Reproductive - First Aid Flashcards
Important Genes of Embryogenesis:
- produced at base of limbs in zone of polarizing activity
- involved in patterning along anteroposterior axis and CNS development
- mutation can cause holoprosencephaly
Sonic Hedgehog Gene
Important Genes of Embryogenesis:
- produced at apical ectodermal ridge (thickened ectoderm at distal end of each developing limb)
- necessary for proper organization along dorsal-ventral axis
Wnt-7 Gene
Important Genes of Embryogenesis:
- produced at apical ectodermal ridge
- stimulates mitosis of underlying mesoderm, providing for lengthening of limbs
Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Gene
“Look at that Fetus, Growing Fingers.”
Important Genes of Embryogenesis:
- involved in segmental organization of embryo in a craniocaudal direction
- code for transcription factors
- mutations → appendages in wrong locations
Homeobox (Hox) Genes
Early Embryonic Development
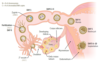
Early Fetal Development:
hCG secretion begins around the time of implantation of blastocyst
Week 1
Blastocyst “sticks” at day 6.
Early Fetal Development:
bilaminar disc (epiblast, hypoblast)
Week 2
2 weeks = 2 layers
Early Fetal Development:
- gastrulation forms trilaminar embryonic disc
- cells from epiblast invaginate → primitive streak → endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm
- notochord arises from midline mesoderm
- overlying ectoderm becomes neural plate
Week 3
3 weeks = 3 layers
Early Fetal Development:
- neural tube formed by neuroectoderm and closes by week 4
- organogenesis
- extremely susceptible to teratogens
Weeks 3–8
(Embryonic Period)
Early Fetal Development:
- heart begins to beat
- upper and lower limb buds begin to form
Week 4
4 weeks = 4 limbs and 4 heart chambers
Early Fetal Development:
fetal cardiac activity visible by transvaginal ultrasound
Week 6
Early Fetal Development:
fetal movements start
Week 8
Gait at week 8.
Early Fetal Development:
genitalia have male/female characteristics
Week 10
tenitalia
Embryologic Derivatives:
external/outer layer
Ectoderm
Ectoderm:
- epidermis
- adenohypophysis (from Rathke pouch)
- lens of eye
- epithelial linings of oral cavity, sensory organs of ear, and olfactory epithelium
- anal canal below the pectinate line
- parotid, sweat, and mammary glands
- Craniopharyngioma
- benign Rathke pouch tumor with cholesterol crystals, calcifications
Surface Ectoderm
Ectoderm:
- brain (neurohypophysis, CNS neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, pineal gland)
- retina
- spinal cord
Neural Tube
Ectoderm:
- melanocytes
- myenteric (Auerbach) plexus
- odontoblasts
- endocardial cushions
- laryngeal cartilage
- parafollicular cells of the thyroid
- PNS (dorsal root ganglia, cranial nerves, autonomic ganglia)
- adrenal medulla and all ganglia
- spiral membrane (aorticopulmonary septum)
- Schwann cells
- pia and arachnoid
- bones of skull
Neural Crest
MMOtEL PPASS:
- Melanocytes
- Myenteric (Auerbach) plexus
- Odontoblasts
- Endocardial cushions
- Laryngeal cartilage
- Parafollicular cells of the thyroid
- PNS (dorsal root ganglia, cranial nerves, autonomic ganglia)
- Adrenal medulla and all ganglia
- Spiral membrane (aorticopulmonary septum)
- Schwann cells
Embryologic Derivatives:
- muscle, bone, connective tissue, serous linings of body cavities (eg. peritoneum, pericardium, pleura), spleen (derived from foregut mesentery), cardiovascular structures, lymphatics, blood, wall of gut tube, upper vagina, kidneys, adrenal cortex, dermis, testes, ovaries
- notochord induces ectoderm to form neuroectoderm (neural plate)
- its only postnatal derivative is the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc
Mesoderm
middle/“meat” layer
Mesodermal Defects = VACTERL:
- Vertebral defects
- Anal atresia
- Cardiac defects
- Tracheo-Esophageal fistula
- Renal defects
- Limb defects (bone and muscle)
Embryologic Derivatives:
- gut tube epithelium (including anal canal above the pectinate line)
- most of urethra and lower vagina (derived from urogenital sinus)
- luminal epithelial derivatives (eg. lungs, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, eustachian tube, thymus, parathyroid, thyroid follicular cells)
Endoderm
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
absent organ due to absent primordial tissue
Agenesis
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
absent organ despite presence of primordial tissue
Aplasia
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
- incomplete organ development
- primordial tissue present
Hypoplasia
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
2° breakdown of previously normal tissue or structure (eg. amniotic band syndrome)
Disruption
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
- extrinsic disruption
- occurs after embryonic period
Deformation
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
- intrinsic disruption
- occurs during embryonic period (weeks 3–8)
Malformation
Types of Errors in Morphogenesis:
abnormalities result from a single 1° embryologic event (eg. oligohydramnios → Potter sequence)
Sequence
_____ are agents or factors that causes malformation of an embryo. Most susceptible in 3rd–8th weeks (embryonic period—organogenesis) of pregnancy. Before week 3, “all-or-none” effects. After week 8, growth and function affected.
Teratogens
Teratogens:
- medication
- renal damage
ACE inhibitors
Teratogens:
- medication
- absence of digits
- multiple anomalies
Alkylating Agents
Teratogens:
- medication
- ototoxicity
Aminoglycosides
A mean guy hit the baby in the ear.
Teratogens:
- medication
- neural tube defects, cardiac defects, cleft palate, skeletal abnormalities (eg. phalanx/nail hypoplasia, facial dysmorphism)
- high-dose folate supplementation recommended
Antiepileptic Drugs
- Valproate
- Carbamazepine
- Phenytoin
- Phenobarbital
Teratogens:
- medication
- vaginal clear cell adenocarcinoma, congenital
- Müllerian anomalies
Diethylstilbestrol
Teratogens:
- medication
- neural tube defects
Folate Antagonists
- Trimethoprim
- Methotrexate
- Antiepileptic Drugs
Teratogens:
- medication
- multiple severe birth defects
- contraception mandatory
Isotretinoin
Teratogens:
- medication
- Ebstein anomaly (apical displacement of tricuspid valve)
Lithium
Teratogens:
- medication
- aplasia cutis congenita
Methimazole
Teratogens:
- medication
- discolored teeth
- inhibited bone growth
Tetracyclines
Teethracyclines
Teratogens:
- medication
- limb defects (phocomelia, micromelia—“flipper” limbs)
Thalidomide
Tha-limb-domide
Teratogens:
- medication
- bone deformities
- fetal hemorrhage
- abortion
- ophthalmologic abnormalities
Warfarin
Do not wage warfare on the baby; keep it heppy with heparin (does not cross placenta).
Teratogens:
- substance abuse
- common cause of birth defects and intellectual disability
- fetal _____ syndrome
Alcohol
Teratogens:
- substance abuse
- low birth weight
- preterm birth
- IUGR
- placental abruption
- vasoconstriction
Cocaine
Teratogens:
- substance abuse
- low birth weight (leading cause in developed countries)
- preterm labor
- placental problems
- IUGR, SIDS, ADHD
- vasoconstriction
- impaired O2 delivery
Smoking
- Nicotine → vasoconstriction
- CO → impaired O2 delivery
Teratogens:
- congenital goiter
- hypothyroidism (cretinism)
Iodine (lack or excess)
Teratogens:
- Caudal Regression Syndrome
- anal atresia to sirenomelia
- congenital heart defects (eg. VSD, transposition of the great vessels)
- neural tube defects, macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, polycythemia
Maternal Diabetes
Teratogens:
- neurotoxicity
- highest in swordfish, shark, tilefish, and king mackerel
Methylmercury
Teratogens:
- spontaneous abortions
- birth defects (cleft palate, cardiac)
Vitamin A Excess
Teratogens:
- microcephaly
- intellectual disability
- minimized by lead shielding
X-rays
Teratogens:
- leading cause of intellectual disability in the US
- ↑ incidence of congenital abnormalities, including pre- and postnatal developmental retardation, microcephaly, facial abnormalities (eg. smooth philtrum, thin vermillion border [upper lip], small palpebral fissures), limb dislocation, and heart defects
- heart-lung fistulas and holoprosencephaly in most severe form
- mechanism is failure of cell migration
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Teratogens:
- complex disorder involving CNS, ANS, and GI systems
- secondary to maternal opiate use/abuse
- risk factors for maternal substance abuse during pregnancy include poor mental health, poor prenatal care, low SES, lack of family support, and HCV
- universal screening for substance abuse is recommended in all pregnant patients
- newborns may present with uncoordinated sucking reflexes, irritability, high-pitched crying, tremors, tachypnea, sneezing, diarrhea, and possibly seizures
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
Twinning
- Dizygotic (“fraternal”) twins arise from 2 eggs that are separately fertilized by 2 different sperm (always 2 zygotes) and will have 2 separate amniotic sacs and 2 separate placentas (chorions).
- Monozygotic (“identical”) twins arise from 1 fertilized egg (1 egg + 1 sperm) that splits in early pregnancy.
- The timing of cleavage determines chorionicity (number of chorions) and amnionicity (number of amnions) (SCAB):
- 0–4 days: Separate chorion and amnion
- 4–8 days: shared Chorion
- 8–12 days: shared Amnion
- 13+ days: shared Body (conjoined)

Placenta
1º site of nutrient and gas exchange between mother and fetus

Placenta
- fetal component
- inner layer of chorionic villi
Cytotrophoblast
Cytotrophoblast makes cells
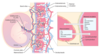
Placenta
- fetal component
- outer layer of chorionic villi
- synthesizes and secretes hormones, eg. hCG (structurally similar to LH; stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone during first trimester)
- lacks MHC-I expression → ↓chance of attack by maternal immune system
Syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast synthesizes hormones

Placenta:
- maternal component
- derived from endometrium
- maternal blood in lacunae
Decidua Basalis
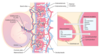
Umbilical Cord
-
Umbilical Arteries (2)
- return deoxygenated blood from fetal internal iliac arteries to placenta
-
Umbilical Vein (1)
- supplies oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
- drains into IVC via liver or via ductus venosus
- Single umbilical artery (2-vessel cord) is associated with congenital and chromosomal anomalies.
- Umbilical arteries and vein are derived from allantois.

