Antimicrobials - First Aid Flashcards
Antimicrobial Therapy

Antimicrobials:
IV Penicillin
Penicillin G
Antimicrobials:
IM Penicillin
Penicillin G
Antimicrobials:
Oral Penicillin
Penicillin V
Antimicrobials:
prototype β-lactam antibiotics
- Penicillin G (IV and IM form)
- Penicillin V (oral form)
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- D-Ala-D-Ala structural analog
- bind _____-binding proteins (transpeptidases)
- block transpeptidase cross-linking of peptidoglycan in cell wall
- activate autolytic enzymes
- Penicillin G
- Penicillin V
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- mostly used for gram ⊕ organisms (S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, Actinomyces)
- also used for gram ⊝ cocci (N. meningitidis) and spirochetes (T. pallidum)
- bactericidal for gram ⊕ cocci, gram ⊕ rods, gram ⊝ cocci, and spirochetes
- β-lactamase sensitive
- Penicillin G
- Penicillin V
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hypersensitivity reactions
- direct Coombs ⊕ hemolytic anemia
- drug-induced interstitial nephritis
- Penicillin G
- Penicillin V
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- β-lactamase cleaves the β-lactam ring
- mutations in _____-binding proteins
- Penicillin G
- Penicillin V
Penicillinase-Sensitive Penicillins
- Amoxicillin
- Ampicillin
- Aminopenicillins
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- same as penicillin
- wider spectrum
- combine with clavulanic acid to protect against destruction by β-lactamas
Penicillinase-Sensitive Penicillins
- Amoxicillin
- Ampicillin
- Aminopenicillins
AMinoPenicillins are AMPed-up penicillin.
AmOxicillin has greater Oral bioavailability than ampicillin.
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- extended-spectrum penicillin
- H. influenzae
- H. pylori
- E. coli
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Proteus mirabilis
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Enterococci
Penicillinase-Sensitive Penicillins
- Amoxicillin
- Ampicillin
- Aminopenicillins
Ampicillin/Amoxicillin HHELPSS kill Enterococci.
- H. influenzae
- H. pylori
- E. coli
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Proteus mirabilis
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Enterococci
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hypersensitivity reactions
- rash
- pseudomembranous colitis
Penicillinase-Sensitive Penicillins
- Amoxicillin
- Ampicillin
- Aminopenicillins
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- Penicillinase (a type of β-lactamase) cleaves β-lactam ring
Penicillinase-Sensitive Penicillins
- Amoxicillin
- Ampicillin
- Aminopenicillins
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins
- Dicloxacillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- same as penicillin
- narrow spectrum
- bulky R group blocks access of β-lactamase to β-lactam ring
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins
- Dicloxacillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- S. aureus (except MRSA)
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins
- Dicloxacillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
“Use naf (Nafcillin) for staph.”
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hypersensitivity reactions
- interstitial nephritis
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins
- Dicloxacillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- MRSA has altered penicillin-binding protein target site
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins
- Dicloxacillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
Antipseudomonal Penicillins
- Piperacillin
- Ticarcillin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- same as penicillin
- extended spectrum
- penicillinase sensitive
- use with β-lactamase inhibitors
Antipseudomonal Penicillins
- Piperacillin
- Ticarcillin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Pseudomonas spp.
- Gram ⊝ Rods
Antipseudomonal Penicillins
- Piperacillin
- Ticarcillin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hypersensitivity reactions
Antipseudomonal Penicillins
- Piperacillin
- Ticarcillin
_____ are often added to penicillin antibiotics to protect the antibiotic from destruction by β-lactamase (penicillinase).
β-Lactamase Inhibitors
β-Lactamase Inhibitors
CAST
- Clavulanic Acid
- Avibactam
- Sulbactam
- Tazobactam
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- β-lactam drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis but are less susceptible to penicillinases
- bactericidal
Cephalosporins
Organisms typically not covered by 1st–4th generation cephalosporins are _____.
LAME:
- Listeria
- Atypicals (Chlamydia, Mycoplasma)
- MRSA
- Enterococci
1st Generation Cephalosporins
- Cefazolin
- Cephalexin
2nd Generation Cephalosporins
- Cefaclor
- Cefoxitin
- Cefuroxime
- Cefotetan
2nd graders wear fake fox fur to tea parties.
3rd Generation Cephalosporins
- Ceftazidime
- Cefpodoxime
- Cefotaxime
- Ceftriaxone
Taz’s tornado blows taxis and trees (3) away.
