S1 - Waves and Heat (complete) Flashcards
Wave
A travelling vibration which transfers energy.
Give an example of a wave
Water, sound, light, radio, etc…
Amplitude
Height of a wave from middle to peak or trough.

Wavelength
Length of a complete wave.

Frequency
Number of waves per second.
(If waves shown in picture happen in 1 second, the frequency is 2 waves per second.)

What does the arrow show?

Amplitude
What does the arrow show?

Wavelength
Refraction
Change of a wave’s speed (and possibly direction) when it changes medium.
(medium = air, glass, plastic, etc; what the light travels through)
How will light refract through this block?


How will light refract through this block?


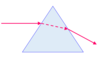
How will light refract through this prism?

Convex lens
Lens which converges light to a focus.

Concave lens
Lens which spreads light out.

Name this type of lens

Concave
Name this type of lens

Convex
How will a concave lens refract light?

The rays bend away from each other and never cross.

How will a convex lens refract light?

The rays bend towards each other and come to a focus.

Short sight
Can see close objects clearly but not distant ones.
Long sight
Can see distant objects clearly but not close ones.
What type of lens is used to correct long sight?
Convex

What type of lens is used to correct short sight?
Concave

Rainbow
White light spread out showing it is a mixture of 7 colours.

List the 7 colours of the rainbow (in correct order): red, …..
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet.
The total “rainbow” of all light, of which visible light is just a tiny part.
Electromagnetic spectrum
Finish the electromagnetic spectrum (in correct order):
gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, …
infra-red, microwaves, radio.
Finish the electromagnetic spectrum (in correct order):
gamma rays, X-rays, …………………, microwaves, radio.
ultraviolet, visible light, infra-red
Finish the electromagnetic spectrum (in correct order):
……… visible light, infra-red, microwaves, radio.
gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet,….
A form of energy due to the vibrations or movement of matter particles.
Heat
A measure of the average heat energy of the particles in an object.
Temperature
Heat flows in solids via ________.
conduction
Conduction works like this:
- Particles __________ the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to ____________.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They _________ into their ______________ particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in ___________.
Conduction works like this:
- Particles nearest the heat source start to vibrate more.
- They bump into their neighbouring particles and make them vibrate more.
- This is how heat travels in solids.
Heat flows in liquids and gases via ________.
convection
When air or water heat up, they become _____________, so they travel upwards.
When air or water heat up, they become less dense, so they travel upwards.
When air or water heat up, they become less dense, so they travel _____________.
When air or water heat up, they become less dense, so they travel upwards.
What type of heat transfer does this show?

Convection
Heat travels across a vacuum via _______.
radiation
What type of objects are good at radiating and absorbing heat?
(2 things)
Dark and dull
(e.g. black T-shirt)
What type of objects are poor at radiating and absorbing heat?
(2 things)
Light and shiny
(e.g. shiny tin can)
Give one way to reduce heat loss from a house
Any one of:
double glazing, draught excluders, loft insulation, cavity insulation, closed curtains, carpets, etc.