Urachus
- In the 3rd week the yolk sac forms the allantois, which extends into urogenital sinus.
- Allantois becomes the urachus, a duct between fetal bladder and umbilicus.
- Failure of urachus to involute can lead to anomalies that may increase risk of infection and/or malignancy (eg. adenocarcinoma) if not treated.
- Obliterated urachus is represented by the median umbilical ligament after birth, which is covered by median umbilical fold of the peritoneum.

Urachus:
total failure of urachus to obliterate → urine discharge from umbilicus
Patent Urachus

Urachus:
- partial failure of urachus to obliterate
- fluid-filled cavity lined with uroepithelium, between umbilicus and bladder
- cyst can become infected and present as painful mass below umbilicus
Urachal Cyst
Urachus:
slight failure of urachus to obliterate → outpouching of bladder
Vesicourachal Diverticulum

Vitelline Duct
- connects yolk sac to midgut lumen
- 7th week—obliteration of vitelline duct (omphalomesenteric duct)

Vitelline Duct:
vitelline duct fails to close → meconium discharge from umbilicus
Vitelline Fistula

Vitelline Duct:
- partial closure of vitelline duct, with patent portion attached to ileum (true diverticulum)
- may have heterotopic gastric and/or pancreatic tissue → melena, hematochezia, abdominal pain
Meckel Diverticulum

Aortic Arch Derivatives
Develop into arterial system.

Aortic Arch Derivatives:
part of maxillary artery (branch of external carotid)
1st
1st arch is maximal

Aortic Arch Derivatives:
- stapedial artery
- hyoid artery
2nd
second = stapedial

Aortic Arch Derivatives:
- common carotid artery
- proximal part of internal Carotid artery
3rd
Carotid = C is the 3rd letter of alphabet

Aortic Arch Derivatives:
- left—aortic arch
- right—proximal part of right subclavian artery
4th
4th arch (4 limbs) = systemic

Aortic Arch Derivatives:
- proximal part of pulmonary arteries
- ductus arteriosus
6th

Branchial Apparatus
- Composed of branchial clefts, arches, and pouches.
-
Branchial Clefts
- __derived from ectoderm
- also called branchial grooves
-
Branchial Arches
- derived from mesoderm (muscles, arteries) and neural crest (bones, cartilage)
-
Branchial Pouches
- derived from endoderm
-
CAP covers outside to inside:
- Clefts = ectoderm
- Arches = mesoderm + neural crest
- Pouches = endoderm

Branchial Cleft Derivatives:
develops into external auditory meatus
1st cleft
Branchial Cleft Derivatives:
form temporary cervical sinuses, which are obliterated by proliferation of 2nd arch mesenchyme
2nd through 4th clefts
Branchial Cleft Derivatives:
branchial cleft cyst within lateral neck, anterior to sternocleidomastoid muscle
Persistent Cervical Sinus
Branchial Arch Derivatives:
- Cartilage:
- maxillary process → maxilla, zygomatic bone
- mandibular process → Meckel cartilage, → mandible
- malleus and incus
- sphenomandibular ligament
- Muscles:
- muscles of mastication (temporalis, masseter, lateral and medial pterygoids)
- mylohyoid
- anterior belly of digastric
- tensor tympani
- anterior 2⁄3 of tongue
- tensor veli palatini
- Nerves:
- CN V3—chew
- Pierre Robin Sequence
- micrognathia, glossoptosis, cleft palate, airway obstruction
- Treacher Collins Syndrome
- neural crest dysfunction → mandibular hypoplasia, facial abnormalities
1st Branchial Arch
When at the restaurant of the golden arches, children tend to first chew (1), then smile (2), then swallow stylishly (3) or simply swallow (4), and then speak (6).
Branchial Arch Derivatives:
- Cartilage:
- Reichert Cartilage:
- stapes
- styloid process
- lesser horn of hyoid
- stylohyoid ligament
- Reichert Cartilage:
- Muscles:
- muscles of facial expression
- stapedius
- stylohyoid
- platysma
- posterior belly of digastric
- Nerves:
- CN VII—facial expression, smile
- Pierre Robin Sequence
- micrognathia, glossoptosis, cleft palate, airway obstruction
- Treacher Collins Syndrome
- neural crest dysfunction → mandibular hypoplasia, facial abnormalities
2nd Branchial Arch
When at the restaurant of the golden arches, children tend to first chew (1), then smile (2), then swallow stylishly (3) or simply swallow (4), and then speak (6).
Branchial Arch Derivatives:
- Cartilage:
- greater horn of hyoid
- Muscles:
- stylopharyngeus (innervated by
glossopharyngeal nerve)
- stylopharyngeus (innervated by
- Nerves:
- CN IX—stylopharyngeus, swallow
3rd Branchial Arch
When at the restaurant of the golden arches, children tend to first chew (1), then smile (2), then swallow stylishly (3) or simply swallow (4), and then speak (6).
Branchial Arch Derivatives:
- Cartilage:
- arytenoids
- cricoid
- corniculate
- cuneiform
- thyroid
- Muscles:
- most pharyngeal constrictors
- cricothyroid
- levator veli palatini
all intrinsic muscles of larynx except cricothyroid
- Nerves:
- CN X—superior laryngeal branch, swallow
- 6th arch: CN X—recurrent/inferior laryngeal branch, speak
4th–6th Branchial Arches
- 4th Arch
- most pharyngeal constrictors, cricothyroid, and levator veli palatini
- CN X—superior laryngeal branch, swallow
- 6th Arch
- all intrinsic muscles of larynx except cricothyroid
- CN X (recurrent/inferior laryngeal branch) speak
- Arches 3 and 4 form posterior 1⁄3 of tongue.
- Arch 5 makes no major developmental contributions.
Sing and ACCCT:
- Arytenoids
- Cricoid
- Corniculate
- Cuneiform
- Thyroid
When at the restaurant of the golden arches, children tend to first chew (1), then smile (2), then swallow stylishly (3) or simply swallow (4), and then speak (6).
Branchial Pouch Derivatives:
- middle ear cavity
- eustachian tube
- mastoid air cells
- contributes to endoderm-lined structures of ear
1st Branchial Pouch
ears, tonsils, bottom-to-top:
- 1 (ears)
- 2 (tonsils)
- 3 dorsal (bottom = inferior parathyroids)
- 3 ventral (to = thymus)
- 4 (top = superior parathyroids)
Branchial Pouch Derivatives:
epithelial lining of palatine tonsil
2nd Branchial Pouch
ears, tonsils, bottom-to-top:
- 1 (ears)
- 2 (tonsils)
- 3 dorsal (bottom = inferior parathyroids)
- 3 ventral (to = thymus)
- 4 (top = superior parathyroids)
Branchial Pouch Derivatives:
- dorsal wings → inferio parathyroids
- ventral wings → thymus
- contributes to 3 structures (thymus, left and right inferior parathyroids)
- end up below 4th-pouch structures
3rd Branchial Pouch
ears, tonsils, bottom-to-top:
- 1 (ears)
- 2 (tonsils)
- 3 dorsal (bottom = inferior parathyroids)
- 3 ventral (to = thymus)
- 4 (top = superior parathyroids)
Branchial Pouch Derivatives:
- dorsal wings → superior parathyroids
- ventral wings → ultimobranchial body → parafollicular cells of thyroid
4th Branchial Pouch
ears, tonsils, bottom-to-top:
- 1 (ears)
- 2 (tonsils)
- 3 dorsal (bottom = inferior parathyroids)
- 3 ventral (to = thymus)
- 4 (top = superior parathyroids)
Branchial Pouch:
- chromosome 22q11 deletion
- aberrant development of 3rd and 4th pouches → T-cell deficiency (thymic aplasia) and hypocalcemia (failure of parathyroid development)
- associated with cardiac defects (conotruncal anomalies)
DiGeorge Syndrome
Cleft Lip and Palate
- Cleft Lip
- failure of fusion of the maxillary an merged medial nasal processes (formation of 1° palate)
- Cleft Palate
- failure of fusion of the two lateral palatine shelves or failure of fusion of lateral palatine shelves with the nasal septum and/or median palatine shelf (formation of 2° palate)
- Cleft lip and cleft palate have distinct, multifactorial etiologies, but often occur together.

Genital Embryology:
Female
- default development
- mesonephric duct degenerates and paramesonephric duct develops

Genital Embryology:
Male
- SRY gene on Y chromosome—produces testis-determining factor → testes development
- Sertoli cells secrete Müllerian inhibitory factor (MIF) that suppresses development of paramesonephric ducts.
- Leydig cells secrete androgens that stimulate development of mesonephric ducts.

Genital Embryology:
Paramesonephric (Müllerian) Duct
- develops into female internal structures—fallopian tubes, uterus, upper portion of vagina (lower portion from urogenital sinus)
- male remnant is appendix testis

Genital Embryology:
may present as 1° amenorrhea (due to a lack of uterine development) in females with fully developed 2° sexual characteristics (functional ovaries)
Müllerian Agenesis
(Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome)
Genital Embryology:
Mesonephric (Wolffian) Duct
- develops into male internal structures (except prostate)
-
SEED:
- Seminal vesicles
- Epididymis
- Ejaculatory duct
- Ductus deferens
-
SEED:
- female remnant is Gartner duct

Sexual Differentiation
① no Sertoli cells or lack of Müllerian inhibitory factor → develop both male and female internal genitalia and male external genitalia
② 5α-reductase deficiency—inability to convert testosterone into DHT → male internal genitalia, ambiguous external genitalia until puberty (when ↑ testosterone levels cause masculinization)
In the testes:
- Leydig cells Leads to male (internal and external) sexual differentiation.
- Sertoli cells Shuts down female (internal) sexual differentiation.