4th Generation Cephalosporins
Cefepime
5th Generation Cephalosporins
Ceftaroline
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊕ Cocci
- Proteus mirabilis
- E. coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- used prior to surgery to prevent S. aureus wound infections
1st Generation Cephalosporins
- Cefazolin—prior to surgery, S. aureus
- Cephalexin
PEcK:
- Proteus mirabilis
- E. coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊕ Cocci
- H. influenzae
- Enterobacter aerogenes
- Neisseria spp.
- Serratia marcescens
- Proteus mirabilis
- E. coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
2nd Generation Cephalosporins
- Cefaclor
- Cefoxitin
- Cefuroxime
- Cefotetan
HENS PEcK:
- H. influenzae
- Enterobacter aerogenes
- Neisseria spp.
- Serratia marcescens
- Proteus mirabilis
- E. coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- serious gram ⊝ infections resistant to other β-lactams
- can cross blood-brain barrier
3rd Generation Cephalosporins
- Ceftazidime—Pseudomonas
- Cefpodoxime
- Cefotaxime
- Ceftriaxone—meningitis, gonorrhea, disseminated Lyme disease
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊝
- ↑ activity against Pseudomonas and gram ⊕ organisms
4th Generation Cephalosporins
- Cefepime
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- broad gram ⊕ and gram ⊝ organism coverage
- Listeria
- MRSA
- Enterococcus faecalis
- does not cover Pseudomonas
5th Generation Cephalosporins
- Ceftaroline
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hypersensitivity reactions
- autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- disulfiram-like reaction
- vitamin K deficiency
- low rate of cross-reactivity even in penicillin-allergic patients
- ↑ nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides
Cephalosporins
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- inactivated by _____ases (a type of β-lactamase)
- structural change in penicillin-binding proteins (transpeptidases)
Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
DIME:
- Doripenem
- Imipenem
- Meropenem
- Ertapenem
DIME antibiotics are given when there is a 10/10 (life-threatening) infection.
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- broad-spectrum
- β-lactamase–resistant
- always administered with Cilastatin (inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase I) to ↓ inactivation of drug in renal tubules
Carbapenems
- Imipenem
With imipenem, “the kill is lastin’ with Cilastatin.”
Newer Carbapenems
- Ertapenem (limited Pseudomonas coverage)
- Doripenem
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊕ Cocci
- Gram ⊝ Rods
- Anaerobes
- wide spectrum and significant side effects limit use to life-threatening infections or after other drugs have failed
Carbapenems
- Doripenem
- Imipenem
- Meropenem—↓ risk of seizures, stable to dehydropeptidase I
- Ertapenem
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- GI distress
- rash
- CNS toxicity (seizures) at high plasma levels
Carbapenems
- Doripenem
- Imipenem
- Meropenem
- Ertapenem
Monobactams
Aztreonam
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- less susceptible to β-lactamases
- prevents peptidoglycan cross-linking by binding to penicillin-binding protein 3
- synergistic with aminoglycosides
- no cross-allergenicity with penicillins
Monobactams
- Aztreonam
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊝ Rods
- no activity against gram ⊕ rods or anaerobes
- for penicillin-allergic patients and those with renal insufficiency who cannot tolerate aminoglycosides
Monobactams
- Aztreonam
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- usually nontoxic
- occasional GI upset
Monobactams
- Aztreonam
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibits cell wall peptidoglycan formation by binding D-Ala-D-Ala portion of cell wall precursors
- bactericidal against most bacteria (bacteriostatic against C. difficile)
- not susceptible to β-lactamases
Vancomycin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊕
- serious, multidrug-resistant organisms, including MRSA, S. epidermidis, sensitive Enterococcus species, and Clostridium difficile (oral dose for pseudomembranous colitis)
Vancomycin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- well tolerated in general
- nephrotoxicity
- ototoxicity
- thrombophlebitis
- Red Man Syndrome
- diffuse flushing
- largely preventable by pretreatment with antihistamines and slow infusion rate
- DRESS Syndrome
- drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms
Vancomycin
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- occurs in bacteria (eg, Enterococcus) via amino acid modification of D-Ala-D-Ala to D-Ala-D-Lac
Vancomycin
If you Lack a D-Ala (dollar), you can’t ride the van.
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors

_____ specifically target smaller bacterial ribosome (70S, made of 30S and 50S subunits), leaving human ribosome (80S) unaffected.
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Protein synthesis inhibitors are all bacteriostatic, except _____.
