Respiratory Pathology Flashcards
Condition
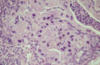
Inclusion Body Rhinitis
Condition

Interstitial Emphysema
T/F: In cats, pnumonias are more common than upper respiratory infections.
False
Possible etiologies for Equine Viral Rhinopneumonitis
EHV -1
EHV -4
Viruses that cause pneumonia in Cattle
Bovine Herpesvirus -1
Par-Influenza Virus - 3
Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus - BRSV
Etiology of Porcine Enzootic Pneumonia
Mycoplasma hyponeumoniae
Cattle: Disease that causes chronic necrotizing bronchopneumonia. Histologic appearance shows caseous necrosis.
Mycoplasma bovis Pneumonia
Disease in sheep that is similar to Shipping Fever in cattle?
Ovine Penumonic Mannheimosis
Condition
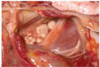
Guttural Pouch Empyema
Etiology of Verminous Bronchitis/Pneumonia in Swine
Metastrongylus spp
Condition

Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
Condition
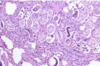
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus infection
Syndrome caused by type I hypersensitivity in cows sensitized by their own milk casein and lactalbumin
Milk Allergy
Condition

Glasser’s Disease
Condition

Shipping Fever
Cattle: Disease occurs several days to weeks after shipment. Causes fibrinous bronchopneumonia and marbling of pulmonary parenchyma. Histologic appearance shows coagulative necrosis.
Pneumonic Mannheimosis - Shipping Fever
Highly contagious and often fatal respiratory disease of pigs 2-5 months of age characterized by fibrinous bronchopneumonia on the dorsal area of the caudal lung lobe.
Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia
Etiology of Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
Respiratory disease of equids that causes transient broncho-interstitial pnumonia. Histological appearance shows foamy eosinophilic proteinaceous material within alveoli
Equine Adenovirus
___________________________
Common complication in Arabian foals with SCID
What are these called?
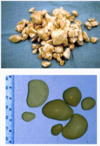
Chondroids
Type of necrosis seen on histology associated with Pneumonic Mannheimiosis

Coagulative Necrosis
Condition and Etiology

Stranges
Streptococcus equi
Condition

Fibrinous Rhinitis
Etiology of Respiratory Hisophilosis in cattle
Histophilus somni
What pigment is stained? What stain is used?

Hemosiderin Laden Macrophages - Heart Failure Cells
Iron (Perls) Stain
Condition

Viral Pneumonia
Etiology of Septicemic Pasteurellosis
Mannheimia haemolytica (Biotype A)
Bibersteinia (Pasteurella) trehalosi (Biotype T)
Condition

Mesothelioma
Systemic characteristics of what condition?

Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis
Condition

Tracheal Collapse
Condition
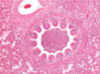
Bovine Enzootic Pneumonia
Respiratory disease of pigs characterized by mild bronchointerstitial, necrotizing bronchiolitis
Porcine Respiratory Coronavirus - PRC
Mucous accumulation and Goblet Cell metaplasia are characteristic of what condition?

Recurrent Airway Obstruction (RAO)
Condition

Ethmoidal Hematoma
Etiology of Glassers Disease
Haemophilus parasuis
MDx

Multifocal subpleural pneumonitis
Condition
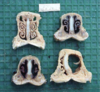
Atrophic Rhinitis
Condition

Guttural Pouch Tympany
Parasite of cats that causes subpleural nodules containing larvae and eggs.
Aelurostrongylus abstrusu
Condition

Nasal Neoplasia
Condition

Pyothorax
Pathogenesis of Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis
Type II hypersensitivity reaction to inhaled organic antigens and local deposition of Ag-Ab complexes in the lungs
Etiology of Verminous Bronchitis/Pneumonia in Cattle
Dictyocaulus viviparus
Pathogenesis of Bovine Pulmonary Edema and Emphysema
- Cattle grazing “fog” pastures
- L-Tryptophan metabolized in rumen to 3 methylindole
- Absorbed into blood and carried to lungs
- Metabolized by mixed function oxidases of non-ciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells to pneumotoxic compound
Condition