Uterine (Müllerian Duct) Anomalies:
- common anomaly
- incomplete resorption of septum
- ↓ fertility and early miscarriage/pregnancy loss
- treated with septoplasty
Septate Uterus

Uterine (Müllerian Duct) Anomalies:
- incomplete fusion of Müllerian ducts
- ↑ risk of complicated pregnancy, early pregnancy loss, malpresentation, prematurity
Bicornuate Uterus

Uterine (Müllerian Duct) Anomalies:
- complete failure of fusion → double uterus, cervix, vagina
- pregnancy possible
Uterus Didelphys

Male/Female Genital Homologs

Congenital Penile Abnormalities:
- abnormal opening of penile urethra on ventral surface of penis due to failure of urethral folds to fuse
- more common than epispadias
- associated with inguinal hernia and cryptorchidism
Hypospadias

Congenital Penile Abnormalities:
- abnormal opening of penile urethra on dorsal surface of penis due to faulty positioning of genital tubercle
- associated with exstrophy of the bladder is
Epispadias
When you have Epispadias, you hit your Eye when you pEE.

Descent of Testes and Ovaries:
- band of fibrous tissue
- Male Remnant:
- anchors testes within scrotum
- Female Remnant:
- ovarian ligament + round ligament of uterus
Gubernaculum
Descent of Testes and Ovaries:
- evagination of peritoneum
- Male Remnant:
- forms tunica vaginalis
- Female Remnant:
- obliterated
Processus Vaginalis
Gonadal Venous Drainage
- right ovary/testis → right gonadal vein → IVC
- left ovary/testis → left gonadal vein → left renal vein → IVC
- “Left gonadal vein takes the Longest way.”
- Because the left spermatic vein enters the left renal vein at a 90° angle, flow is less laminar on left than on right → left venous pressure > right venous pressure → varicocele more common on the left.
Gonadal Lymphatic Drainage
- ovaries/testes → para-aortic lymph nodes
- body of uterus/superior bladder → external iliac nodes
- prostate/cervix/corpus cavernosum/proximal vagina → internal iliac nodes
- distal vagina/vulva/scrotum/distal anus → superficial inguinal nodes
- glans penis → deep inguinal nodes
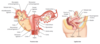
Female Reproductive Anatomy

Female Reproductive Anatomy:
- connects ovaries to lateral pelvic wall
- contains ovarian vessels
- also called suspensory ligament of the ovary
- ligate vessels during oophorectomy to avoid bleeding
- ureter courses retroperitoneally, close to gonadal vessels → at risk of injury during ligation of ovarian vessels
Infundibulopelvic Ligament

Female Reproductive Anatomy:
- connects cervix to side wall of pelvis
- contains uterine vessels
- ureter at risk of injury during ligation of uterine vessels in hysterectomy
Cardinal ligament

Female Reproductive Anatomy:
- connects uterine horn to labia majora
- derivative of gubernaculum
- travels through round inguinal canal
- above the artery of Sampson
Round Ligament of the Uterus

Female Reproductive Anatomy:
- connects uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries to pelvic side wall
- contains ovaries, fallopian tubes, and round ligaments of uterus
- fold of peritoneum that comprises the mesosalpinx, mesometrium, and mesovarium
Broad Ligament

Female Reproductive Anatomy:
- medial pole of ovary to uterine horn
- derivative of gubernaculum
Ovarian Ligament
Ovarian Ligament Latches to Lateral uterus.
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
Vagina
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
Ectocervix
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
Transformation Zone
squamocolumnar junction
- most common area for cervical cancer
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
Endocervix
simple columnar epithelium
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
Uterus
simple columnar epithelium
- proliferative phase—long tubular glands
- secretory phase—coiled glands
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
Fallopian Tube
ciliated simple columnar epithelium
Female Reproductive Epithelial Histology:
outer surface of the ovaries
simple cuboidal epithelium
- germinal epithelium covering surface of ovary
Male Reproductive Anatomy
Pathway of Sperm during Ejaculation—SEVEN UP:
- Seminiferous tubules
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Ejaculatory ducts
- (Nothing)
- Urethra
- Penis

_____ occurs almost exclusively in men. Suspect if blood seen at urethral meatus. Urethral catheterization is relatively contraindicated.
Urethral Injury
Urethral Injury:
- bulbar (spongy) urethra
- perineal straddle injury
- blood accumulates in scrotum
- if Buck fascia is torn, urine escapes into perineal space
- blood at urethral meatus and scrotal hematoma
Anterior Urethral Injury

Urethral Injury:
- membranous urethra
- pelvic fracture
- urine leaks into retropubic space
- blood at urethral meatus and high-riding prostate
Posterior Urethral Injury

Autonomic Innervation of Male Sexual Response
Point, Squeeze, and Shoot.
- Erection
-
Parasympathetic nervous system (pelvic splanchnic nerves, S2-S4):
- NO → ↑ cGMP → smooth muscle relaxation → vasodilation → proerectile
- PDE-5 inhibitors (eg. Sildenafil) ↓ cGMP breakdown
- Norepinephrine → ↑ [Ca2+]in → smooth muscle contraction → vasoconstriction → antierectile
- NO → ↑ cGMP → smooth muscle relaxation → vasodilation → proerectile
-
Parasympathetic nervous system (pelvic splanchnic nerves, S2-S4):
- Emission
- Sympathetic nervous system (hypogastric nerve, T11-L2)
- Ejaculation
- visceral and Somatic nerves (pudendal nerve)
Seminiferous Tubules

Seminiferous Tubules:
- maintain germ cell pool and produce 1° spermatocytes
- line seminiferous tubules
- germ cells
Spermatogonia

Seminiferous Tubules:
- secrete inhibin B → inhibit FSH
- secrete androgen-binding protein → maintain local levels of testosterone
- produce MIF
- tight junctions between adjacent _____ form blood-testis barrier → isolate gametes from autoimmune attack
- support and nourish developing spermatozoa
- regulate spermatogenesis
- temperature sensitive
- ↓ sperm production and ↓ inhibin B with ↑ temperature
- line seminiferous tubules
- non-germ cells
- convert testosterone and androstenedione to estrogens via aromatase
- homolog of female granulosa cells ↑ temperature seen in varicocele, cryptorchidism
Sertoli Cells
Sertoli cells Support Sperm Synthesis and inhibit FSH.

Seminiferous Tubules:
- secrete testosterone in the presence of LH
- testosterone production unaffected by temperature
- interstitium
- endocrine cells
- homolog of female theca interna cells
Leydig Cells
LH stimulates Leydig cells.

Estrogen
- Sources:
- ovary (17β-estradiol)
- placenta (estriol)
- adipose tissue (estrone via aromatization)
- Potency: estradiol > estrone > estriol
- Function:
- development of genitalia and breast
- female fat distribution
- growth of follicle
- endometrial proliferation
- ↑ myometrial excitability
- upregulation of estrogen, LH, and progesterone receptors
- feedback inhibition of FSH and LH, then LH surge
- stimulation of prolactin secretion
- ↑ transport proteins, SHBG
- ↑ HDL
- ↓ LDL
- Pregnancy:
- 50-fold ↑ in estradiol and estrone
- 1000-fold ↑ in estriol (indicator of fetal well-being)
- Estrogen receptors expressed in cytoplasm; translocate to nucleus when bound by estrogen.

Progesterone
- Source:
- corpus luteum
- placenta
- adrenal cortex
- testes
- Function:
- stimulation of endometrial glandular secretions and spiral artery development
- maintenance of pregnancy
- ↓ myometrial excitability
- production of thick cervical mucus, which inhibits sperm entry into uterus
- ↑ body temperature
- inhibition of gonadotropins (LH, FSH)
- uterine smooth muscle relaxation (preventing contractions)
- ↓ estrogen receptor expression
- prevents endometrial hyperplasia
- Fall in progesterone after delivery disinhibits prolactin → lactation.
- ↑ progesterone is indicative of ovulation.
- Progesterone is pro-gestation.
- Prolactin is pro-lactation.
Oogenesis
- 1° oocytes begin meiosis I during fetal life and complete meiosis I just prior to ovulation.
- Meiosis I is arrested in PrOphase I for years until Ovulation (1° oocytes).
- Meiosis II is arrested in Metaphase II until fertilization (2° oocytes). “An egg met a sperm.”
- If fertilization does not occur within 1 day, the 2° oocyte degenerates.

