Semester II Midterm (Dustin) - Important Distinguishing Characteristics Flashcards
(23 cards)
What glands are these?
In which organ are they located, then?

Brunner’s Glands - produce alkaline mucus
only found in the tela submucosa of the Duodenum - neutralizing the acidic chyme
Also noted by numerous tall folds of Kerckring (aka Plicae Circularis) with short intestinal crypts
This is a Liver (H-E) slide, what are these 3 vessels?

Purple = Portal Vein Branch, larger/thinner walled than the:
Yellow = Interlobular Artery/Arteriole a branch of the Proper Hepatic
Green = Bile Duct identified from its lining of simple cuboidal epithelium
Together they make up the Portal (or Hepatic) Triad (or Area), situated a short distance away from the Central Vein

What is the overall gland/organ, based on the frequency of the glands you see here?
What are these glands?

Sublingual Gland: mixed seromucous, but predominantly mucus (2/3)
Mucus acini: poorly stained, lumen often shown as elongated.
- Nuclei are condensed at the base
- Synthesize mucus, which is stained red by Mucicarmin
Serous Acini often form semilunar caps called “demilunes of Gianuzzi” surrounding mucus acini

What is this?
How do you know?

Lymph Node
- Contains Follicles w/ Germinal Centers, clear Medulla and Cortex regions (Spleen has no cortex or medullary regions)
- No Central Arteriole as in Spleen

What is the overall gland/organ, based on the frequency of the glands you see here?
What are these glands?

Submandibular Gland: Mixed seromucus, but predominantly serous (2/3)

In case of Hemotoxylin-Mucicarmin Stain, mucus will be reddish with mucicarmin, but all serous acini and other glands/ducts will be stained greyish blue with hemotoxylin.
How do you differentiate a capillary from an arteriole or venule?
Capillaries
- 6-9 micrometer diameter, roughly the same to slightly larger than an erythrocyte
- No muscular/adventitia layers
- May see elongated/flattened cells embracing the endothelial cells (pericytes)

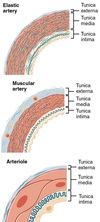
How do you differentiate between Medium/Muscular Arteries, Large/Elastic Arteries, and Arterioles?
Apart from larger size, Elastic Arteries have:
- Relatively thick Tunica Media with layers of circular smooth muscle (flat nuclei) and many fenestrated elastic sheets (may have RF staining -> elastin dark violet and can’t see smooth muscle)
- T. Adventitia relatively thinner than Media, contains prominent vasa vasorum/nerves
Muscular Arteries:
- Prominent Internal Elastic Membrane (wavy feature) btwn T. Intima & Media
- Less elastin in T. Media and relatively more smooth muscle
- Elastic fibers in T. Adventitia
- The 3 layers are relatively similar in thickness
Arterioles:
- No internal elastic membrane or elastic elements
- Has max 5 layers of smooth muscle (which differentiates from capillary with no smooth muscle)
What is different between the Spleen with “Total” H-E stain and “Washed Out” / “Perfused” stain?

The Washed Out stain removes the mobile parts that were in the tissue, this mainly being Red Pulp (erythrocytes)
White Pulp (darker due to lymphocytes) with fixed structures remain, including splenic follicles, PALS, sinusoids, reticulin fibers, stave cells, capsule, etc.

Which organ is this, based on the type of glands and their frequency that you see here?

Pancreas
- Divided into Lobules that exclusively contain Serous Acini
- No fat like in Parotid Gland! Also no salivary ducts!
- Contains endocrine Islets of Langerhans (paler regions)

What organ is this?
What are the darker spheres with pale centers?
What makes them unique from similar structures?

Spleen
The dark spheres with pale centers are Splenic Follicles / Malpighian Corpuscles
They contain a central arteriole in the margins
The dense, darker periphery is called a corona and contains B-lymphocytes, the paler core is called the germinal center

Which organ is this?
How do you know?