Atrophic rhinitis
Common etiologies of mycotic pneumonia in dogs
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Histoplasmosis
Condition
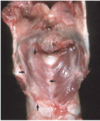
Laryngeal Hemiplegia
Condition
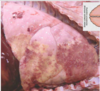
Aspiration Pneumonia
Condition

Chronic enzootic pneumonia
Etiology of Nocardiosis
Nocardia asteroides
Condition

Bovine Tuberculosis
Respiratory disease of foals causing chronic pyogranulomatous pneumonia.
Rhodococcus equi Bronchopneumonia
Condition and Etiology
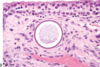
Condition

Guttural Pouch Mycosis
Respiratory disease of pigs characterized by progressive emaciation, interstitial pneumonia and is often complicated by secondary infection with pneumocytis carinii.
Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting Syndrome - PMWS
T/F: Primary pulmonary neoplasms are rare in animals, however metastatic neoplasms are relatively common.
True
Condition

Mycotic Pneumonia
MDx

Chronic suppurative bronchopneumonia
Condition

Mycoplasma bovis pneumonia
Condition

Porcine Enzootic Pneumonia
Clinical sign of what condition?
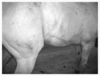
Recurrent Airway Obstruction (RAO)
Condition

Squamous Cell Carcinoma
MDx

Granulomatous Pneumonia
Disease that causes catarrhal bronchitis and histologically eosinophilc and granulomatous infection.
Verminous Bronchitis/ Pneumonia
Etiology of Ovine Progressive Pneumonia
Maedi-Visna Virus
Disease that causes llymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, non suppurative encephalitis, lymphocytic arthritis, lymphofollicular mastitis and vasculitis in sheep
Ovine Progressive Pneumonia - OPP
Marbling appearance of the pulmonary parencyma is consistent with what condition?
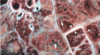
Pneumonic Mannheimiosis
Condition

Mycotic Pnumonia
Condition
Etiology

Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis
Feline Herpesvirus 1
Condition

Chylothorax
Etiology of Verminous Bronchitis/Pneumonia in Equids
Dictyocaulus arnfieldi
Pathogenesis of Rhodococcus equi bronchopneumonia
- Cytokines, lysosomal enzymes and bacterial toxins are responsible for extensive caseous necrosis of the lungs and recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils, macrophages and giant cells containing numerous intracytoplasmic organisms
Condition and MDx
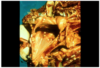
Guttural Pouch Mycosis
MDx

Fibrinous pleuritis
Non-infectious pneumonias of dogs
Uremia
Paraquat Toxicity
Condition

Ovine Pulmonary Carcinoma
Multifactorial respiratory disease of pig characterized by suppurative or catarrhal bronchopneumonia with BALT hyperplasia.
Porcine Enzootic Pneumonia
Bovine Enzootic Pneumonia causes what type of lesion
Chronic suppurative bronchopneumonia
Condition

Bastard Strangles
Condition

Nasal Fibrosarcoma
Respiratory disease of sheep that affects lambs 5-12 months old causing necrotizing pharyngitis and tonsilitis, septicemia with disseminated intravascular thrombosis and bacteremia
Septicemic Pasteurellosis
Viruses that cause pneumonias in sheep
Par-Influenza Virus - 3
RSV
Respiratory disease of pigs that is characterized by fibrinou pleuritis and pneumonia.
Glasser’s Disease
Possible etiologies for Bovine Enzootic Pneumonia
Respiratory Viruses
Mycoplasma
Chlamydophila
Describe how the ingestion of moldy potatos can cause respiratory disease in cattle
Moldy potatos contain 4-ipomeanol which is metabolized by mixed function oxydaes in the lung to potent pnumotoxicant
Etiology of Bovine Tuberculosis
Mycoplasma bovis
Respiratory disease characterized by chronic pleuritis with sulfer granules
Nocardiosis
Condition