Ovulation
- ↑ estrogen, ↑ GnRH receptors on anterior pituitary
- Estrogen surge then stimulates LH release → ovulation (rupture of follicle).
- ↑ temperature (progesterone induced)
_____ is the transient mid-cycle ovulatory pain (“middle hurts”); classically associated with peritoneal irritation (eg. follicular swelling/rupture, fallopian tube contraction). Can mimic appendicitis.
Mittelschmerz
Menstrual Cycle
- Follicular phase can vary in length.
- Luteal phase is 14 days.
- ovulation day + 14 days = menstruation
- Follicular growth is fastest during 2nd week of the follicular phase.
- Estrogen stimulates endometrial proliferation.
- Progesterone maintains endometrium to support implantation.
- ↓ progesterone → ↓ fertility

Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- Characterized as either heavy menstrual bleeding (AUB/HMB) or intermenstrual bleeding (AUB/IMB).
- These are further subcategorized by PALMCOEIN:
- Structural Causes (PALM):
- Polyp
- Adenomyosis
- Leiomyoma
- Malignancy/hyperplasia
- Non-Structural Causes (COEIN):
- Coagulopathy
- Ovulatory
- Endometrial
- Iatrogenic
- Not yet classified
- Structural Causes (PALM):
- Terms such as dysfunctional uterine bleeding, menorrhagia, oligomenorrhea are no longer recommended.
Pregnancy
- Fertilization most commonly occurs in upper end of fallopian tube (the ampulla).
- Occurs within 1 day of ovulation.
- Implantation within the wall of the uterus occurs 6 days after fertilization.
- Syncytiotrophoblasts secrete hCG, which is detectable in blood 1 week after conception and on home test in urine 2 weeks after conception.
- Gestational Age—calculated from date of last menstrual period
- Embryonic Age—calculated from date of conception (gestational age minus 2 weeks)
- Physiologic adaptations in pregnancy:
- ↑ cardiac output (↑ preload, ↓ afterload, ↑ HR → ↑ placental and uterus perfusion)
- anemia (↑↑ plasma, ↑ RBCs)
- hypercoagulability (to ↓ blood loss at
- delivery)
- hyperventilation (eliminate fetal CO2)
- Placental hormone secretion generally increases over the course of pregnancy, but hCG peaks at 8–10 weeks.

Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
- Source: syncytiotrophoblast of placenta
- Function:
- Maintains corpus luteum (and thus progesterone) for first 8–10 weeks of pregnancy by acting like LH (otherwise no luteal cell stimulation → abortion).
- After 8–10 weeks, placenta synthesizes its own estriol and progesterone and corpus luteum degenerates.
- Used to detect pregnancy because it appears early in urine.
- Has identical α subunit as LH, FSH, TSH (states of ↑ hCG can cause hyperthyroidism).
- β subunit is unique (pregnancy tests detect β subunit).
- hCG is ↑ in multiple gestations, hydatidiform moles, choriocarcinomas, and Down syndrome.
- hCG is ↓ in ectopic/failing pregnancy, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome.
Human Placental Lactogen
- also known as Chorionic Somatomammotropin
- Source: syncytiotrophoblast of placenta
- Function:
- Stimulates insulin production; overall ↑ insulin resistance.
- Maternal hypoglycemia from insulin resistance leads to lipolysis, which preserves available glucose and amino acids for the fetus.
- Gestational diabetes can occur if maternal pancreatic function cannot overcome the insulin resistance.
Apgar Score
- Assessment of newborn vital signs following delivery via a 10-point scale evaluated at 1 minute and 5 minutes.
- Apgar score is based on Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity, and Respiration.
- Apgar scores < 7 require further evaluation.
- If Apgar score remains low at later time points, there is ↑ risk the child will develop long-term neurologic damage.

Infant/Child Development
- Milestone dates are ranges that have been approximated and vary by source.
- Children not meeting milestones may need assessment for potential developmental delay.

Low Birth Weight
- Defined as < 2500 g.
- Caused by prematurity or intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
- Associated with ↑ risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and with ↑ overall mortality.
- Other problems include impaired thermoregulation and immune function, hypoglycemia, polycythemia, and impaired neurocognitive/emotional development.
- Complications include infections, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, intraventricular hemorrhage, and persistent fetal circulation.
Lactation
- After parturition and delivery of placenta, rapid ↓ in progesterone disinhibits and initiates lactation.
- Suckling is required to maintain milk production and ejection, since ↑ nerve stimulation → ↑ oxytocin and prolactin.
- Prolactin—induces and maintains lactation and ↓ reproductive function.
- Oxytocin—assists in milk letdown; also promotes uterine contractions.
- Breast milk is the ideal nutrition for infants < 6 months old.
- Contains maternal immunoglobulins (conferring passive immunity; mostly IgA), macrophages, lymphocytes.
- Breast milk reduces infant infections and is associated with ↓ risk for child to develop asthma, allergies, diabetes mellitus, and obesity.
- Guidelines recommend exclusively breastfed infants get vitamin D and possibly iron supplementation.
- Breastfeeding ↓ maternal risk of breast and ovarian cancer and facilitates mother-child bonding.
Menopause
- Diagnosed by amenorrhea for 12 months.
- ↓ estrogen production due to age-linked decline in number of ovarian follicles.
- Average age at onset is 51 years (earlier in smokers).
- Usually preceded by 4–5 years of abnormal menstrual cycles.
- Source of estrogen (estrone) after menopause becomes peripheral conversion of androgens, ↑ androgens → hirsutism.
- ↑↑ FSH is specific for menopause (loss of negative feedback on FSH due to ↓ estrogen).
- Hormonal Changes:
- ↓ estrogen
- ↑↑ FSH
- ↑ LH (no surge)
- ↑ GnRH
- Causes HAVOCS:
- Hot flashes
- Atrophy of the Vagina
- Osteoporosis
- Coronary artery disease
- Sleep disturbances
- Menopause before age 40 suggests 1° ovarian insufficiency (premature ovarian failure).
Androgens
- Testosterone, Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), and Androstenedione
- Sources:
- DHT and Testosterone (Testis)
- AnDrostenedione (ADrenal)
- Potency: DHT > testosterone > androstenedione
- Function:
- Testosterone:
- differentiation of epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles (internal genitalia, except prostate).
- growth spurt: penis, seminal vesicles, sperm, muscle, RBCs
- deepening of voice
- closing of epiphyseal plates (via estroge converted from testosterone)
- libido
- DHT:
- Early—differentiation of penis, scrotum, prostate
- Late—prostate growth, balding, sebaceous gland activity
- Testosterone:
- Testosterone is converted to DHT by 5α-reductase, which is inhibited by Finasteride.
- In the male, androgens are converted to estrogen by cytochrome P-450 aromatase (primarily in adipose tissue and testis).
- Aromatase is the key enzyme in conversion of androgens to estrogen.
- Exogenous testosterone → inhibition of hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis → ↓ intratesticular testosterone → ↓ testicular size → azoospermia.
Spermatogenesis
- Spermatogenesis begins at puberty with spermatogonia.
- Full development takes 2 months.
- Occurs in seminiferous tubules.
- Produces spermatids that undergo spermiogenesis (loss of cytoplasmic contents, gain of acrosomal cap) to form mature spermatozoon.
- “Gonium” is going to be a sperm.
- “Zoon” is “zooming” to the egg.

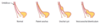
Tanner Stages of Sexual Development
Tanner stage is assigned independently to genitalia, pubic hair, and breast (eg. a person can have Tanner stage 2 genitalia, Tanner stage 3 pubic hair).

