Lab Exam Flashcards
Morphological Diagnosis

Catharal enteritis
Lesions caused by thiamine deficiency in carnivores are typically found in what area of the brain?
Caudal colliculi
Morphological diagnosis
Multifocal ulceration and gastric hyperplasia
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Adrenocortical Hyperplasia
Morphological Diagnosis

Suppurative pneumonia
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Nodular Thyroid Hyperplasia
Two areas of the brain that are affected in Nigropallidal encephalomalacia
Globus Pallidus
Substantia nigra
Morphological Diagnosis

Inguinal hernia incarceration
Morphological Diagnosis

Coronary artherosclerosis
Morphological Diagnosis

Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing (ulcerative) gastritis
Morphological Diagnosis

Lymphocytic Thyroiditis
Morphologic Diagnosis

Hepatic Cirrhosis
Condition

Hepatosis Dietetica of Swine - Massive Hepatic Necrosis
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Parathyroid Hyperplasia
Morphological Diagnosis

Enlarged lymph nodes with diffuse dark brown to black pigmentation
Condition

Fatty Liver Syndrome
What complication can arise from this lesion?

Bronchopneumonia
Morphological Diagnosis
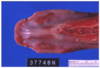
Ulcerative stomatitis
Morphological Diagnosis

Reticulum Lymphosarcoma
Morphologial Diagnosis

Fibrino-hemorrhagic and necrotizing pneumonia
Disease

Chronic Nephritis
Morphological Diganosis

Chronic Hepatic Congestion
Morphological Diagnosis

Pyogranulomatous Pneumonia
Etiology

Pasturella
Morphological Diagnosis and Pathogenesis

Etiology

Ulceration due to Gastrophillus spp
Hyperplasia due to Trichostrongylus axei
Etiology

Feline Peritonitis Virus
Morphological Diagnosis

Proliferation ileitis
Disease

Brown Bowel Syndrome
Etiology

Fusarium verticilloides
Condition

Torsion of the Umbilical Cord
Cause of this disease?

Vitamin E deficiency
Possible differential diagnosis

NSAID over-use
Uremic Ulcers
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Splenomegaly
Disease

Embolic Pneumonia
Lesions associated with uremia are secondary to:
Damage to endothelial cells
Altered calcium-phosphorus metabolism
Ammonia secretion
Decreased erythropoietin and increased erythrocyte fragility
Etiology

Lawsonia intracellularis
Describe this tissue

Normal rumen from a llama
Disease

Melanoma
Morphological Diagnosis

Cholangial hepatitis
Morphologial Diagnosis

Ulcerative glossitis and esophagitis
Etiologial Diagnosis

Ascaridial Enteritis
Morphological Diagnosis

Necrohemorrhagic enteritis
Disease

Spiral Swine Dysentery
Etiology

Gastrophillus spp
Morphological Diagnosis

Atrophic Rhinitis
Etiology

Fascioloides magna
Describe this tissue

Normal esophagus of a cat
Pathogenesis of thiamine deficiency in carnivores
Ingestion of increased amounts of fish
Etiology

Rhodococcus Equi
Cause

Thiamine Deficiency
Disease

Equine Leukoencephalomalacia - Moldy Corn Toxicity
Etiology

Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus
Morphological Diagnosis

Multifocal granulomatous vasculitis/peritonitis
Etiology

Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Disease and Etiology
Caseous Lymphadenitis
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Disease

Nigropallidal Encephalomalacia
Disease
Thymic Thymoma
What would you expect on bloodwork with this lesion?

Decreased Glucose Concentration
Etiology

Mycotic dermatitis
Morphologic diagnosis of this liver from a rabbit

Chronic multifocal cholangial hepatitis
Morphological Diagnosis

Oral Papillomatosis
Lesion associated with what disease

Calcinosus cutus associated with Cushings Disease (Hyperadrenocorticism)
Morpholoical Diagnosis

Acute segmental hemorrhagic enteritis
Etiologic Diagnosis

Intestinal Coccidiosis
Morphological Diagnosis

Multifocal to coalescing hyperplastic dermatitis with hyperkeratosis
Morphological Diagnosis

Intestinal intussusception
Animals that die of renal failure do so by a combination of
Electrolyte imbalances
Metabolic acidosis
Cardiotoxicity due to increased serum K+
Pulmonary edema
Etiologic Diagnosis

Uremic Pneumonitis
Morphological Diagnosis

Ulcerative Stomatitis
Describe this condition

Eponychium - “Golden Slippers”
Normal protective covering of hoofed animals
What dis?

