Hematopoietic System Pathology Flashcards
Morphological diagnosis

Acute multifocal necrotizing hepatitis and splenitis
Splenomegaly caused by

Amyloidosis
Indications for examining bone marrow
Unexplained cytopenia
Maturation defects or morphologic abnormalities in blood cells
Potential myelo/lympho-proliferative disease
Potential malignancies
Condition

Splenic Hemangioma
Etiology of Strangles
Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Condition
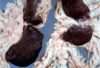
Multiple “Spleens”
Autosomal recessive bone marrow disorder that disrupts the sequence of steps leading to the migration of leukocytes into sites of inflammation leading to bone marrow hyperplasia
Bovine Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Syndrome - BLAD
Differential diagnosis for hyperplastic splenitis
Aleutian Disease
Equine Infectious Anemia
Differential diagnosis for splenic thrombosis/ infarction
Classicial Swine Fever (Hog Cholera)
Lymphosarcoma
Splenic nodules with a blood consistency can be
Hematomas
Incompletely contracted areas of spleen
Acute splenic infarcts
Vascular neoplasms
Bloody spleen can be generally caused by
Congestion
Acute Hyperemia
Acute Hemolytic Anemia
Disease in pigs that causes diffuse granulomatous lymphadenitis
Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting Disease
Morphological Diagnosis

Necrotizing splenitis
Malignant bone marrow neoplasm of histiocytic origin.
Histocytic Sarcoma
Disease in which carbon particles are retained in macrophages, medulla of lymph node appears black.
Anthracosis
________________________________
Common finding in animals living in polluted urban areas
Disease of the spleen that causes necrotizing splenitis characterized by white-grey milliary foci scarttered throughout the splenic parenchyma.
Tularemia - Rabbit Fever
Condition

Histiocytic Sarcoma
Hemal Nodes
Prominant in ruminants, small, dark red similar architecture
Bone Marrow Hypoplasia/ Atrophy may be the result of
Myelophthisis
Abnormality of hematopoietic cells
Etiology of Cytauxzoonosis
Cytauxzoon felis
Disease

Multiple Myeloma
Condition
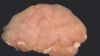
Splenic hemangiosarcoma
Etiology
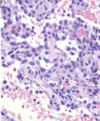
Histoplasma capsulatum
Disease that causes granulomatous lymphadenitis characterized by B and T lymphoid depletion and “botryoid” intracytoplasmic inclusions in macrophages.
Post Weaning Multisystemic Wasting Disease - PMWD
Etiology of granulomatous splenitis
Mycobacterium avium
Etiologic Agent and Disease

Francisella tularensis
Tularemia
Disease of the raptors characterized by acute multifocal milliary necrotizing hepatitis and splenitis.
Herpes Inclusio Body Disease - Hepatosplenitis
Splenic infarction in pigs is an indication of what disease

Classical Swine Fever - Hog Cholera
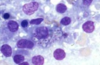
Disease caused by the organism in these tissue aspirates of the lymph node and spleen of a cat

Cytauxzoonosis
Dogs with benign splenic masses had a significantly (higher/lower) mean to splenic volume ration and (higher/lower) splenic weight as a percentage of body weight than did dogs with hemangiosarcoma.
Dogs with benign splenic masses had a significantly (higher/lower) mean to splenic volume ration and (higher/lower) splenic weight as a percentage of body weight than did dogs with hemangiosarcoma.
Lesion associated with this lymph node asipirate

Granulomatous Lymphadenitis
Splenomegaly due to diffuse enlargement can be due to
Congestion
Cell proliferation/ infiltration
Accumulation of extracellular material
Lesion
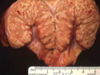
Granulomatous Lymphadenitis
Disease characterized by mandibular, pharyngeal, parotid lymph node abscesation and fistulization
Strangles
Morphological Diagnosis

Bone Marrow Hyperplasia
Disease of 3-6 week old chicks that causes lymphoid depletion by targeting pre-B lymphocytes
Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD)
Disease of the spleen characterized by grey-white to yellow, hard dry encrustations on the capsule, usually along the margins of teh spleen but can be elsewhere.
Siderofibrosis
Disease of equids characterized by abscesses anywhere in the body other than the pharyngeal area
Bastard Strangles
Condition

Splenic Hematoma
Lymph node abscess in a horse what is the etiology?

Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Pathogenesis of Bone Marrow Hyperplasia
Increased cell production in the marrow in response to poietins and interleukins → decreased cell numbers in blood caused by increased peripheral demand → adequate numbers of hypofunctional cells in peripheral blood
Etiology of Anthrax
Bacillus anthracis
Bone marrow necrosis may result in what clinical pathology finding?
Pancytopenia
Lesions associated with what disease of chickens?

Marek’s Disease
Abnormality

None - normal active bone marrow
Disease characterized by increased yellow marrow and is usually accompanied by marrow degeneration. Clinical pathology findings include anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Bone Marrow Hypoplasia / Atrophy
Differential Diagnosis for hemosiderosis of the spleen
Decreased rate of erythropoiesis
Rapid destruction of RBC
Chronic heart failure
Iron dextran injection
Brownish discoloration observed in lymph nodes draining areas of hemorrhage
Hemosiderosis
Etiology of Caseous Lymphadenitis
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Condition
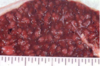
Lymphoid Hyperplasia
(Cutaneous / Extramedullary) Plasmacytomas are typically malignant
Extramedullary Plasmacytomas
Disease

Multiple Myeloma
Etiology of Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD)
Avian Bursal Disease Virus
Condition

Thymic Lymphosarcoma
Disease of the spleen that causes acute splenitis. It is characterized by acute death, bloated carcass, rapid-post mortem autolysis and blood oozing from body orifices.
Anthrax
Likely etiology of suppurative osteomyelitis
Bacterial infection
Differential Diagnosis for focal areas of necrosis in lymph node
Yersina Pestis
Toxoplasmosis
Salmonellosis
Tularemia
Tyzzer’s Disease
Feline Infectious Peritonitis
Disease of the bone marrow that is often fatal due to occulusion of lumina of vessles in the lung, brain, liver, lymph node and spleen.
Cytauxzoonosis
Etiology of Tularemia
Francisella tularensis
Normal Myeloid: Erythroid Ratio
1.5 : 1
What should you evaluate on a core biopsy of bone marrow
Cellularity
Myeloid: Erythroid Ratio
Disease and Etiology

Granulomatous Splenitis
Mycobacterium avium
Etiology of bubonic plague
Yersinia pestis
Possible causes of bone marrow hyperplasia
Bovine Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Syndrome - BLAD
IHA
Equine Infectious Anemia
Spleen of a cow that acutely died and was found bloated what is the most likely disease?

Anthrax
Disease
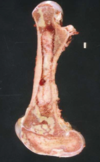
Bone Marrow Lymphoma
Condition

Splenic Lymphosarcoma
Condition

Thymic Lymphoma
Common features of myelo/lympho-proliferative disease
Anemia
Hypercellular Marrow
Leukemic Cells in peripheral circulation
Megaloblastic alteration in erythroid cells
Thrombocytopenia
Hepato/Spleno-megaly
During gestation, hematopoietic cells originate in the
Liver, Spleen and Bone Marrow
Disease of 2-5 month old chickens characterized by lymphocytic infiltrates and peripheral neuritis.
Marek’s Disease
Condition

Splenic Hemangiosarcoma
Etiology of Herpes Inclusion Body Disease
Columbid Herpesvirus 1 (CoHV-1)
Condition
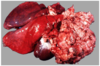
Thymoma
Differential Diagnosis for Acute Passive Congestion of the spleen
Barbiturate induced
Equine Infectious Anemia
Gastrosplenic Torsion/ Volvulus
Malignant tumor of plasma cells that secretes Ig/Ig subunit. It is characterized by increased numbers of plasma cells in BM, monoclonal gammopathy, osteolysis, light chain proteinuria, hypercalcemia, cytopenias, and renal amyloidosis.
Multiple Myeloma
Disease characterized by painful, swollen lymph nodes with focal areas of necrosis.
Bubonic Plague
Meat spleen can be generally caused by
Phagocytosis
Proliferation of Cells
Storage of material
Disease of equines that is characterized by immune mediated hemolysis and decreased erythropoeisis leading to bone marrow hyperplasia
Equine Infectious Anemia
Primary neoplasias of the bone marrow are divided into
Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Myeloproliferative Disorders
Condition
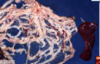
Splenosis
______________________________
Splenic rupture lead to seeding of the omentum and formation of numerous “accessory spleens”
Splenic nodules with a firm consistency could be
Splenic nodular hyperplasia
Fibrohistiocytic nodules
Primary neoplasms
Secondary neoplasms
Granulomas
Abscesses
Etiology
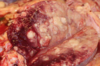
Bovine Enzootic Leukosis
Degenerative lesion of the spleen