Aneuploidy most commonly due to _____.
Meiotic Nondisjunction
Sex Chromosome Disorders:
- Male, 47, XXY
- testicular atrophy, eunuchoid body shape, tall, long extremities, gynecomastia, female hair distribution
- may present with developmental delay
- presence of inactivated X chromosome (Barr body)
- common cause of hypogonadism seen in infertility work-up
- dysgenesis of seminiferous tubules → ↓ inhibin B → ↑ FSH
- abnormal Leydig cell function → ↓ testosterone → ↑ LH → ↑ estrogen
Klinefelter Syndrome
Sex Chromosome Disorders:
- Female, 45, XO
- short stature (if untreated; preventable with growth hormone therapy), ovarian dysgenesis (streak ovary), shield chest, bicuspid aortic valve, coarctation (femoral < brachial pulse), lymphatic defects (result in webbed neck or cystic hygroma, lymphedema in hands and feet), horseshoe kidney
- most common cause of 1° amenorrhea
- no Barr body
- menopause before menarche
- ↓ estrogen leads to ↑LH, FSH
- sometimes due to mitotic error → mosaicism (eg. 45, XO/46, XX)
- pregnancy is possible in some cases (IVF, exogenous estradiol-17β and progesterone)
Turner Syndrome
Sex Chromosome Disorders:
- 47, XYY
- phenotypically normal (usually undiagnosed), very tall
- normal fertility
- may be associated with severe acne, learning disability, and autism spectrum disorders
Double Y Males
Sex Chromosome Disorders:
- 46, XX > 46, XY
- both ovarian and testicular tissue present (ovotestis)
- ambiguous genitalia
- previously called true hermaphroditism
Ovotesticular Disorder of Sex Development
Diagnosing Disorders of Sex Hormones:
- ↑ Testosterone
- ↑ LH
Defective Androgen Receptor
Diagnosing Disorders of Sex Hormones:
- ↑ Testosterone
- ↓ LH
Testosterone-Secreting Tumor
- exogenous steroids
Diagnosing Disorders of Sex Hormones:
- ↓ Testosterone
- ↑ LH
1° Hypergonadotropic Hypogonadism
Diagnosing Disorders of Sex Hormones:
- ↓ Testosterone
- ↓ LH
2° Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Other Disorders of Sex Development
- Disagreement between the phenotypic sex (external genitalia, influenced by hormonal levels) and the gonadal sex (testes vs. ovaries, corresponds with Y chromosome).
- Includes the terms pseudohermaphrodite, hermaphrodite, and intersex.
Other Disorders of Sex Development:
- ovaries present, but external genitalia are virilized or ambiguous
- due to excessive and inappropriate exposure to androgenic steroids during early gestation (eg. congenital adrenal hyperplasia or exogenous administration of androgens during pregnancy)
46, XX DSD
Other Disorders of Sex Development:
- testes present, but external genitalia are female or ambiguous
- most common form is androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization)
46, XY DSD
Disorders by Physical Characteristics:
- ⊕ Uterus
- ⊝ Breasts
Hypergonadotropic Hypogonadism
- Turner syndrome
- genetic mosaicism
- pure gonadal dysgenesis
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
- CNS lesions
- Kallmann syndrome
Disorders by Physical Characteristics:
- ⊝ Uterus
- ⊕ Breasts
Uterovaginal Agenesis
- genotypic female
Androgen Insensitivity
- genotypic male
Disorders by Physical Characteristics:
- ⊝ Uterus
- ⊝ Breasts
male genotype with insufficient production of testosterone
Reproductive Pathology:
- inability to synthesize estrogens from androgens
- masculinization of female (46, XX DSD) infants (ambiguous genitalia)
- ↑ serum testosterone and androstenedione
- can present with maternal virilization during pregnancy (fetal androgens cross the placenta)
Placental Aromatase Deficiency
Reproductive Pathology:
- defect in androgen receptor resulting in normal-appearing female (46, XY DSD)
- female external genitalia with scant axillary and pubic hair
- rudimentary vagina
- uterus and fallopian tubes absent
- patients develop normal functioning testes (often found in labia majora; surgically removed to prevent malignancy)
- ↑ testosterone, estrogen, and LH (vs. sex chromosome disorders)
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Reproductive Pathology:
- autosomal recessive
- sex limited to genetic males (46, XY DSD)
- inability to convert testosterone to DHT
- ambiguous genitalia until puberty, when ↑ testosterone causes masculinization/↑ growth of external genitalia
- testosterone/estrogen levels are normal
- LH is normal or ↑
- internal genitalia are normal
5α-Reductase Deficiency
Reproductive Pathology:
- failure to complete puberty
- a form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- defective migration of GnRH-releasing neurons and subsequent failure of GnRH-releasing olfactory bulbs to develop → ↓ synthesis of GnRH in the hypothalamus
- hyposmia/anosmia
- ↓ GnRH, FSH, LH, and testosterone
- infertility (low sperm count in males; amenorrhea in females)
Kallmann Syndrome
Hydatidiform Mole
- cystic swelling of chorionic villi and proliferation of chorionic epithelium (only trophoblast)
- presents with vaginal bleeding, uterine enlargement more than expected, pelvic pressure/pain
- associated with hCG-mediated sequelae: early preeclampsia (before 20 weeks), theca-lutein cysts, hyperemesis gravidarum, and hyperthyroidism
- Treatment:
- dilation and curettage
- Methotrexate
- monitor β-hCG
Hydatidiform Mole:
- Karyotype: 46, XX; 46, XY
- Components:
- most commonly enucleated egg + single sperm (subsequently duplicates paternal DNA)
- Fetal Parts: No
- Uterine Size: ↑
- hCG: ↑↑↑↑
- Imaging:
- “honeycombed” uterus or “clusters of grapes”
- “snowstorm” on ultrasound
- Risk of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia: 15–20%
- Risk of Choriocarcinoma: 2%
Complete Mole
Hydatidiform Mole:
- Karyotype: 69, XXX; 69, XXY; 69, XYY
- Components: 2 sperm + 1 egg
- Fetal Parts: Yes
- Uterine Size: —
- hCG: ↑
- Imaging: fetal parts
- Risk of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia: < 5%
- Risk of Choriocarcinoma: rare
Partial Mole
partial = fetal parts
Reproductive Pathology:
- rare
- can develop during or after pregnancy in mother or baby
- malignancy of trophoblastic tissue (cytotrophoblasts, syncytiotrophoblasts)
- no chorionic villi present
- ↑ frequency of bilateral/multiple theca-lutein cysts
- presents with abnormal ↑ β-hCG, shortness of breath, and hemoptysis
- hematogenous spread to lungs → “cannonball” metastases
Choriocarcinoma
Pregnancy Complications:
- premature separation (partial or complete) of placenta from uterine wall before delivery of infant
- Risk Factors:
- trauma (eg. motor vehicle accident)
- smoking
- hypertension
- preeclampsia
- cocaine abuse
- Presentation:
- abrupt
- painful bleeding (concealed or apparent) in third trimester
- possible DIC
- maternal shock
- fetal distress
- life threatening for mother and fetus
Abruptio Placentae

Pregnancy Complications:
- defective decidual layer → abnormal attachment and separation after delivery
- Risk Factors:
- prior C-section or uterine surgery involving myometrium
- inflammation
- placenta previa
- advanced maternal age
- multiparity
- Three types distinguishable by the depth of penetration:
-
Placenta Accreta
- placenta attaches to myometrium without penetrating it
- most common type
-
Placenta Increta
- placenta penetrates into myometrium
-
Placenta Percreta
- placenta penetrates (“perforates”) through myometrium and into uterine serosa (invades entire uterine wall)
- can result in placental attachment to rectum or bladder (can result in hematuria)
-
Placenta Accreta
- Presentation:
- often detected on ultrasound prior to delivery
- no separation of placenta after delivery → postpartum bleeding (can cause Sheehan syndrome)
Morbidly Adherent Placenta

Pregnancy Complications:
- attachment of placenta to lower uterine segment over (or < 2 cm from) internal cervical os
- Risk Factors:
- multiparity
- prior C-section
- associated with painless third-trimester bleeding
Placenta Previa
A “preview” of the placenta is visible through cervix.
Pregnancy Complications:
- fetal vessels run over, or in close proximity to, cervical os
- may result in vessel rupture, exsanguination, and fetal death
- presents with triad of membrane rupture, painless vaginal bleeding, and fetal bradycardia (< 110 beats/min)
- emergency C-section usually indicated
- frequently associated with velamentous umbilical cord insertion (cord inserts in chorioamniotic membrane rather than placenta → fetal vessels travel to placenta unprotected by Wharton jelly)
Vasa Previa

