct
Identify A
- greater omentum
- coronary ligament
- triangular ligament
- falciform ligament
- lesser omentum
- hepatogastric ligament

Identify A
- greater omentum
- coronary ligament
- triangular ligament
* *4. falciform ligament** - lesser omentum
- hepatogastric ligament
This is a transverse section through the vertebral body of L1. The structure labelled A
is the second part (descending part) of the duodenum. Identify B
A. gallgladder
B. jejunum
C. tail of pancreas
D. 3rd part of duodenum
E. head of pancreas

This is a transverse section through the vertebral body of L1. The structure labelled A
is the second part (descending part) of the duodenum. Identify B
A. gallgladder
B. jejunum
C. tail of pancreas
D. 3rd part of duodenum
E. head of pancreas
Identify E on the coeliac arteriogram
- right gastric artery
- splenic artery
- left gastric artery
- gastroduodenal artery
- common hepatic artery

Identify E on the coeliac arteriogram
- right gastric artery
- splenic artery
- left gastric artery
* *4. gastroduodenal artery** - common hepatic artery
Which of the following processes causes the transformation of structure B to structure A?
Acetylation
Phosphorylation
Transamination
Hydroxylation
Methylation
Glycosylation

Which of the following processes causes the transformation of structure B to structure A?
Acetylation
Phosphorylation
Transamination
Hydroxylation
Methylation
Glycosylation
Which of the following best describes C?
Hinge joint
Condylar joint
Plane joint
Ball and Socket joint
Saddle joint

Which of the following best describes C?
Hinge joint
Condylar joint
Plane joint
Ball and Socket joint
Saddle joint
Which bone(s) does A articulate with?
Frontal + zygomatic bones only
All cranial bones
Frontal, zygomatic and maxillary bones only
Ethmoid, frontal, zygomatic bones only
Lacrimal and nasal bones only

Which bone(s) does A articulate with?
Frontal + zygomatic bones only
All cranial bones
Frontal, zygomatic and maxillary bones only
Ethmoid, frontal, zygomatic bones only
Lacrimal and nasal bones only
Which of the following characteristics best applies to structure A?
It attaches to the xiphoid process through the costal cartilage of rib
It attaches to the body of the sternum directly
It attaches to the body of the sternum through the costal cartilage of rib
It does not attach to the sternum entirely
It attaches to the xiphoid process directly

Which of the following characteristics best applies to structure A?
It attaches to the xiphoid process through the costal cartilage of rib
It attaches to the body of the sternum directly
It attaches to the body of the sternum through the costal cartilage of rib 7
It does not attach to the sternum entirely
It attaches to the xiphoid process directly
Under normal physiological conditions, lymphocytes are most likely found in which of the following structures?
A
B
C
D

Under normal physiological conditions, lymphocytes are most likely found in which of the following structures?
A
B
C
D
The lamina propria is a layer of loose connective tissue deep to the epithelium, and superficial to the muscularis mucosae. Within the gut wall, lymphocytes are predominantly found in the lamina propria.
Which of the labelled intercellular junctions connect intermediate filaments?
A
B
C
A + B
A + C

Which of the labelled intercellular junctions connect intermediate filaments?
A
B
C
A + B
A + C
What is A?
Left coronary artery
Left anterior descending artery
Left circumflex artery
Left marginal artery
Right coronary artery

What is A?
Left coronary artery
Left anterior descending artery
Left circumflex artery
Left marginal artery
Right coronary artery
Which of the following is a likely property of this tissue?
Contraction occurs spontaneously and following neural stimulation at the neuromuscular junction
Contraction occurs spontaneously
No stem cells or ability to divide
Hypertrophies but has no stem cells and no cell division
Helps to secrete products of exocrine glands
Has stem cells called satellite cells which give rise to myogenic precursors

Which of the following is a likely property of this tissue?
Contraction occurs spontaneously and following neural stimulation at the neuromuscular junction
Contraction occurs spontaneously
No stem cells or ability to divide
Hypertrophies but has no stem cells and no cell division
Helps to secrete products of exocrine glands
Has stem cells called satellite cells which give rise to myogenic precursors
Julia Madel, a 54-year-old lifelong smoker, has been on a Caribbean cruise with her husband. For the last four days, she has been vomiting twice a day. Yesterday she began to convulse and had muscle cramps, so was taken to the sickbay.
Which letter on this arterial blood gas chart would most probably match Julia arterial blood?
A
B
C
D
E

Julia Madel, a 54-year-old lifelong smoker, has been on a Caribbean cruise with her husband. For the last four days, she has been vomiting twice a day. Yesterday she began to convulse and had muscle cramps, so was taken to the sickbay.
Which letter on this arterial blood gas chart would most probably match Julia arterial blood?
A
B
C
D
E
Vomiting leads to a loss of metabolically generated acid, HCl, from the stomach, which when prolonged can cause metabolic alkalosis.
This image represents the fluid distribution in a healthy adult male. Based on the volume of extracellular fluid, estimate his total body weight (kg).

