S1 - Model of Matter (complete) Flashcards
(38 cards)
Matter
Stuff everything is made of.
Particle
A very small piece of matter.
Solid
A state of matter with tightly packed particles.

Liquid
A state of matter with particles that can slide over each other.

Gas
A state of matter with widely spaced, fast moving particles.

Solid, liquid or gas?

Liquid
Solid, liquid or gas?

Gas
Solid, liquid or gas?

Solid
Which will take the shape of the container they are in:
solid, liquid, gas?
Liquid and gas
Which can be compressed:
solid, liquid, gas?
Gas
Are particles in solids completely still?
No, they vibrate.
How can we show these particles are vibrating?

Add curved lines

Why are gases easy to compress?
Large spaces between particles (so we can push them closer).

What happens to solids when you heat them?
They expand (get bigger).
A metal bar gets longer after heating. Why?
Particles vibrate more, so spaces between particles get bigger.
Fill in the blank in the diagram


Fill in the blank in the diagram


Fill in the blank in the diagram

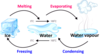
Fill in the blank in the diagram


Melting
Solid turning into a liquid.
Boiling
Liquid turning into a gas.
Freezing
Liquid turning into a solid.
Condensing
Gas turning into a liquid.
Melting point
Temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
(0 ºC for water.)