Reproductive Pathology Flashcards
Causes abortion and focal non-suppurative encephalitis in bovine

Neospora caninum
Male Torti or Calico cats are an example of what type of sex disorder?

Chromosomal Sex Disorder
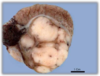
Condition

Teratoma
Male torties or calico cats are an example of what type of sex disorder?
Chromosomal Sex Disorder
Condition

Paraovrian Cysts
________________________________
More specifically hydatids of morgagni
Hippomanes, Yolk Sac Remnants and Allantoic Pouches are typically
Incidental findings
Etiology of Contagious Agalactia of goats
Mycoplasma agalactiae
Condition

Mast Cell Tumor
Metritis
Inflammation of all layers of the uterine wall
Imperfect fusion of the paramesonephric ducts can result in what sex disorders
Double Vagina
Double Cervix
Uterus Didelphys
Sex disorder characterized by the failure of fusion of the paramesonephric ducts with the urogenital sinus resulting in a tissue band running across the vagina just cranial to the opening of the urethra.
Imperforate Hymen
Histologic appearance of what condition

Sertoli Cell Tumor
Endometrial biopsys are commonly used in what species?
Equids
Condition

Uterine Prolapse
Causes abortion in cattle at 7-9 months of gestation. Characterized by chronic necrotizing placentitis. Fetuses may show signs of pneumonia.
Brucella abortus
Perimetritis
Inflammation extending to tissues surrounding uterus
Causes abortion between 2-3 months of pregnancy in swine, also has a high incidence of stillborn and weak piglets at term.
Brucella suis
Condition

Hematocele
Equine umbilical cords that are too short can cause
Premature separation of the placenta at the site of attachment
Mastitis in the ewe and goat is usually caused by
Staphylococcus aureus
Mannhemia haemolytica
Condition

Fibropapillomas
Condition characterized by suppurative inflammation and accumulation of pus in the uterine lumen, typically develops a few weeks after estrus.
Pyometra
Causes embryonic loss or overt abortion in cattle. Protozoa can be found in preputial washes, vaginal mucosis and stomach contents of aborted fetus.
Tritrichomonas foetus
XXY
Klinefelter