- Aminoglycosides (bactericidal)
- Linezolid (variable)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
30S inhibitors
- Aminoglycosides
- Tetracyclines
50S inhibitors
- Chloramphenicol
- Clindamycin
- Erythromycin (Macrolides)
- Linezolid
“Buy AT 30, CCEL (sell) at 50.”
Aminoglycosides
GNATS:
- Gentamicin
- Neomycin
- Amikacin
- Tobramycin
- Streptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- bactericidal
- irreversible inhibition of initiation complex through binding of the 30S subunit
- can cause misreading of mRNA
- also block translocation
- require O2 for uptake
- ineffective against anaerobes
Aminoglycosides
- Gentamicin
- Neomycin
- Amikacin
- Tobramycin
- Streptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- severe gram ⊝ rod infections
- synergistic with β-lactam antibiotics
- bowel surgery
Aminoglycosides
- Gentamicin
- Neomycin—bowel surgery
- Amikacin
- Tobramycin
- Streptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- nephrotoxicity
- neuromuscular blockade
- ototoxicity (especially when used with loop diuretics)
- teratogen
Aminoglycosides
- Gentamicin
- Neomycin
- Amikacin
- Tobramycin
- Streptomycin
“Mean” (aminoglycoside) GNATS caNNOT kill anaerobes.
- Nephrotoxicity
- Neuromuscular blockade
- Ototoxicity
- Teratogen
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- bacterial transferase enzymes inactivate the drug by acetylation, phosphorylation, or adenylation
Aminoglycosides
- Gentamicin
- Neomycin
- Amikacin
- Tobramycin
- Streptomycin
Tetracyclines
- Tetracycline
- Doxycycline
- Minocycline
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- bacteriostatic
- bind to 30S and prevent attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA
- limited CNS penetration
- not taken with milk (Ca2+), antacids (Ca2+ or Mg2+), or iron-containing preparations because divalent cations inhibit drugs’ absorption in the gut
Tetracyclines
- Tetracycline
- Doxycycline—fecally eliminated, can be used in patients with renal failure
- Minocycline
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Borrelia burgdorferi
- M. pneumoniae
- drugs’ ability to accumulate intracellularly makes them very effective against Rickettsia and Chlamydia
- also used to treat acne
Tetracyclines
- Tetracycline
- Doxycycline—MRSA
- Minocycline
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- GI distress
- discoloration of teeth and inhibition of bone growth in children
- photosensitivity
- contraindicated in pregnancy
Tetracyclines
- Tetracycline
- Doxycycline
- Minocycline
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- ↓ uptake or ↑ efflux out of bacterial cells by plasmid-encoded transport pumps
Tetracyclines
- Tetracycline
- Doxycycline
- Minocycline
Glycylcyclines
Tigecycline
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- tetracycline derivative
- binds to 30S, inhibiting protein synthesis
- generally bacteriostatic
Glycylcyclines
- Tigecycline
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- broad-spectrum anaerobic, gram ⊝, and gram ⊕ coverage
- multidrug-resistant organisms (MRSA, VRE) or infections requiring deep tissue penetration
Glycylcyclines
- Tigecycline
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- GI symptoms: nausea, vomiting
Glycylcyclines
- Tigecycline
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- blocks peptidyltransferase at 50S ribosomal subunit
- bacteriostatic
Chloramphenicol
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- meningitis (Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae) and rickettsial diseases (eg. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever [Rickettsia rickettsii]).