Thymus
- No Follicles - Has Lobules instead
- Hassal Bodies: reddish onion-like degenerated epitheloid reticular cells that are clustered in the medulla
- Often much adipose tissue is present

Which plexus is which?
(Base this on the surrounding tissue)

Blue = Submucosal / Meissner’s Plexus
Yellow = Myenteric Plexus of Auerbach - between two layers of muscularis externa

Slide & Stain?
What part of this is stained blue?
Above the blue, what part is stained bright pinkish-red?

Develping Tooth (Azan)
Blue:
- Predentin (uncalcified, less dense, more blue. lower part)
- Dentin (denser, bluish-pink due to calcification)
Above the blue, bright pinkish-red:
- Enamel Prism

What type of epithelium does Filiform Papillae have?
Partially keratinized stratified-squamous epithelium

What is the Peri-Arteriolar Lymphoid Sheath (PALS)?
What makes it unique from a similar structure?

PALS is a Spleen structure, similar to follicles but with NO Germinative Center
- Near central/”penicillar” arteriole

These structures are only visible on one corner of the tissue surrounding the lumen, so what are they? Which organ are they in?
What distinguishes this from other tissue that is histologically similar?

Peyer’s Patches - lymphatic follicle aggregations found within the tela submucosa
indicative of only the Ileum, appearing opposite to the mesentary (antimesenterial)
- Do not appear in Jejunum (the most clear way to tell), also Ileum has fewer folds and shorter villi
- Appendix also has lymphatic clusters (but NOT Peyers Patches) but they are dispersed throughout. Also it has no villi or folds, and fewer/shorter crypts

What are the main differences between the lingual and palatine tonsil slides?

lingual
- shallow, wide crypts
-
3 Characteristics of Tongue:
- visible skeletal muscle (going in 3 different directions)
- mucous acini
- adipose tissue
palatine
- deep, narrow, branching crypts
- surrounded by capsule

Which one is the artery and which one is the vein? Why?

1 is the Vein because:
- Lumen is flat and larger
- T. Media is much thinner than artery
- T. Adventitia is thicker than for the artery
2 is the (Small) Artery because:
- Lumen is round and smaller
- Between T. Intima and Media is wavy/light refractive structure of internal elastic membrane
- T. Media thicker with circular smooth muscle fibers and relatively little elastic fibers compared to Elastic Artery
What is the overall gland/organ, based on the frequency of the glands you see here?
What are the types of glands?

Parotid Gland - exclusively serous, no mucous glands
Also contains:
- Intercalated Ducts, which drain into:
- Striated Ducts (have basal striations), which drain into:
- Interlobular Ducts
- Adipose Tissue
Serous glands: basophilic, secrete amylase.
- *Don’t confuse with Serous with Mucus Acinus stained by Mucicarmin! That will be more reddish and the nuclei will be flatter, but serous glands will have round nuclei and granules.*
- **Not Pancreas! That doesn’t have adipocytes in lobules and has no salivary ducts!*

What are the3 main histological characteristics of the Tongue?
- Glands of merocrine secretion: serous (von Ebner’s glands. basophilic) and/or mucous (poorly-stained)
- Striated muscle in longitudinal and cross section
- Adipose tissue
This is a Liver (H-E) slide, what are these 3 arrows pointing to?

Orange = Hepatocytes - arranged in irregular, anastomosing cords that radiate from the Central Vein (Blue) and form into hepatic plates
The hepatic plates are separated by Sinusoids (Brown)
The walls of the sinusoids are formed in part by macrophages called Kupffer cells (difficult to distinguish) and in part by typical endothelial cells.

What organ is this?
What layers are these arrows pointing to?
What is unique about this organ for the GI system?

Gall Bladder (H-E)
Green arrow points to Cuticulated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Red arrow points to Lamina Propria
Gall Bladder has:
- NO Submucosa or Muscularis Mucosae
- May either have normal Tunica Serosa or Tunica Adventitia (fixing gall bladder to liver)

How can you distinguish Circumvallate Papillae from Fungiform?

Circumvallate Papillae:
- Significantly larger and less numerous
- Found in the dorsum of the tongue
- Surrounded by a cleft (or furrow, like a deep moat) into which serous (von Ebner’s) glands empty into at the base of the cleft
- Much more likely to contain taste buds