Answer: 62.5
Extracellular fluid makes up approximately 20% of the bodyweight of a healthy adult male.
Which of the following phases of mitosis has the longest duration?
A only
A & D
B & E
D & E
C only
A & C

Which of the following phases of mitosis has the longest duration?
A only
A & D
B & E
D & E
C only
A & C
During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the nuclear envelope degrades. Additionally, the centrosomes move to opposite poles and begin to send out mitotic spindle fibres. This is the longest phase of the mitotic cell cycle.
Which of the following is the best description of the thumb’s movement in this image?
Combination of flexion, medial rotation and abduction
Combination of extension, lateral rotation and adduction
Combination of flexion, lateral rotation and adduction
Combination of extension, medial rotation and adduction
Combination of flexion and lateral rotation

Which of the following is the best description of the thumb’s movement in this image?
Combination of flexion, medial rotation and abduction
Combination of extension, lateral rotation and adduction
Combination of flexion, lateral rotation and adduction
Combination of extension, medial rotation and adduction
Combination of flexion and lateral rotation
Based on the appearance of the left shoulder in this image, which movement of the shoulder would be most affected?
Adduction
Abduction (first 15 degrees)
Abduction (after first 15 degrees)
External rotation
Internal rotation

Based on the appearance of the left shoulder in this image, which movement of the shoulder would be most affected?
Adduction
Abduction (first 15 degrees)
Abduction (after first 15 degrees)
External rotation
Internal rotation
Which of the following is G?
Ulnar nerve
Median nerve
Brachial artery
Radial nerve
Musculocutaneous nerve

Which of the following is G?
Ulnar nerve
Median nerve
Brachial artery
Radial nerve
Musculocutaneous nerve
Ia primary afferents, carrying information from muscle spindles, synapse in this
area.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G

Ia primary afferents, carrying information from muscle spindles, synapse in this
area.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Lesion of this region leads to spastic paralysis.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G

Lesion of this region leads to spastic paralysis.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G

Axons carrying nociceptive information decussate in which area?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G

Axons carrying nociceptive information decussate in which area?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G

The corticospinal tract is identified by which letter?
A
B
C
D
E
F

The corticospinal tract is identified by which letter?
A
B
C
D
E
F

What is indicated by the arrows in the reticular formation shown in these diagrams?
- substantia nigra
- raphe nuclei
- ventral tegmental area
- locus coeruleus
- basal pons

What is indicated by the arrows in the reticular formation shown in these diagrams?
- substantia nigra
* *2. raphe nuclei** - ventral tegmental area
- locus coeruleus
- basal pons
The arrow indicates which cranial nerve?
- Glossopharyngeal (IX)
- Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
- Facial (VII)
- Vagus (X)
- Hypoglossal (XII)
- Accessory (XI)

The arrow indicates which cranial nerve?
- Glossopharyngeal (IX)
- Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
- Facial (VII)
* *4. Vagus (X)** - Hypoglossal (XII)
- Accessory (XI)
In the diagram of the pupillary eye reflex shown, what is A?
- sympathetic ganglion
- ciliary ganglion
- pretectal nucleus
- oculomotor nucleus
- medial vestibular nucleus
- Edinger Westphal nucleus

In the diagram of the pupillary eye reflex shown, what is A?
- sympathetic ganglion
- ciliary ganglion
* *3. pretectal nucleus** - oculomotor nucleus
- medial vestibular nucleus
- Edinger Westphal nucleus
What is A?
- superior thyroid artery
- inferior thyroid artery
- descending laryngeal artery
- recurrent laryngeal nerve
- vagus nerve

What is A?
- *1. superior thyroid artery**
2. inferior thyroid artery
3. descending laryngeal artery
4. recurrent laryngeal nerve
5. vagus nerve
What is A?
- left testicular vein
- ureter
- left testicular artery
- inferior mesenteric artery
- inferior mesenteric vein

What is A?
1. left testicular vein
2. ureter
3. left testicular artery
4. inferior mesenteric artery
5. inferior mesenteric vein
what is A?
- ureter
- ovarian artery
- ovarian vein
- inferior mesenteric artery
- renal artery

what is A?
- *1. ureter**
2. ovarian artery
3. ovarian vein
4. inferior mesenteric artery
5. renal artery
What is A?
- sphincter urethrae
- prostate gland
- internal urethral sphincter
- bulbosponiosus
- detruser muscle

What is A?
1. sphincter urethrae
2. prostate gland
3. internal urethral sphincter
4. bulbosponiosus
5. detruser muscle
What is A?
- splenic artery
- left renal artery
- inferior phrenic artery
- pancreatic artery
- left gastric artery

What is A?
- *1. splenic artery**
2. left renal artery
3. inferior phrenic artery
4. pancreatic artery
5. left gastric artery
What is the structure labelled A?
External iliac artery
Lateral sacral artery
Superior gluteal artery
Inferior gluteal artery
Internal iliac artery

What is the structure labelled A?
External iliac artery
Lateral sacral artery
Superior gluteal artery
Inferior gluteal artery
Internal iliac artery
Other labelled structures (in this image):
A → Superior gluteal artery
B → External iliac artery
C → Lateral sacral artery
D → Inferior gluteal artery
E → Internal iliac artery
Which of the following hormones is responsible for maintaining this morphology?
LH
FSH
Oestrogen
Progesterone
hCG
Which of the following hormones is responsible for maintaining this morphology?
LH
FSH
Oestrogen
Progesterone
hCG
Which of the following structures is affected by B9 deficiency?
A
B
C
D
E

Which of the following structures is affected by B9 deficiency?
A
B
C
D
E
Which of the following nerve roots form the nerve that runs through E?
L1-L4
L2-L4
L2-L5
L4-S2
L5-S1
Umbilical artery

Which of the following nerve roots form the nerve that runs through E?
L1-L4
L2-L4
L2-L5
L4-S2
L5-S1
Umbilical artery
The nerve roots of the obturator nerve is L2-L4
This image depicts the layers of the inguinal canal in a male.
Which structure forms the internal spermatic fascia within the spermatic cord?
A
B
C
D
E

This image depicts the layers of the inguinal canal in a male.
Which structure forms the internal spermatic fascia within the spermatic cord?
A
B
C
D
E
What is B? [1]

Dura mater