- limited use due to toxicity but often still used in developing countries because of low cost
Chloramphenicol
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- anemia (dose dependent)
- aplastic anemia (dose independent)
- gray baby syndrome (in premature infants because they lack liver UDP-glucuronosyltransferase)
Chloramphenicol
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- plasmid-encoded acetyltransferase inactivates the drug
Chloramphenicol
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- blocks peptide transfer (translocation) at 50S ribosomal subunit
- bacteriostatic
Clindamycin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- anaerobic infections (eg. Bacteroides spp.,Clostridium perfringens) in aspiration pneumonia, lung abscesses, and oral
- infections
- also effective against invasive group A streptococcal infection
- treats anaerobic infections above the diaphragm vs. metronidazole
Clindamycin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- pseudomembranous colitis (C. difficile overgrowth)
- fever
- diarrhea
Clindamycin
Oxazolidinones
Linezolid
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 50S subunit and preventing formation of the initiation complex
Oxazolidinones
- Linezolid
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊕
- MRSA
- VRE
Oxazolidinones
- Linezolid
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- bone marrow suppression (especially thrombocytopenia)
- peripheral neuropathy
- serotonin syndrome
Oxazolidinones
- Linezolid
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- point mutation of ribosomal RNA
Oxazolidinones
- Linezolid
Macrolides
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit protein synthesis by blocking translocation (“macroslides”)
- bind to the 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit
- bacteriostatic
Macrolides
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- atypical pneumonias (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Legionella)
- STIs (Chlamydia)
- Gram ⊕ Cocci (streptococcal infections in patients allergic to penicillin)
- B. pertussis
Macrolides
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- gastrointestinal motility issues
- arrhythmia caused by prolonged QT interval
- acute cholestatic hepatitis
- rash
- eosinophilia
- increases serum concentration of theophylline and oral anticoagulants
Macrolides
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin—inhibit cytochrome P-450
- Erythromycin—inhibit cytochrome P-450
MACRO:
- gastrointestinal Motility
- Arrhythmia
- acute Cholestatic hepatitis
- Rash
- eOsinophilia
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- methylation of 23S rRNA-binding site prevents binding of drug
Macrolides
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
Polymyxins
- Colistin (Polymyxin E)
- Polymyxin B
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- cation polypeptides that bind to phospholipids on cell membrane of gram ⊝ bacteria
- disrupt cell membrane integrity → leakage of cellular components → cell death
Polymyxins
- Colistin (Polymyxin E)
- Polymyxin B
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- salvage therapy for multidrug-resistant gram ⊝ bacteria (eg. P. aeruginosa, E. coli, K. pneumoniae)
Polymyxins
- Colistin (Polymyxin E)
- Polymyxin B—component of a triple antibiotic ointment used for superficial skin infections
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- nephrotoxicity
- neurotoxicity (eg. slurred speech, weakness, paresthesias)
- respiratory failure
Polymyxins
- Colistin (Polymyxin E)
- Polymyxin B
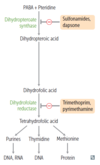
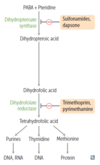
Sulfonamides
- Sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
- Sulfisoxazole
- Sulfadiazine
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit dihydropteroate synthase, thus inhibiting folate synthesis
- bacteriostatic (bactericidal when combined with trimethoprim)
Sulfonamides
- Sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
- Sulfisoxazole
- Sulfadiazine
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊕
- Gram ⊝
- Nocardia
Sulfonamides
- Sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
- Sulfisoxazole
- Sulfadiazine
*TMP-SMX for simple UTI
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hypersensitivity reactions
- hemolysis if G6PD deficient
- nephrotoxicity (tubulointerstitial nephritis)
- photosensitivity
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- kernicterus in infants
- displace other drugs from albumin (eg. warfarin)
Sulfonamides
- Sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
- Sulfisoxazole
- Sulfadiazine
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- altered enzyme (bacterial dihydropteroate synthase), ↓ uptake, or ↑ PABA synthesis
Sulfonamides
- Sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
- Sulfisoxazole
- Sulfadiazine
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- similar to sulfonamides
- structurally distinct agent
Dapsone
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Leprosy (lepromatous and tuberculoid)
- Pneumocystis jirovecii prophylaxis
Dapsone
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hemolysis if G6PD deficient
- methemoglobinemia
Dapsone
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase
- bacteriostatic
Trimethoprim

Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- used in combination with sulfonamides
- causing sequential block of folate synthesis
- combination used for UTIs
- Shigella
- Salmonella
- Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia treatment and prophylaxis
- Toxoplasmosis prophylaxis
Trimethoprim
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- megaloblastic anemia
- leukopenia
- granulocytopenia
- may be avoided with coadministration of folinic acid
Trimethoprim
TMP Treats Marrow Poorly.
Fluoroquinolones
- Ciprofloxacin
- Enoxacin
- Norfloxacin
- Ofloxacin
- Gemifloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
Respiratory Fluoroquinolones
- Gemifloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit prokaryotic enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV
- bactericidal
- must not be taken with antacids
Fluoroquinolones
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Gram ⊝ Rods of urinary and GI tracts (including Pseudomonas)
- some gram ⊕ organisms
- otitis externa
Fluoroquinolones
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- GI upset
- superinfections
- skin rashes
- headache
- dizziness
- less commonly, can cause leg cramps and myalgias
- contraindicated in pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children < 18 years old due to possible damage to cartilage
- some may prolong QT interval
- tendonitis or tendon rupture in people > 60 years old and in patients taking prednisone
Fluoroquinolones
- Ciprofloxacin —inhibits cytochrome P-450
Fluoroquinolones hurt attachments to your bones.
