Semester I Midterm Images Flashcards
(51 cards)

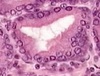
simple columnar epithelium
(gall bladder, H-E)
zoomed OUT
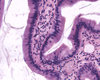
pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
(epidymis, HE)
zoomed out

pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
(epidymis, HE)
zoomed IN
simple columnar epithelium (gall bladder, H-E)

stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium
(esophagus, H-E)
zoomed out

stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium
(esophagus, H-E)
Answer given, but there are other unidentified layers and components

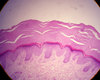
Stratified Squamous Keratinizing Epithelium
palm skin HE
skin in general is keratinizing epithelium
layers, from outside:
1 keratinizing (dead cells) in corneal layer/stratum corneum
2 dying cells in lucidal layer/stratum lucidum
3 keratohyalin granules in the granular layer/stratum granulosum
4 spinous layer/ stratum spinosum
below is basal layer, dermis, hypodermis etc
Note the layers

Stratified Squamous Keratinizing Epithelium
palm skin HE
skin in general is keratinizing epithelium
layers, from outside:
1 keratinizing (dead cells) in corneal layer/stratum corneum
2 dying cells in lucidal layer/stratum lucidum
3 keratohyalin granules in the granular layer/stratum granulosum
4 spinous layer/ stratum spinosum
below is basal layer, dermis, hypodermis etc
Stratified Squamous Keratinizing Epithelium

palm skin HE
skin in general is keratinizing epithelium
layers, from outside:
1 keratinizing (dead cells) in corneal layer/stratum corneum
2 dying cells in lucidal layer/stratum lucidum
3 keratohyalin granules in the granular layer/stratum granulosum
4 spinous layer/ stratum spinosum
below is basal layer
dermis (MEISSNER BODIES in dermal border)
hypodermis (contains Vater Pacini bodies)
look for sweat glands
{body may be called corpuscles}
1

stratum corneum/corneal layer
contains dead skin cells (keratinizing epithelium)
2
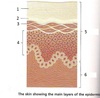
stratum lucidum
contains dying skin cells
3

stratum granulosum
5

epidermis
-made of stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
6
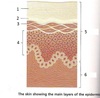
dermis
contains Meissner’s Corpuscles closer to border with epidermis
(in image below, Vater Pacini corpuscle should be more in the hypodermis)

2

stratum basale
1

stratum spinosum
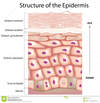

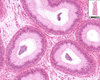
stratified columnar epithelium
(penis - urethra, HE)
zoomed out

stratified columnar epithelium
(penis - urethra, HE)
zoomed in

transitional epithelium
urinary bladder (HE)
this is for STRETCHING

transitional epithelium
urinary bladder (HE)
this is for STRETCHING
note “umbrella” cells

goblet cells
colon, HE

colon HE
goblet cells

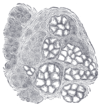
scalp HE
sebaceous gland (holocrine)
Holocrine glands are glands that secrete whole cells that have completely broken down for elimination from the body (no other types of secretion kill the entire cell). Sebaceous glands are the only type of holocrine glands.
They are located parallel to hair follicles and are usually between hair follicles and the arrector pili muscles that support the follicles, allowing them to contract and tighten around the hair. Before secretion, the whole cells of the sebaceous glands first swell with lipids and other moisturizing agents. Then they break down, die and ooze out to engulf the surface of the skin.
When sebaceous glands disintegrate, they are secreted as a substance called “sebum.” This sebum, though a form of waste, is beneficial since it provides lubrication for hair follicles, reducing hair breakage and giving moisture to dry scalp and dry skin all over the body.

scalp HE
sebaceous gland (holocrine)
Holocrine glands are glands that secrete whole cells that have completely broken down for elimination from the body (no other types of secretion kill the entire cell). Sebaceous glands are the only type of holocrine glands.
They are located parallel to hair follicles and are usually between hair follicles and the arrector pili muscles that support the follicles, allowing them to contract and tighten around the hair. Before secretion, the whole cells of the sebaceous glands first swell with lipids and other moisturizing agents. Then they break down, die and ooze out to engulf the surface of the skin.
When sebaceous glands disintegrate, they are secreted as a substance called “sebum.” This sebum, though a form of waste, is beneficial since it provides lubrication for hair follicles, reducing hair breakage and giving moisture to dry scalp and dry skin all over the body.