Pregnancy Complications:
- Due to 4 T’s:
- Tone (uterine atony; most common)
- Trauma (lacerations, incisions, uterine rupture)
- Thrombin (coagulopathy)
- Tissue (retained products of conception)
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Pregnancy Complications:
- implantation of fertilized ovum in a site other than the uterus
- most often in ampulla of fallopian tube
- suspect with history of amenorrhea, lower-than-expected rise in hCG based on dates, and sudden lower abdominal pain
- confirm with ultrasound
- often clinically mistaken for appendicitis
- pain +/− bleeding
- Risk Factors:
- prior _____
- history of infertility
- salpingitis (PID)
- ruptured appendix
- prior tubal surgery
- smoking
- advanced maternal age
Ectopic Pregnancy
Amniotic Fluid Abnormalities:
- too much amniotic fluid
- often idiopathic, but associated with fetal malformations (eg. esophageal/duodenal atresia, anencephaly; both result in inability to swallow amniotic fluid), maternal diabetes, fetal anemia, and multiple gestations
Polyhydramnios
Amniotic Fluid Abnormalities:
- too little amniotic fluid
- associated with placental insufficiency, bilateral renal agenesis, posterior urethral valves (in males) and resultant inability to excrete urine
- any profound _____ can cause Potter sequence
Oligohydramnios
Hypertension in Pregnancy:
- BP > 140/90 mmHg after 20th week of gestation
- no pre-existing hypertension
- no proteinuria or end-organ damage
- Treatment:
- antihypertensives
- deliver at 37–39 weeks
Gestational Hypertension
Hypertensive Moms Love Nifedipine.
- Hydralazine
- α-Methyldopa
- Labetalol
- Nifedipine
Hypertension in Pregnancy:
- new-onset hypertension with either proteinuria or end-organ dysfunction after 20th week of gestation (< 20 weeks suggests molar pregnancy)
- caused by abnormal placental spiral arteries → endothelial dysfunction, vasoconstriction, ischemia
- incidence ↑ in patients with pre-existing hypertension, diabetes, chronic renal disease, and autoimmune disorders (eg. antiphospholipid antibody syndrome)
- Complications:
- placental abruption
- coagulopathy
- renal failure
- pulmonary edema
- uteroplacental insufficiency
- may lead to eclampsia (+ seizures) and/or HELLP syndrome
- Treatment:
- antihypertensives
- IV magnesium sulfate (to prevent seizure)
- definitive is delivery of fetus
Preeclampsia
Hypertension in Pregnancy:
- preeclampsia + maternal seizures
- maternal death due to stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, or ARDS
- Treatment:
- IV magnesium sulfate
- antihypertensives
- immediate delivery
Eclampsia
Hypertension in Pregnancy:
- hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets
- a manifestation of severe preeclampsia
- blood smear shows schistocytes
- can lead to DIC and hepatic subcapsular hematomas → rupture → severe hypotension
- Treatment: immediate delivery
HELLP syndrome
- Hemolysis
- Elevated Liver Enzymes
- Low Platelets
Gynecologic Tumor Epidemiology
- Incidence (US):
- endometrial > ovarian > cervical
- cervical cancer is more common worldwide due to lack of screening or HPV vaccination
- Prognosis:
- Cervical—best prognosis, diagnosed < 45 years old
- Endometrial—middle-aged, about 55 years old
- Ovarian—worst prognosis, > 65 years
- CEOs often go from best to worst as they get older.
Vulvar Pathology:
- non-neoplastic
- due to blockage of Bartholin gland duct causing accumulation of gland fluid
- may lead to abscess 2° to obstruction and inflammation
- usually in reproductive-age females
- associated with N. gonorrhoeae infections
Bartholin Cyst and Abscess
Vulvar Pathology:
- non-neoplastic
- thinning of epidermis with fibrosis/sclerosis of dermis
- presents with porcelain-white plaques with a red or violet border
- skin fragility with erosions can be observed
- most common in postmenopausal women
- benign, but slightly increased risk for SCC
Lichen Sclerosus
Vulvar Pathology:
- non-neoplastic
- hyperplasia of vulvar squamous epithelium
- presents with leathery, thick vulvar skin with enhanced skin markings due to chronic rubbing or scratching
- benign, no risk of SCC
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Vulvar Pathology:
- neoplastic
- carcinoma from squamous epithelial lining of vulva
- rare
- presents with leukoplakia
- biopsy often required to distinguish carcinoma from other causes
- HPV-Related
- associated with high-risk HPV types 16, 18
- Risk Factors:
- multiple partners
- early coitarche
- Risk Factors:
- usually in reproductive-age females
- associated with high-risk HPV types 16, 18
- Non-HPV
- usually from long-standing lichen sclerosus
- females > 70 years old
Vulvar Carcinoma
Vulvar Pathology:
- neoplastic
- intraepithelial adenocarcinoma
- carcinoma in situ
- low risk of underlying carcinoma
- presents with pruritus, erythema, crusting, and ulcers
Extramammary Paget Disease
Vaginal Tumors:
- usually 2° to cervical SCC
- 1° vaginal carcinoma is rare
Vaginal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Vaginal Tumors:
affects women who had exposure to DES in utero
Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma
Vaginal Tumors:
- embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma variant
- affects girls < 4 years old
- spindle-shaped cells
- desmin ⊕
- presents with clear, grape-like, polypoid mass emerging from vagina
Sarcoma Botryoides
Cervical Pathology:
- disordered epithelial growth
- begins at basal layer of squamocolumnar junction (transformation zone) and extends outward
- classified as CIN 1, CIN 2, or CIN 3 (severe, irreversible dysplasia), depending on extent of dysplasia
- associated with HPV-16 and HPV-18, which produce both the E6 gene product (inhibits p53) and E7 gene product (inhibits pRb)
- koilocytes are pathognomonic of HPV infection
- may progress slowly to invasive carcinoma if left untreated
- typically asymptomatic (detected with Pap smear) or presents as abnormal vaginal bleeding (often postcoital)
- Risk Factors:
- multiple sexual partners (#1)
- smoking
- early coitarche
- DES exposure
- immunocompromise (eg. HIV, transplant)
Dysplasia and Carcinoma in situ
Cervical Pathology:
- often squamous cell carcinoma
- pap smear can detect cervical dysplasia before it progresses
- diagnosed via colposcopy and biopsy
- lateral invasion can block ureters → renal failure
Invasive Carcinoma
Reproductive Pathology:
- also known as premature ovarian failure
- premature atresia of ovarian follicles in women of reproductive age
- most often idiopathic
- associated with chromosomal abnormalities (especially in females < 30 years)
- need karyotype screening
- patients present with signs of menopause after puberty but before age 40
- ↓ estrogen, ↑ LH, ↑ FSH
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
Most Common Causes of Anovulation
- pregnancy
- PCOS
- obesity
- HPO axis abnormalities
- premature ovarian failure
- hyperprolactinemia
- thyroid disorders
- eating disorders
- competitive athletics
- Cushing syndrome
- adrenal insufficiency
- chromosomal abnormalities (eg. Turner syndrome)
Reproductive Pathology:
- also known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- hyperinsulinemia and/or insulin resistance are hypothesized to alter hypothalamic hormonal feedback response → ↑ LH:FSH, ↑ androgens (eg. testosterone) from theca interna cells, ↓ rate of follicular maturation → unruptured follicles (cysts) + anovulation
- common cause of ↓ fertility in women
- enlarged, bilateral cystic ovaries
- presents with amenorrhea/oligomenorrhea, hirsutism, acne, and ↓ fertility
- associated with obesity
- ↑ risk of endometrial cancer 2° to unopposed estrogen from repeated anovulatory cycles
- Treatment:
- cycle regulation via weight reduction (↓ peripheral estrone formation) and OCPs (prevent endometrial hyperplasia due to unopposed estrogen)
- Clomiphene and Metformin to induce ovulation
- Spironolactone and Ketoconazole (antiandrogens) to treat hirsutism
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Ovarian Cysts:
- distention of unruptured graafian follicle
- may be associated with hyperestrogenism and endometrial hyperplasia
- most common ovarian mass in young women
Follicular Cyst
Ovarian Cysts:
- often bilateral/multiple
- due to gonadotropin stimulation
- associated with choriocarcinoma and hydatidiform moles
Theca-Lutein Cyst
Reproductive Pathology:
- most common adnexal mass in women > 55 years old
- can be benign or malignant
- arise from surface epithelium, germ cells, or sex cord stromal tissue
- majority of malignant tumors are epithelial (serous cystadenocarcinoma most common)
- risk ↑with advanced age, infertility, endometriosis, PCOS, genetic predisposition BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, Lynch syndrome, and strong family history
- risk ↓ with previous pregnancy, history of breastfeeding, OCPs, and tubal ligation
- presents with adnexal mass, abdominal distension, bowel obstruction, pleural effusion
- monitor response to therapy/relapse by measuring CA 125 levels (not good for screening)
Ovarian Neoplasms
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- surface epithelium tumor (benign)
- most common ovarian neoplasm
- lined with fallopian tube–like epithelium
- often bilateral
Serous Cystadenoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- surface epithelium tumor (benign)
- multiloculated, large
- lined by mucus-secreting epithelium
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- surface epithelium tumor (benign)
- endometriosis within ovary with cyst formation
- presents with pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia
- symptoms may vary with menstrual cycle
- “Chocolate Cyst”
- endometrioma filled with dark, reddish-brown blood
- complex mass on ultrasound
Endometrioma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- germ cell tumor (benign)
- most common ovarian tumor in females 10–30 years old
- cystic mass containing elements from all 3 germ layers (eg. teeth, hair, sebum)
- can present with pain 2° to ovarian enlargement or torsion
- a monodermal form with thyroid tissue (struma ovarii) uncommonly presents with hyperthyroidism
Mature Cystic Teratoma (Dermoid Cyst)
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- sex cord stromal tumor (benign)
- bundles of spindle-shaped fibroblasts
- Meigs Syndrome
- triad of ovarian fibroma, ascites, and hydrothorax
- “pulling” sensation in groin
Fibroma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- sex cord stromal tumor (benign)
- like granulosa cell tumors, may produce estrogen
- usually presents as abnormal uterine bleeding in a postmenopausal woman
Thecoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- resembles bladder epithelium (transitional cell tumor)
- solid tumor that is pale yellow-tan and appears encapsulated
- “coffee bean” nuclei on H&E stain
- usually benign
Brenner Tumor
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- surface epithelium tumor (malignant)
- most common malignant ovarian neoplasm
- frequently bilateral
- Psammoma bodies
Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- surface epithelium tumor (malignant)
- rare malignant mucinous ovarian epithelial tumor
- may be metastatic from appendiceal or other GI tumors
- can result in pseudomyxoma peritonei—intraperitoneal accumulation of mucinous material
Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- germ cell tumor (malignant)
- most common in adolescents
- equivalent to male seminoma but rarer
- 1% of all ovarian tumors
- 30% of germ cell tumors
- sheets of uniform “fried egg” cells
- hCG, LDH = tumor markers
Dysgerminoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- germ cell tumor (malignant)
- aggressive
- contains fetal tissue, neuroectoderm
- commonly diagnosed before age 20
- typically represented by immature/embryonic-like neural tissue
Immature Teratoma
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- germ cell tumor (malignant)
- also known as ovarian endodermal sinus tumor
- aggressive
- in ovaries or testes and sacrococcygeal area in young children
- most common tumor in male infants
- yellow, friable (hemorrhagic), solid mass
- 50% have Schiller-Duval bodies (resemble glomeruli)
- AFP = tumor marker
Yolk Sac Tumor
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- sex cord stromal tumor (malignant)
- most common malignant stromal tumor
- predominantly women in their 50s
- often produces estrogen and/or progesterone and presents with postmenopausal bleeding, sexual precocity (in pre-adolescents), and breast tendernessh
- histology shows Call-Exner bodies (granulosa cells arranged haphazardly around collections of eosinophilic fluid, resembling primordial follicles)
Granulosa Cell Tumor
“Give Granny a Call!”
Ovarian Neoplasms:
- GI malignancy that metastasizes to ovaries → mucin-secreting signet cell adenocarcinoma
- commonly presents as bilateral ovarian masses
Krukenberg Tumor
Endometrial Conditions:
- well-circumscribed collection of endometrial tissue within uterine wall
- may contain smooth muscle cells
- can extend into endometrial cavity in the form of a polyp
- may be asymptomatic or present with painless abnormal uterine bleeding
Polyp
Endometrial Conditions:
- extension of endometrial tissue (glandular) into uterine myometrium
- caused by hyperplasia of basal layer of endometrium
- presents with dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, and uniformly enlarged, soft, globular uterus
- Treatment:
- GnRH agonists
- hysterectomy or excision of an organized adenomyoma
Adenomyosis
Endometrial Conditions:
- adhesions and/or fibrosis of the endometrium
- presents with ↓ fertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, abnormal uterine bleeding, and pelvic pain
- often associated with dilation and curettage of intrauterine cavity
Asherman Syndrome
Endometrial Conditions:
- most common tumor in females
- often presents with multiple discrete tumor
- ↑ incidence in African Americans
- benign smooth muscle tumor
- malignant transformation to leiomyosarcoma is rare
- estrogen sensitive—tumor size ↑ with pregnancy and ↓ with menopause
- peak occurrence at 20–40 years old
- may be asymptomatic, cause abnormal uterine bleeding, or result in miscarriage
- severe bleeding may lead to iron deficiency anemia
- whorled pattern of smooth muscle bundles with well-demarcated borders
Leiomyoma (Fibroid)
Endometrial Conditions:
- abnormal endometrial gland proliferation usually caused by excess estrogen stimulation
- ↑ risk for endometrial carcinoma
- nuclear atypia is greater risk factor than complex (vs. simple) architecture
- presents as postmenopausal vaginal bleeding
- risk factors include anovulatory cycles, hormone replacement therapy, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and granulosa cell tumor
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial Conditions:
- most common gynecologic malignancy
- peak occurrence at 55–65 years old
- presents with vaginal bleeding
- typically preceded by endometrial hyperplasia
- risk factors include prolonged use of estrogen without progestins, obesity, diabetes, hypertension, nulliparity, late menopause, early menarche, and Lynch syndrome
Endometrial Carcinoma
Endometrial Conditions:
Inflammation of endometrium D associated with retained products of conception following delivery,
miscarriage, abortion, or with foreign body (eg, IUD). Retained material in uterus promotes
infection by bacterial flora from vagina or intestinal tract. Chronic endometritis characterized by
presence of plasma cells on histology.
Treatment: gentamicin + clindamycin +/− ampicillin.
Endometritis
Endometrial Conditions:
- non-neoplastic endometrium-like glands/stroma outside endometrial cavity
- can be found anywhere
- most common sites are ovary (frequently bilateral), pelvis, peritoneum
- in ovary, appears as endometrioma (blood-filled “chocolate cysts”)
- may be due to retrograde flow, metaplastic transformation of multipotent cells, transportation of endometrial tissue via lymphatic system
- characterized by cyclic pelvic pain, bleeding, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, dyschezia (pain with defecation), and infertility
- normal-sized uterus
- Treatment:
- NSAIDs
- continuous OCPs
- progestins
- GnRH agonists
- Danazol
- laparoscopic removal
Endometriosis
Breast Pathology