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- chromosome-encoded mutation in DNA gyrase, plasmid-mediated resistance, efflux pumps
Fluoroquinolones
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- lipopeptide that disrupts cell membranes of gram ⊕ cocci by creating transmembrane channels
Daptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- S. aureus skin infections (especially MRSA)
- bacteremia
- endocarditis
- VRE
- not used for pneumonia (avidly binds to and is inactivated by surfactant)
Daptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- myopathy
- rhabdomyolysis
Daptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- forms toxic free radical metabolites in the bacterial cell that damage DNA
- bactericidal
- antiprotozoal
Metronidazole
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- treats Giardia, Entamoeba, Trichomonas, Gardnerella vaginalis, Anaerobes (Bacteroides, C. difficile)
- can be used in place of amoxicillin in H. pylori “triple therapy” in case of penicillin allergy
- treats anaerobic infection below the diaphragm vs. clindamycin (anaerobic infections above diaphragm)
Metronidazole
GET GAP on the Metro with metronidazole!
- Giardia
- Entamoeba
- Trichomonas
- Gardnerella vaginalis
- Anaerobes (Bacteroides, C. difficile)
- H. Pylori
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- Disulfiram-like reaction (severe flushing, tachycardia, hypotension) with alcohol
- headache,
- metallic taste
Metronidazole
Antimycobacterial Drugs:
M. tuberculosis Prophylaxis
Isoniazid
Antimycobacterial Drugs:
M. tuberculosis Treatment
RIPE for Treatment:
- Rifampin
- Isoniazid
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
Antimycobacterial Drugs:
M. avium–intracellulare Prophylaxis
- Azithromycin
- Rifabutin
Antimycobacterial Drugs:
M. avium–intracellulare Treatment
- Azithromycin or Clarithromycin + Ethambutol
- can add Rifabutin or Ciprofloxacin
*More drug resistant than M. tuberculosis
Antimycobacterial Drugs:
M. leprae Prophylaxis
N/A
Antimycobacterial Drugs:
M. leprae Treatment
- Tuberculoid
- long-term treatment
- Dapsone
- Rifampin
- Lepromatous
- add Clofazimine
Mycobacterial Cell

Rifamycins
- Rifampin
- Rifabutin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
inhibit DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Rifamycins
- Rifampin
- Rifabutin
Rifampin’s 4 R’s:
- RNA polymerase inhibitor
- Ramps up microsomal cytochrome P-450
- Red/orange body fluids
- Rapid resistance if used alone
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- delay resistance to Dapsone when used for leprosy
- used for meningococcal prophylaxis and chemoprophylaxis in contacts of children with H. influenzae type b
Rifamycins
- Rifampin
- Rifabutin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- minor hepatotoxicity and drug interactions (↑ cytochrome P-450)
- orange body fluids (nonhazardous side effect)
Rifamycins
- Rifampin
- Rifabutin—favored in patients with HIV infection due to less cytochrome P-450 stimulation
Rifampin’s 4 R’s:
- RNA polymerase inhibitor
- Ramps up microsomal cytochrome P-450
- Red/orange body fluids
- Rapid resistance if used alone
Rifampin ramps up cytochrome P-450, but rifabutin does not.
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- mutations reduce drug binding to RNA polymerase
- monotherapy rapidly leads to resistance
Rifamycins
- Rifampin
- Rifabutin
Rifampin’s 4 R’s:
- RNA polymerase inhibitor
- Ramps up microsomal cytochrome P-450
- Red/orange body fluids
- Rapid resistance if used alone
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- ↓ synthesis of mycolic acids
- bacterial catalase-peroxidase (encoded by KatG) needed to convert INH to active metabolite
Isoniazid
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- the only agent used as solo prophylaxis against TB
- also used as monotherapy for latent TB
- different half-lives in fast vs. slow acetylators
Isoniazid
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hepatotoxicity
- P-450 inhibition
- drug-induced SLE
- anion gap metabolic acidosis
- vitamin B6 deficiency (peripheral neuropathy, sideroblastic anemia)
- administer with Pyridoxine (B6)
Isoniazid
INH Injures Neurons and Hepatocytes.