Phytobezours
Possible differential diagnosis?

BVD
Mucosal disease
MCF
Morphological Diagnosis

Bilaterally symmetric encephalomalacia
__________________________________
Lesions located in the basal nuclei
Morphological Diagnosis

Granulomatious Enteritis
Condition

Hepatic Fracture
What is the most likely pathological process?

Disorder of growth
Etiology

Clostridium perfringens type D
Describe this lesion

Contraction of the tissue caused by loss of parenchyma with scarring. The cortical surface is irregular and nodular and will not be easily removed.
Morphological Diagnosis

Necrotizing placentitis
Describe this abnormality

Meconium Staining - sign of fetal distress
Morphologic Diagnsosis

Parasitic Hepatitis
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Islet Cell Carcinoma
Stains used to confirm diagnosis of a fungal infection?
GMS Stain
PAS Stain
Possible Differentital Diagnosis

Malignant Melanoma
Myeloblastoma
Fibrosarcoma
SCC
Etiologic diagnosis of this liver from a rabbit

Hepatic coccidiosis
Describe the pathogenesis of anemia related to renal insufficiency

- Decreased EPO due to renal damage
- Uremia causes blood loss into the GI tract
Disease

Canine Parvoviral Enteritis
Morphological Diganosis

Bilaterally Symmetric Encephalomalacia
Ethylene glycol toxicosis can cause what type of renal damage?
Renal Tubular Necrosis
Morphological diagnosis of lesion caused by thiamine deficiency in cattle.
Polioencephalomalacia
Condition

Renal Atherosclerosis
Etiology

Pasturella
Normal gestation for a horse is
11 months
Etiology

Dipylidium caninum
Morphological Diagnosis

Necrohemorrhagic colitis
Misplacement of nasogastric tube caused what disease in this foal?

Aspiration pneumonia
Morphological Diagnosis

Dystrophic mineralization of gastric mucosa
Possible DDX
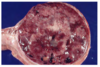
Adrenocortical adenoma
Theochromocytoma
Etiology

Parvovirus Type 2
Disease characterized by enlarged spleen, acute death, bloating and bleeding from orifices.

Anthrax
Morphological Diagnosis

Megaesophagus
What is this tissue?

Esophagus from Leatherback Seaturtle
Morphological Diagnosis

Nasal Adenocarcinoma
Etiologic Diagnosis

Uremic Gastritis
Etiology

Brachyspira hyodysenteriae
Morphological Diagnosis

Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Disease

Porcine Contagious Pleural Pneumonia
Morphological Diagnosis

Megaesophagus and persistant right aotic arch (PRAA)
Disease

Melanoma
Etiology

Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis
Morphological Diagnosis

Acquired stenosis (jejunal stricture)
Morphological Diagnosis

Ulceration, perforation and rupture of the duodenum
Morphological Diagnosis

Palatoschisis
Pathogenesis

- Kidney not filtering waste the way it should
- Urea builds up in the blood
- In oral cavity, urea is metabolized to ammonia which is caustic
Morphological Diagnosis

Leukoencephalomalacia
Morphological Diagnosis

Multifocal Ulceration
Morphological Diagnosis

Multifocal to Coalesing necrotizing gastritis
What are two ways you can differentiate whether an animal was stillborn or died after birth.
Presence of intacted eponychium in hoofed animals = likely stillborn
Lung tissue
Possible DDx?

Barbiturate Euthanasia
Splenic torsion and volvulus
Lymphosarcoma
Etiology

Bovien Leukemia Virus
Possible differential diagnosis

Hypothyroidism
Diabetes mellitus
Disease

Caseous Lymphaditis
These plants can cause what disease in horses? What is the toxin?

Nigropallidal Encephalomalacia
Repin Toxin
______________________________
Yellow Star Thistle and Russian Knapweed
Morphological Diagnosis

Dental Calculus (Plaque)
Cause of this lesion?

Pituitary Adenoma (Mars distalis)