Bovine Pulmonary Edema and Emphysema - “Fog Fever”
Cattle: Part of a disease complex that causes suppurative or fibrinous bronchopneumonia that may be indistinguishable from Shipping Fever.
Respiratory Histophilosis
Etiology of Ovine Pulmonary Carcinoma
Transmissible Retrovirus
Histology shows syncytial cells with what condition?
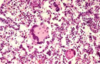
Viral Pneumonia
Etiology of Verminous Bronchitis/Pneumonia in Sheep and Goats
Dictyocaulus filaria
Condition

Pneumonic Mannheimiosis
“Shipping Fever”
Condition and MDx

Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS)
Patchy pulmonary atelectasis
Condition

Verminous Bronchitis / Pneumonia
Condition

Necrotic Laryngitis - Calf Diphtheria
Condition

Pulmonary Anthracosis
Condition

Uremic Pneumonitis
Disease that histologically consists of hyaline membranes, type II pneumocyte hyperplasia and interstital fibrosis with cellular infiltrates.
Atypical Interstital Pneumonia (AIP) of Cattle
Condition

Hydrothorax
Infectious pneumonias of dogs
Infectious Tracheobronchitis
Canine Distemper
Canine Adenovirus 2
Canine Herpes virus 1
Canine Influenza Virus
Condition and MDx
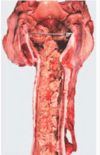
Infectious Bovine Rhinotrachitis
Ulcerative and necrotizing laryngo-tracheitis
Condition

Pulmonary Atelectasis
Calves with what disease are highly susceptible to bronchopneumonia?
Bovine Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency
Histology shows hyaline membranes, type II pneumocyte hyperplasia and interstitial fibrosis with cellular infiltrates with this condition

Atypical Interstitial Pneumonias
Condition

Feline Calicivirus
Disease that causes multifocal granulomatous pneumonia in cattle.
Bovine Tuberculosis
Respiratory disease of equids causing a multifocal, necrotizing and hemorrhagic pneumonia
Mycotic pneumonia
Condition

Pulmonary Edema
Granulomatous pneumonia in dogs is commonly associated with what disease?
Mycotic Pneumonia
Condition

Respiratory Histophilosis
Respiratory disease of dogs characterized by broncho-interstitial pneumonia and often complicated by secondary bacterial infections.
Canine Distemper
Mesothelioma in cattle can be caused by
Congential anomaly
Inhalation of asbestos
Syndromes that make up Atypical Interstitial Pneunomia
Bovine Pulmonary Edema and Emphysema
Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis
Reinfection Syndrome
Milk Allergy
Moldy Potato Toxicity
Respiratory disease of pigs that causes interstitial pneumonia, late term abortions, stillbirths and is often complicated by secondary infection with Pneumocytis carinii.
Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome - PRRS
Condition

Hemothorax
Condition
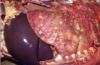
Rhodococcus equi pnumonia
Disease that causes edema and interstital pneumonia by different pathogenesis’
Atypical Interstitial Pneumonia (AIP)
Cattle: Cause transient rhino-tracheitis and broncho-interstitial pnumonia with formation of eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies and formation of syncytial cells.
Viral Pneumonia
Etiology of Shipping Fever
Mannheimia haemolytica
Condition

Canine Distemper
Etiology of Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting Syndrome - PMWS
Porcine Circovirus 2
Condition and Etiology

Granulomatous rhinitis
Rhinosporidium seeberi
Multifocal subpleural pneumonitis of sheep is caused by what etiologic agent?
Muellerius capillaris
Condition

Bullous emphysema
Syndrome caused by hypersensitivity to Dictyocaulus spp or BRSV
Reinfection Syndrome
MDx

Chronic pleuritis with “sulfur” granules
Condition and Etiology

Enzootic Nasal Carcinoma/Adenocarcinoma
Enzootic Nasal Tumor Virus
Condition
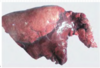
Bovine Enzootic Pneumonia
Possible eitology of Equine Mycotic Pnumonia
Aspergillus
Respiratory disease of sheep that affects young ( < 1 year) causing suppurative bronchopneumonia
Chronic Enzootic Pneumonia
Condition

Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia