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- mutations leading to underexpression of KatG
Isoniazid
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- uncertain
- a prodrug that is converted to the active compound Pyrazinoic acid
- works best at acidic pH (eg. in host phagolysosomes)
Pyrazinamide
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- hyperuricemia
- hepatotoxicity
Pyrazinamide
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- ↓ carbohydrate polymerization of mycobacterium cell wall by blocking arabinosyltransferase
Ethambutol
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- optic neuropathy (red-green color blindness)
Ethambutol
Eyethambutol
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- interferes with 30S component of ribosome
Streptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- tinnitus
- vertigo
- ataxia
- nephrotoxicity
Streptomycin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
- Streptomycin (2nd line)
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
high risk for endocarditis and undergoing surgical or dental procedures
Amoxicillin
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
exposure to gonorrhea
Ceftriaxone
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
history of recurrent UTIs
TMP-SMX
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
exposure to meningococcal infection
- Ceftriaxone
- Ciprofloxacin
- Rifampin
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
pregnant woman carrying group B strep
- Penicillin G
- Ampicillin
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
prevention of gonococcal conjunctivitis in newborn
Erythromycin eye ointment
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
prevention of postsurgical infection due to S. aureus
Cefazolin
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
prophylaxis of strep pharyngitis in child with prior rheumatic fever
- Benzathine Penicillin G
- Oral Penicillin V
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis:
exposure to syphilis
Benzathine Penicillin G
Prophylaxis in HIV patients:
- CD4 < 200 cells/mm3
- Pneumocystis pneumonia
TMP-SMX
Prophylaxis in HIV patients:
- CD4 < 100 cells/mm3
- Pneumocystis pneumonia
- Toxoplasmosis
TMP-SMX
Prophylaxis in HIV patients:
- CD4 < 50 cells/mm3
- Mycobacterium avium Complex
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
Treatment of Highly Resistant Bacteria:
MRSA
- Vancomycin
- Daptomycin
- Linezolid
- Tigecycline
- Ceftaroline
- Doxycycline
Treatment of Highly Resistant Bacteria:
VRE
- Linezolid
- Streptogramins (Quinupristin, Dalfopristin)
Treatment of Highly Resistant Bacteria:
Multidrug-Resistant P. aeruginosa
- Polymyxin B
- Polymyxin E (Colistin)
Treatment of Highly Resistant Bacteria:
Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- Polymyxin B
- Polymyxin E (Colistin)
Antifungal Therapy

Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- binds ergosterol (unique to fungi)
- forms membrane pores that allow leakage of electrolytes
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin “tears” holes in the fungal membrane by forming pores.
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- serious, systemic mycoses
- Cryptococcus (amphotericin B with/without flucytosine for cryptococcal meningitis)
- Blastomyces
- Coccidioides
- Histoplasma
- Candida
- Mucor
- intrathecally for fungal meningitis
- supplement K+ and Mg2+ because of altered renal tubule permeability
Amphotericin B
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- fever/chills (“shake and bake”)
- hypotension
- nephrotoxicity
- arrhythmias
- anemia
- IV phlebitis
- hydration ↓ nephrotoxicity
- liposomal form ↓ toxicity
Amphotericin B
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- same as Amphotericin B
- topical use only as too toxic for systemic use
Nystatin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- “swish and swallow” for oral candidiasis (thrush)
- topical for diaper rash or vaginal candidiasis
Nystatin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibits DNA and RNA biosynthesis by conversion to 5-fluorouracil by cytosine deaminase
Flucytosine
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- systemic fungal infections (especially meningitis caused by Cryptococcus) in combination with amphotericin B
Flucytosine
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- bone marrow suppression
Flucytosine
Azoles
- Clotrimazole
- Fluconazole
- Isavuconazole
- Itraconazole
- Ketoconazole
- Miconazole
- Voriconazole
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit fungal sterol (ergosterol) synthesis by inhibiting the cytochrome P-450 enzyme that converts lanosterol to ergosterol
Azoles
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- local and less serious systemic mycoses
Azoles
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- for chronic suppression of cryptococcal meningitis in AIDS patients and candidal infections of all types
Fluconazole
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Blastomyces
- Coccidioides
- Histoplasma
Itraconazole
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- topical fungal infections
- Clotrimazole
- Miconazole
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Aspergillus
- Candida
Voriconazole
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- Aspergillus
- Mucor
Isavuconazole
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- testosterone synthesis inhibition (gynecomastia)
- liver dysfunction (inhibits cytochrome P-450)
Azoles
Ketoconazole—gynecomastia
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibits the fungal enzyme squalene epoxidase
Terbinafine
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- dermatophytoses (especially onychomycosis—fungal infection of finger or toe nails)
Terbinafine
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- GI upset
- headaches
- hepatotoxicity
- taste disturbance
Terbinafine
Echinocandins
- Anidulafungin
- Caspofungin
- Micafungin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit cell wall synthesis by inhibiting synthesis of β-glucan
