Department Images 1-52 (Skipped a few shitty images) (Dustin) Flashcards
(48 cards)
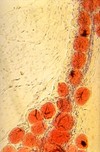
What type of epithelium?

Simple Squamous Endothelium
(this is in endocardium)
What type of epithelium? Where is it?
What kind of staining?

Mesothelium - simple squamous epithelium. From peritoneum (frog)
Silver nitrate impregnation
What type of epithelium?

Single layer simple simple cuboidal
(In kidney papilla)

What type of epithelium?
What do you call the thin pink stripe that covers the surface of the cells?
Simple columnar (Gall Bladder)
Pink Stripe = Cuticle, made up of microvilli
What type of epithelium? Where is it?
What kind of staining?

Pigment epithelium (Retina)
Native staining (unstained)
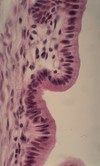
What type of epithelium?
Which tissue?
What are the paler parts of the epithelium?

Pseudostratified Columnar Ciliated Epithelium
(Respiratory epithelium, Trachea)
Pseudostrat = all cells rest on basement membrane, but not all extend to the surface
Paler parts = Goblet Cells (not very visible in this image but they’re there)
Note: epididymis also has pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium, but don’t see goblet cells
What type of epithelium is this?

Stratified Columnar (Urethra)
What type of epithelium?
What layers do the 3 colored arrows point to?

Stratified Squamous Non-keratinizing epithelium (esophagus)
Black = Stratum Planocellular
Green = Stratum Spinosum / Polygonale
Red = Stratum Basale / Germinativum
What type of epithelium is this?
What are the outermost cells called?
And what are the middle layer of epithelium cells called?

Transitional Epithelium - Urinary Bladder
Outermost = Umbrella Cells
Middle = Pear-shaped or Piriform Cells
What type of epithelium is this?
What is the pink layer called?
The layer with the darker-colored dots?
And the layer at the bottom of the image?

Stratified Squamous Keratinizing Epithelium
(Non-Hairy, Palm Skin)
Pink layer = stratum lucidum
Dark dots = stratum granulosum
Bottom of image = stratum corneum (most external layer)
What type of glands are these?
(Not sure how exactly to distinguish it from others without more in the frame)
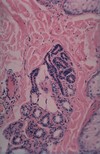
Sweat glands
Most sweat glands in the body are classified as eccrine. However, there are also apocrine sweat glands that are the ones around the armpits of humans and are more associated with pheromones.
What type of tissue is this?
What type of staining?
What is stained blue
What is stained red?

Hairy Skin (hair follicles most prominent in picture)
Azan Staining
Blue = collagen and elastic fibers
Red = nuclei, hair follicles,
(not seen, but also epidermis, muscle tissue, and RBC’s are red)
What are the large paler cells in the outer layer?

Goblet cells
(in duodenum)
What glands are shown here? What type of secretion do they do?
What do they produce?

Sebaceous Glands
Undergo holocrine secretion
Produce Sebum
What gland is this?
What type of secretion?

Prostate Gland
Apocrine secretion (or more technically, pseudo-apocrine)
Note that the lumen is widely dilated, and there is a thin layer of smooth muscle surrounding the gland (two features to help identify it)
Also remember corpora amylacea or prostatic stones can be found within the lumen

What gland is this? How do you know?

Parotid Gland
It’s exclusively serous with significant adipose tissue
(Lacrimal gland has those two in common, but serous cells are paler / more eosinophilic)

What gland is this? How do you know?

Submandibular Gland
Mixture of serous and mucus acini, but predominantly serous
(mucus acini are poorly stained)

What gland is this? What type of staining?

Submandibular gland,
Mucicarmin Stain
What gland is this?

Sublingual Gland
It’s 2/3 mucus acini, 1/3 serous

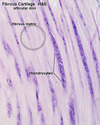
What tissue is shown in the image?

Collagen fiber fabric of a tendon (H-E)
Elongated tendonocytes are seen between collagen fibers, do not mix them up with fibrocartilage!

What type of fibers?
What stain?

Elastic fibers (surrounding carotid artery)
Resorchin-Fuchsin staining
What type of fibers?
Stain?

Reticular fibers of liver
Silver stain
What is shown here?
Staining? What does that differentiate?

Scalp skin
Hornowsky Stain
Red = Collagen
Black/dark violet = Elastic fibers
What stain and organ?
What is stained blue, and what is stained red?

Azan stain for Scalp Skin
- Blue = Connective tissue
- Red = epithelial cells, glands, muscle tissue, and vessels (nuclei = red)
Elastic fibers are stained the same color as collagen, the Hornowsky stain differentiates those