Semester II, Weeks 1-3 (Vessels, Lymph, Mouth) Flashcards
What tissue is this?
How can you tell?
What are the labeled layers?

Elastic Artery
- tunica media has many parallel elastic fibers called fenestrated elastic membranes throughout, with “fishbone” oriented smooth muscle nuclei visible between them
- arrow - tunica intima
- M - tunica media
- A - tunica adventitia
If a lumen is visible within the tunica adventitia of a large artery, what is it?
vasa vasorum
(literally “vessels of vessels”)
- small vessels that supply blood to the outer layers of the larger vessel
What are the 3 layers of a blood vessel, from innermost to outermost, and what do they contain?
- tunica intima - endothelium (SSE) + subendothelial loose CT layer
- tunica media - smooth muscles cells, elastic fibers
- tunica adventitia - loose CT, nerve fibers, vasa vasorum
How does the tunica media differ between elastic and muscular arteries?
elastic - **fenestrated elastic membranes **evenly distributed throughout entire tunica media, with “fishbone” oriented smooth muscle nuclei between elastic fiber layers
muscular - tunica media is surrounded by **internal and external elastic laminae **and contains only smooth muscle, without elastic fibers
What is the predominant layer in arteries vs. veins?
arteries - tunica media predominates
veins - tunica adventitia predominates
What is this tissue?
Name the labeled parts.
What layer is the arrow part of?
How are the circled V lumen and the circled A lumen differentiated?

Muscular Artery and Vein
A - adventitia, M - media
circled V - venous lumen, circled A - arterial lumen
arrow - internal elastic lamina (part of intima)
- venous lumens are larger and more “squashed” in shape than the smaller, more circular arterial lumens
What are the small granules within endothelial cells called?
What do they contain?
Weibel-Palade Bodies
- contain von Willebrand Factor and P-selectin for clotting and inflammatory purposes, respectively
What is the central structure here with a lumen?
How can you tell?
How many layers of cells typically surround its lumen?
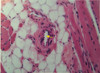
Arteriole
- small, round lumen and thick wall with less than 5 cell layers
What structure is shown here with its lumen indicated by the arrow?
How can you tell?

Venule
- large, amorphous lumen with very thin wall
How can capillaries be identified on slides?
What 3 types of capillaries are there?
- capillaries are extremely small, with a lumen of about 7-9 µm just big enough for 1 RBC
- a capillary wall’s cross-section is made up of just 1-3 endothelial cells
Types:
- continuous
- fenestrated
- sinusoid
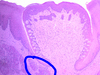
What is this tissue?
How can you tell?
What are the labeled structures?

Palatine Tonsil
- lymphatic follicles indicate a tonsil, deep crypts and a capsule indicate palatine
C - crypt. arrow - capsule, circle arrow - SSNKE lining crypts
What kind of tissue is shown here?
How can you tell?
What are the labeled structures?
What is at the center of structure F?

Tonsil Tissue
(structures shown do not allow differentiation between palatine, lingual, etc.)
- follicles below stratified squamous epithelium indicate tonsils
F - follicle with germinative center
arrow - infiltration of epithelium by lymphocytes
arrow with circle - SSNKE
What is the name for the category of tissue that tonsils and the appendix are in?
MALT
Mucosa Associated Lymph Tissue
What kind of cells make up lymphatic follicles?
**lymphoblasts **in the germinative center with **B lymphocytes **around the edges
What kind of cells surround the follicles?
And what are these areas called (2 possible terms)?
T-Lymphocytes
**Interfollicular Areas **or T-Dependent Zones
This is not an ideal picture, but…
What is the tissue?
How can you tell?
What are the labeled structures?

Lingual Tonsil
crypts and follicles indicate a tonsil;
glands, fat and muscle indicate lingual
F - follicle, C - crypt, D - excretory duct, G - salivary gland
arrow - SSNKE, circle arrow - lymphatic infiltration

What are the main differences between the lingual and palatine tonsil slides?
lingual
- shallow, wide crypts
- visible skeletal muscle, mucous acini, adipose tissue
palatine
- deep, narrow, branching crypts
- surrounded by capsule
What is this organ?
How can you tell?
What surrounds the organ? (not easily seen here)
And what continuations of that surrounding enter into the organ itself?

Lymph Node
- darker outer cortex and lighter inner medulla is characteristic of the lymph node
- CT capsule surrounds the organ and CT trabecules continue from the capsule into the node
What is the darker outer layer of this organ (left) and what is it made up of?
What are the branchings (not clearly visible here) of the darker tissue into the lighter area on the right called?

- Cortex w/ lymphatic follicles
- Medullary Cords made up of plasma cells, macrophages and B-lymphocytes extend from the cortex into medulla
What is the area between the darker outer and lighter inner parts of this organ called?
What does it contain?

Paracortex - between cortex and medulla of lymph node
contains T Lymphocytes
What is the area between the capsule and cortex of this organ called (not clearly visible here)?
What similar areas is it continuous with?
What is in them and what purpose do they serve?

Marginal Sinus lies between capsule and cortex, allows inflow of fluid from afferent vessels…
It’s continuous with Intermediate Sinuses along trabeculae and Medullary Sinuses within the medulla…
They contain reticular cells, fibroblasts and histiocytes (fixed macrophages)
What vessels serve and drain this organ?
Where do they enter/exit?

multiple Afferent Lymph Vessels flow into the node around the cortical edge
one Efferent Lymph Vessel flows out from the hilum where an artery/vein also supply/drain the node
What special vessels allow lymphocytes to enter lymph nodes from the blood?
Where in the node do they enter?
And how do they re-enter the blood when leaving the node?
High Endothelial Venules - post-capillary vessels with cuboidal endothelium
- drain lymphocytes into paracortex
- lymphocytes exit nodes via the efferent lymph vessels > thoracic duct > angulus venosus > blood circulation
What is this organ?
How can you tell?

Spleen
- has lymph follicles and a capsule
- does not have distinct cortex/medulla structure as in nodes
- does not have pits, muscle and adipose tissue as in tonsils