Benign Breast Disease:
- most common in premenopausal women < 35 years old
- present with premenstrual breast pain or lumps
- often bilateral and multifocal
- nonproliferative lesions include simple cysts (fluid-filled duct dilation, blue dome), papillary apocrine change/metaplasia, and stromal fibrosis
- risk of cancer is usually not increased
Fibrocystic Changes
Fibrocystic Changes:
- acini and stromal fibrosis
- associated with calcifications
- slight (1.5–2 ×) ↑ risk for cancer
Sclerosing Adenosis
Fibrocystic Changes:
- cells in terminal ductal or lobular epithelium
- ↑ risk of carcinoma with atypical cells
Epithelial Hyperplasia
Benign Breast Disease:
- inflammatory processes
- benign, usually painless, lump due to injury to breast tissue
- calcified oil cyst on mammography
- necrotic fat and giant cells on biopsy
- up to 50% of patients may not report trauma
Fat Necrosis
Benign Breast Disease:
- inflammatory processes
- occurs during breastfeeding
- ↑ risk of bacterial infection through cracks in nipple
- S. aureus is the most common pathogen
- treat with antibiotics and continue breastfeeding
Lactational Mastitis
Benign Breast Disease:
- benign tumor
- most common in women < 35 years old
- small, well-defined, mobile mass
- ↑ size and tenderness with ↑ estrogen (eg. pregnancy, prior to menstruation)
- risk of cancer is usually not increased
Fibroadenoma
Benign Breast Disease:
- benign tumor
- small fibroepithelial tumor within lactiferous ducts, typically beneath areola
- most common cause of nipple discharge (serous or bloody)
- slight (1.5–2 ×) ↑ risk for cancer
Intraductal Papilloma
Benign Breast Disease:
- benign tumor
- large mass of connective tissue and cysts with “leaf-like” lobulations
- most common in 5th decade
- some may become malignant
Phyllodes Tumor
Benign Breast Disease:
- breast enlargement in males due to ↑ estrogen compared with androgen activity
- physiologic in newborn, pubertal, and elderly males, but may persist after puberty
- other causes include cirrhosis, hypogonadism (eg. Klinefelter syndrome), testicular tumors, and drugs (Spironolactone, hormones, Cimetidine, Finasteride, Ketoconazole)
Gynecomastia
Some Hormones Create Funny Knockers.
- Spironolactone
- Hormones
- Cimetidine
- Finasteride
- Ketoconazole
Malignant Breast Tumors
- commonly postmenopausal
- usually arise from terminal duct lobular unit
- amplification/ overexpression of estrogen/progesterone receptors or c-erbB2 (HER-2, an EGF receptor) is common
- triple negative (ER ⊝, PR ⊝, and Her2/Neu ⊝) more aggressive
- type affects therapy and prognosis
- axillary lymph node involvement indicating metastasis is the most important prognostic factor in early-stage disease
- most often located in upper-outer quadrant of breast.
- Risk Factors:
- ↑ estrogen exposure
- ↑ total number of menstrual cycles
- older age at 1st live birth,
- obesity (↑ estrogen exposure as adipose tissue converts androstenedione to estrone)
- BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations
- African American ethnicity (↑ risk for triple ⊝ breast cancer)
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- noninvasive
- fills ductal lumen
- arises from ductal atypia
- often seen early as microcalcifications on mammography
- early malignancy without basement membrane penetration
Ductal Carcinoma in situ
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- noninvasive
- ductal, central necrosis
- subtype of DCIS
Comedocarcinoma
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- noninvasive
- results from underlying DCIS or invasive breast cancer
- eczematous patches on nipple
- Paget cells = intraepithelial adenocarcinoma cells
Paget Disease
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- invasive
- firm, fibrous, “rock-hard” mass with sharp margins and small, glandular, duct-like cells
- tumor can deform suspensory ligaments → dimpling of skin
- Classic Morphology: “stellate” infiltration
- most common (∼ 75% of all breast cancers)
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- invasive
- orderly row of cells (“single file”), due to ↓ E-cadherin expression
- often bilateral with multiple lesions in the same location
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Lines of cells = Lobular
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- invasive
- fleshy, cellular, lymphocytic infiltrate
- good prognosis
Medullary Carcinoma
Malignant Breast Tumors:
- invasive
- dermal lymphatic invasion by breast carcinoma
- peau d’orange—skin texture resembles orange peel due to edema leading to tightening of Cooper’s suspensory ligament
- neoplastic cells
- block lymphatic drainage
- poor prognosis (50% survival at 5 years)
- often mistaken for mastitis or Paget disease
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Penile Pathology:
- abnormal curvature of penis due to fibrous plaque within tunica albuginea
- associated with erectile dysfunction
- can cause pain and anxiety
- consider surgical repair once curvature stabilizes
- distinct from penile fracture (rupture of corpora cavernosa due to forced bending)
Peyronie Disease
Penile Pathology:
- painful sustained erection lasting > 4 hours
- associated with sickle cell disease (sickled RBCs block venous drainage of corpus cavernosum vascular channels), medications (eg. Sldenafil, Trazodone)
- treat immediately with corporal aspiration, intracavernosal phenylephrine, or surgical decompression to prevent ischemia
Ischemic Priapism
Penile Pathology:
- more common in Asia, Africa, and South America
- Precursor in situ lesions:
- Bowen disease (in penile shaft, presents as leukoplakia)
- erythroplasia of Queyrat (carcinoma in situ of the glans, presents as erythroplakia)
- Bowenoid papulosis (carcinoma in situ of unclear malignant potential, presenting as reddish papules)
- associated with uncircumcised males and HPV
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Reproductive Pathology:
- undescended testis (one or both)
- impaired spermatogenesis (since sperm develop best at temperatures < 37°C)
- can have normal testosterone levels (Leydig cells are mostly unaffected by temperature)
- associated with ↑ risk of germ cell tumors
- prematurity ↑ risk
- ↓ inhibin B, ↑ FSH, ↑ LH
- testosterone ↓ in bilateral cases, normal in unilateral
Cryptorchidism
Reproductive Pathology:
- rotation of testicle around spermatic cord and vascular pedicle
- commonly presents in males 12–18 years old
- characterized by acute, severe pain, high-riding testis, and absent cremasteric reflex
- Treatment:
- surgical correction (orchiopexy) within 6 hours
- manual detorsion if surgical option unavailable in timeframe
- if testis is not viable, orchiectomy
- orchiopexy, when performed, should be bilateral because the contralateral testis is at risk for subsequent torsion
Testicular Torsion
Reproductive Pathology:
- dilated veins in pampiniform plexus due to ↑ venous pressure
- most common cause of scrotal enlargement in adult males
- most often on left side because of ↑ resistance to flow from left gonadal vein drainage into left renal vein
- can cause infertility because of ↑ temperature
- diagnosed by standing clinical exam/Valsalva maneuver (distension on inspection and “bag of worms” on palpation; augmented by Valsalva) or ultrasound with Doppler
- does not transilluminate
- Treatment:
- consider surgical ligation or embolization if associated with pain or infertility
Varicocele
Reproductive Pathology:
- arise in midline locations
- in adults, most commonly in retroperitoneum, mediastinum, pineal, and suprasellar regions
- in infants and young children, sacrococcygeal teratomas are most common
Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors
_____ are benign lesions that present as testicular masses that can be transilluminated (vs. solid testicular tumors).
Scrotal Masses
Scrotal Masses:
- common cause of scrotal swelling in infants
- due to incomplete obliteration of processus vaginalis
- most spontaneously resolve by 1 year old
- transilluminating swelling
Congenital Hydrocele
Scrotal Masses:
- scrotal fluid collection usually 2° to infection, trauma, or tumor
- if bloody → hematocele
Acquired Hydrocele
Scrotal Masses:
- cyst due to dilated epididymal duct or rete testis
- paratesticular fluctuant nodule
Spermatocele
Reproductive Pathology:
- ∼ 95% of all testicular tumors
- most often occur in young men
- Risk Factors:
- cryptorchidism
- Klinefelter syndrome
- can present as a mixed germ cell tumor
- do not transilluminate
- usually not biopsied (risk of seeding scrotum)
- removed via radical orchiectomy
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors:
- malignant
- painless, homogenous testicular enlargement;
- most common testicular tumor
- does not occur in infancy
- large cells in lobules with watery cytoplasm and “fried egg” appearance
- ↑ placental ALP
- highly radiosensitive
- late metastasis
- excellent prognosis
- similar to dysgerminoma in females
Seminoma
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors:
- also known as testicular endodermal sinus tumor
- yellow, mucinous
- aggressive malignancy of testes, analogous to ovarian yolk sac tumor
- Schiller-Duval bodies resemble primitive glomeruli
- ↑ AFP is highly characteristic
- most common testicular tumor in boys < 3 years old
Yolk Sac Tumor
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors:
- malignant
- ↑ hCG
- disordered syncytiotrophoblastic and cytotrophoblastic elements
- hematogenous metastases to lungs and brain
- may produce gynecomastia, symptoms of hyperthyroidism (α-subunit of hCG is structurally similar to LH, FSH, TSH)
Choriocarcinoma
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors:
- unlike in females, mature _____ in adult males may be malignant
- benign in children
Teratoma
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors:
- malignant, hemorrhagic mass with necrosis
- painful
- worse prognosis than seminoma
- often glandular/papillary morphology
- “pure” _____ is rare
- most commonly mixed with other tumor types
- may be associated with ↑ hCG and normal AFP levels when pure (↑ AFP when mixed)
Embryonal Carcinoma
Reproductive Pathology:
- 5% of all testicular tumors
- mostly benign
Testicular Non–Germ Cell Tumors
Testicular Non–Germ Cell Tumors:
- golden brown color
- contains Reinke crystals (eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions)
- produces androgens or estrogens → gynecomastia in men, precocious puberty in boys
Leydig Cell Tumor
Testicular Non–Germ Cell Tumors:
androblastoma from sex cord stroma
Sertoli Cell Tumor
Testicular Non–Germ Cell Tumors:
- most common testicular cancer in older men
- not a 1° cancer
- arises from metastatic lymphoma to testes
- aggressive
Testicular Lymphoma
Reproductive Pathology:
- common in men > 50 years old
- characterized by smooth, elastic, firm nodular enlargement (hyperplasia not hypertrophy) of periurethral (lateral and middle) lobes, which compress the urethra into a vertical slit
- not premalignant
- often presents with ↑ frequency of urination, nocturia, difficulty starting and stopping urine stream, and dysuria
- may lead to distention and hypertrophy of bladder, hydronephrosis, and UTIs
- ↑ free prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
- Treatment:
- α1-antagonists (Terazosin, Tamsulosin), which cause relaxation of smooth muscle
- 5α-reductase inhibitors (eg. Finasteride)
- PDE-5 inhibitors (eg. Tadalafil)
- surgical resection (eg. TURP, ablation)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia

Reproductive Pathology:
- characterized by dysuria, frequency, urgency, and low back pain
- warm, tender, enlarged prostate
- Acute
- in older men most common bacterium is E. coli
- in young males consider C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae
- Chronic
- either bacterial or nonbacterial (eg. 2° to previous infection, nerve problems, chemical irritation)
Prostatitis
Reproductive Pathology:
- common in men > 50 years old
- arises most often from posterior lobe (peripheral zone) of prostate gland and is most frequently diagnosed by ↑ PSA and subsequent needle core biopsies
- prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) and PSA are useful tumor markers (↑ total PSA, with ↓ fraction of free PSA)
- osteoblastic metastases in bone may develop in late stages, as indicated by lower back pain and ↑ serum ALP and PSA
Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
Control of Reproductive Hormones
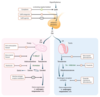
Reproductive Drugs:
- GnRH analog with agonist properties when used in pulsatile fashion
- antagonist properties when used in continuous fashion (downregulates GnRH receptor in pituitary → ↓ FSH and ↓ LH)
- used for uterine fibroids, endometriosis, precocious puberty, prostate cancer, and infertility
- causes hypogonadism, ↓ libido, erectile dysfunction, nausea, and vomiting
Leuprolide
Leuprolide can be used in lieu of GnRH.
Estrogens
- Ethinyl Estradiol
- DES
- Mestranol
Reproductive Drugs:
- bind estrogen receptors
- used for ypogonadism or ovarian failure, menstrual abnormalities (combined OCPs), and hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women
- causes ↑ risk of endometrial cancer (when given without progesterone), bleeding in postmenopausa women, clear cell adenocarcinoma of vagina in females exposed to DES in utero, ↑ risk of thrombi
- Contraindications:
- ER ⊕ breast cancer
- history of DVTs
- tobacco use in women > 35 years old
Estrogens
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators:
- antagonist at estrogen receptors in hypothalamus
- prevents normal feedback inhibition and ↑ release of LH and FSH from pituitary, which stimulates ovulation
- used to treat infertility due to anovulation (eg. PCOS)
- SERMs may cause hot flashes, ovarian enlargement, multiple simultaneous pregnancies, and visual disturbances
Clomiphene
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators:
- antagonist at breast
- agonist at bone and uterus
- ↑ risk of thromboembolic events and endometrial cancer
- used to treat and prevent recurrence of ER/PR ⊕ breast cancer
Tamoxifen
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators:
- antagonist at breast and uterus
- agonist at bone
- ↑ risk of thromboembolic events but no increased risk of endometrial cancer (vs. Tamoxifen)
- used primarily to treat osteoporosis
Raloxifene
Aromatase Inhibitors
- Anastrozole
- Letrozole
- Exemestane
Reproductive Drugs:
- inhibit peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogen
- used for ⊕ breast cancer in postmenopausal women
Aromatase Inhibitors
Reproductive Drugs:
- used for relief or prevention of menopausal symptoms (eg. hot flashes, vaginal atrophy) and osteoporosis (↑ estrogen, ↓ osteoclast activity)
- unopposed estrogen replacement therapy ↑ risk of endometrial cancer, progesterone/progestin is added
- possible increased cardiovascular risk
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Progestins
- Levonorgestrel
- Medroxyprogesterone
- Etonogestrel
- Norethindrone
- Megestrol
Reproductive Drugs:
- bind progesterone receptors
- ↓ growth and ↑ vascularization of endometrium, thicken cervical mucus
- used in contraception (forms include pill, intrauterine device, implant, depot injection), endometrial cancer, abnormal uterine bleeding
Progestins
Progestin Challenge
- presence of withdrawal bleeding excludes anatomic defects (eg. Asherman syndrome) and chronic anovulation without estrogen
Antiprogestins
- Mifepristone
- Ulipristal
Reproductive Drugs:
- competitive inhibitors of progestins at progesterone receptors
- used for termination of pregnancy (Mifepristone with Misoprostol) and emergency contraception (ulipristal)
Antiprogestins
Reproductive Drugs:
- forms include pill, patch, and vaginal ring
- estrogen and progestins inhibit LH/FSH and thus prevent estrogen surge
- no estrogen surge → no LH surge → no ovulation
- progestins cause thickening of cervical mucus, thereby limiting access of sperm to uterus
- progestins also inhibit endometrial proliferation → endometrium is less suitable to the implantation of an embryo
- Contraindications:
- smokers > 35 years old (↑ risk of cardiovascular events)
- patients with ↑ risk of cardiovascular disease (including history of venous thromboembolism, coronary artery disease, stroke)
- migraine (especially with aura)
- breast cancer
- liver disease
Combined Contraception
- Progestins + Ethinyl Estradiol
Reproductive Drugs:
- produces local inflammatory reaction toxic to sperm and ova, preventing fertilization and implantation
- hormone free
- used for long-acting reversible contraception
- most effective emergency contraception
- causes heavier or longer menses, and dysmenorrhea
- risk of PID with insertion (contraindicated in active pelvic infection)
Copper Intrauterine Device
Reproductive Drugs:
- medications that relax the uterus
- include Terbutaline (β2-agonist action), Nifedipine (Ca2+ channel blocker), and Indomethacin (NSAID)
- used to ↓ contraction frequency in preterm labor and allow time for administration of steroids (to promote fetal lung maturity) or transfer to appropriate medical center with obstetrical care
Tocolytics
Reproductive Drugs:
- synthetic androgen that acts as partial agonist at androgen receptors
- used for endometriosis and hereditary angioedema
- causes weight gain, edema, acne, hirsutism, masculinization, ↓ HDL levels, hepatotoxicity, and pseudotumor cerebri
Danazol
Reproductive Drugs:
- agonists at androgen receptors
- used to treat hypogonadism and promote development of 2° sex characteristics
- stimulate anabolism to promote recovery after burn or injury
- causes masculinization in females and ↓ intratesticular testosterone in males by inhibiting release of LH (via negative feedback) → gonadal atrophy
- premature closure of epiphyseal plates
- ↑ LDL, ↓ HDL
- Testosterone
- Methyltestosterone
Antiandrogens:
- 5α-reductase inhibitor (↓ conversion of testosterone to DHT)
- used for BPH and male-pattern baldness
- causes gynecomastia and sexual dysfunction
Finasteride

Antiandrogens:
- nonsteroidal competitive inhibitor at androgen receptors
- used for prostate carcinoma
Flutamide
Antiandrogens:
- inhibits steroid synthesis (inhibits 17,20 desmolase/17α-hydroxylase)
- used in PCOS to reduce androgenic symptoms
- can cause gynecomastia and amenorrhea
Ketoconazole
Antiandrogens:
- inhibits steroid binding (inhibits 17,20 desmolase/17α-hydroxylase)
- used in PCOS to reduce androgenic symptoms
- can cause gynecomastia and amenorrhea
Spironolactone
Reproductive Drugs:
- α1-antagonist used to treat BPH by inhibiting smooth muscle contraction
- selective for α1A/D receptors (found on prostate) vs. vascular α1B receptors
Tamsulosin
Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors
- Sildenafil
- Vardenafil
- Tadalafil
Reproductive Drugs:
- inhibit PDE-5 → ↑ cGMP ↑ prolonged smooth muscle relaxation in response to NO → ↑ blood flow in corpus cavernosum of penis, ↓ pulmonary vascular resistance
- used for erectile dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, and BPH (Tadalafil only)
- causes headache, flushing, dyspepsia, and cyanopia (blue-tinted vision)
- risk of life-threatening hypotension in patients taking nitrates
Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors
Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil fill the penis.
“Hot and sweaty,” but then Headache, Heartburn, and Hypotension.
Reproductive Drugs:
- direct arteriolar vasodilator
- used for androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) and severe refractory hypertension
Minoxidil