Siderofibrosis
Likely etiology of granulomatious osteomyelitis
Fungal infection
Splenic rupture leading to seeding of the omentum and formation of numerous accessory spleens
Splenosis - Splenic Rupture
Differential diagosis for thymic atrophy
EHV 1
FeLV
Feline Panleukemia
BVD
Canine Distemper
Disease of chickens that is characterized by the proliferation of B lymphocytes.
Lymphoid Leukosis
Possible DDX

Multiple Myeloma
Osteomyelitis
Disease

Lymphosarcoma
Etiology

Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Replacement of myeloid tissue by abnormal tissue
Myelophthisis
(Lympho/Myelo)-proliferative diseases are more common.
Lymphoproliferative Diseases
Disease characterized by greenish coored pus that becomes caseous with age.
Caseous Lymphadenitis
Etiology of Marek’s Disease
Herpesvirus
Two common locations for hemangiosarcomas
Subcutis
Right Atrium
Disease
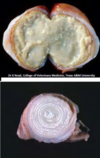
Caseous Lymphadenitis
Condition
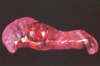
Nodular Hyperplasia
Common disease that causes Myelophthisis
Scurvy - Vitamin C Deficiency
Differential Diagnosis for thymic hypoplasia
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
X- Linked Gene
Describe the appearance of porcine lymph nodes
Inverted cortex and medulla
Disease

Serous Atrophy of Fat
Rare neoplasm of the bone marrow that is usually benign and of the skin or mucous membrane origin.
Cutaneous Plasmocytoma
Non neoplastic canine immunoregulatory disorders
Cutaneous Histocytosis
Systemic Histocytosis
Condition

Histiocytic Sarcoma
Disease of the spleen caused by chronic antigenic stimulation leading to hyperplasia of the monocyte-macrophage or lymphoid/plasma cell population
Hyperplastic splenitis
Etiology

Mycobacterium bovis
Disease
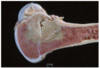
Suppurative Osteomyelitis
Lesion

Myelofibrosis
___________________
Can be caused by Scurvy in guinea pigs
In the embryo, hematopoietic cells originate in the
Yolk Sac
Differential diagnosis for granulomatous lymphadenitis
Mycobacterium bovis
Histoplasma capsulatum
Post weaning Multisystemic Wasting Disease
Disease characterized by hyperplastic cell lines (one or multiple) and red marrow replacement by yellow marrow.
Bone Marrow Hyperplasia
Pathogenesis of Cytauxzoonosis
Schizogenous phase → Macrophages = Systemic Illness
Erythrocytic phase = Anemia
Etiology of Lymphoid leukosis in chickens
Avian Leukosis Virus
Bone marrow disease characterized by ineffective and dysplastic hematopoiesis. Diagnosed based on presence of decreased blasts in bone marrow ( < 30%), cytopenia of > 1 cell line and evidence of dyshematopoiesis.
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
Release of immature cells from the bone marrow indicates
Stress or disease
The bursa of fabricius is populated by what type of lymphocytes
B lymphocytes
Main components of the hematopoietic system
Bone marrow
Blood cells
Lymph nodes and lymphatics
Spleen
Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
Thymus
Clinical pathology associated with Splenic Hemangiosarcomas
Anemia
Thrombocytopenia
Increased hepatic enzymes
Schistocytes
Differential diagnosis for nodular hyperplasia
Lymphoma
Granulomatous infection
Histologic lesion associated with pigs infected with PMWS
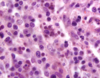
“Botryoid” Intracytoplasmic Inclusions in Macrophages
Primary neoplasia of the lymphnode characterized by mottled pale tane and red appearance that is slightly buldging and nodular.
Lymphosarcoma
Disease and etiology

Herpes inclusion body disease
Columbid herpesvirus 1 (CoHV-1)
Etiology
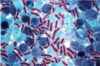
Bacillus anthracis
Indolent cutaneous neoplasm of bone marrow. Probably of dendritic cell origin
Feline Progressive Histiocytosis
Splenomegaly caused by

Barbiturate euthanasia