Echinocandins
- Anidulafungin
- Caspofungin
- Micafungin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- invasive aspergillosis
- Candida
Echinocandins
- Anidulafungin
- Caspofungin
- Micafungin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- GI upset
- flushing (by histamine release)
Echinocandins
- Anidulafungin
- Caspofungin
- Micafungin
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- interferes with microtubule function
- disrupts mitosis
- deposits in keratin-containing tissues (eg. nails)
Griseofulvin
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- oral treatment of superficial infections
- inhibits growth of dermatophytes (tinea, ringworm)
Griseofulvin
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- teratogenic
- carcinogenic
- confusion
- headaches
- disulfiram-like reaction
- ↑ cytochrome P-450 and warfarin metabolism
Griseofulvin
Antiprotozoal Therapy:
Toxoplasmosis
Pyrimethamine
Antiprotozoal Therapy:
Trypanosoma brucei
- Suramin
- Melarsoprol
Antiprotozoal Therapy:
Trypanosoma cruzi
Nifurtimox
Antiprotozoal Therapy:
Leishmaniasis
Sodium Stibogluconate
Anti-Mite/Louse Therapy
- Permethrin
- inhibits Na+ channel deactivation → neuronal membrane depolarization)
- Malathion
- acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
- Lindane
- blocks GABA channels → neurotoxicity
*used to treat scabies (Sarcoptes scabiei) and lice (Pediculus and Pthirus)
Treat PML (Pesty Mites and Lice) with PML (Permethrin, Malathion, Lindane), because they NAG you (Na, AChE, GABA blockade).
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- blocks detoxification of heme into hemozoin
- heme accumulates and is toxic to plasmodia
Chloroquine
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- treatment of plasmodial species other than P. falciparum (frequency of resistance is too high)
- resistance due to membrane pump that ↓ intracellular concentration of drug
Chloroquine
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- retinopathy
- pruritus (especially in dark-skinned individuals)
Chloroquine
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- P. falciparum
- Artemether/Lumefantrine
- Atovaquone/Proguanil
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- life-threatening malaria
- Quinidine—US
- Quinine
- Artesunate
Antihelminthic Therapy
Helminths get PIMP’D.
- Pyrantel pamoate
- Ivermectin
- Mebendazole (microtubule inhibitor)
- Praziquantel
- Diethylcarbamazine.
Antiviral Therapy

Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- inhibit influenza neuraminidase → ↓ release of progeny virus
- Oseltamivir
- Zanamivir
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- treatment and prevention of both influenza A and B
- beginning therapy within 48 hours of symptom onset may shorten duration of illness
- Oseltamivir
- Zanamivir
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- guanosine analogs
- monophosphorylated by HSV/VZV thymidine kinase and not phosphorylated in uninfected cells → few adverse effects
- triphosphate formed by cellular enzymes
- preferentially inhibit viral DNA polymerase by chain termination
- Acyclovir
- Famciclovir
- Valacyclovir
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- HSV and VZV
- weak activity against EBV
- no activity against CMV
- used for HSV-induced mucocutaneous and genital lesions as well as for encephalitis
- prophylaxis in immunocompromised patients
- no effect on latent forms of HSV and VZV
- Acyclovir
- Famciclovir—herpes zoster
- Valacyclovir—prodrug of acyclovir, better oral bioavailability
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- obstructive crystalline nephropathy and acute renal failure if not adequately hydrated
- Acyclovir
- Famciclovir
- Valacyclovir
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- mutated viral thymidine kinase
- Acyclovir
- Famciclovir
- Valacyclovir
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- 5′-monophosphate formed by a CMV viral kinase
- Guanosine analog
- triphosphate formed by cellular kinases
- preferentially inhibits viral DNA polymerase
Ganciclovir
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- CMV
- immunocompromised patients
Ganciclovir
*Valganciclovir—prodrug of ganciclovir, better oral bioavailability
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- bone marrow suppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia)
- renal toxicity
- more toxic to host enzymes than acyclovir
Ganciclovir
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- mutated viral kinase
Ganciclovir
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- Pyrofosphate analog
- viral DNA/RNA polymerase inhibitor and HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitor
- binds to pyrophosphate-binding site of enzyme
- does not require any kinase activation
Foscarnet
Foscarnet = pyrofosphate analog
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- CMV retinitis in immunocompromised patients when Ganciclovir fails
- Acyclovir-resistant HSV
Foscarnet
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- nephrotoxicity
- electrolyte abnormalities (hypo- or hypercalcemia, hypo- or hyperphosphatemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia) can lead to seizures
Foscarnet
Antimicrobials:
Resistance
- mutated DNA polymerase
Foscarnet
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- preferentially inhibits viral DNA polymerase
- does not require phosphorylation by viral kinase
Cidofovir
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- CMV retinitis in immunocompromised patients
- Acyclovir-resistant HSV
- long half-life
Cidofovir
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- nephrotoxicity (coadminister with probenecid and IV saline to ↓ toxicity)
Cidofovir
HIV Therapy
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART)
*often initiated at the time of HIV diagnosis
Strongest Indication for HAART
- low CD4+ cell counts (< 500 cells/mm3)
- high viral load
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) regimen consists of _____.
3 drugs to prevent resistance
- 2 NRTIs
- an integrase inhibitor
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
- Abacavir (ABC)
- Didanosine (ddI)
- Emtricitabine (FTC)
- Lamivudine (3TC)
- Stavudine (d4T)
- Tenofovir (TDF)
- Zidovudine (ZDV, formerly AZT)
HIV Therapy:
- competitively inhibit nucleotide binding to reverse transcriptase and terminate the DNA chain (lack a 3′ OH group)
- need to be phosphorylated to be active
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
Tenofovir is a nucleoTide; the others are nucleosides.
HIV Therapy:
can be used for general prophylaxis and during pregnancy to ↓ risk of fetal transmission
Zidovudine (ZDV, formerly AZT)
HIV Therapy:
- bone marrow suppression (can be reversed with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor [G-CSF] and erythropoietin)
- peripheral neuropathy
- lactic acidosis (nucleosides)
- anemia (ZDV)
- pancreatitis (Didanosine)
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
HIV Therapy:
contraindicated if patient has HLA-B*5701 mutation due to ↑ risk of hypersensitivit
Abacavir
Non-Nucleoside Reverse-Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
- Delavirdine
- Efavirenz
- Nevirapine
HIV Therapy:
- bind to reverse transcriptase at site different from NRTIs
- do not require phosphorylation to be active or compete with nucleotides
- rash and hepatotoxicity are common
Non-Nucleoside Reverse-Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
HIV Therapy:
vivid dreams and CNS symptoms are commo
Efavirenz
HIV Therapy:
NNRTIs contraindicated in pregnancy
- Delavirdine
- Efavirenz
Protease Inhibitors
- Atazanavir
- Darunavir
- Fosamprenavir
- Indinavir
- Lopinavir
- Ritonavir
- Saquinavir
Navir (never) tease a protease.
HIV Therapy:
- assembly of virions depends on HIV-1 protease (pol gene), which cleaves the polypeptide products of HIV mRNA into their functional parts
- prevent maturation of new viruses
- hyperglycemia, GI intolerance (nausea, diarrhea), lipodystrophy (Cushing-like syndrome)
Protease Inhibitors
HIV Therapy:
can “boost” other drug concentrations by inhibiting cytochrome P-450
Ritonavir
HIV Therapy:
- nephropathy
- hematuria
- thrombocytopenia
Indinavir
HIV Therapy:
- potent CYP/UGT inducer
- reduces protease inhibitor concentrations
Rifampin
*use rifabutin instead
Integrase Inhibitors
- Dolutegravir
- Elvitegravir
- Raltegravir
HIV Therapy:
- inhibits HIV genome integration into host cell chromosome by reversibly inhibiting HIV integrase
- ↑ creatine kinase
Integrase Inhibitors
Fusion Inhibitors
- Enfuvirtide
- Maraviroc
HIV Therapy:
- binds gp41, inhibiting viral entry
- skin reaction at injection sites
Enfuvirtide
Enfuvirtide inhibits fusion.
HIV Therapy:
- binds CCR-5 on surface of T cells/monocytes
- inhibits interaction with gp120
Maraviroc
Maraviroc inhibits docking.
Antimicrobials:
Mechanism of Action
- glycoproteins normally synthesized by virus-infected cells, exhibiting a wide range of antiviral and antitumoral properties
Interferons
Antimicrobials:
Clinical Use
- chronic HBV and HVC
- Kaposi sarcoma
- hairy cell leukemia
- condyloma acuminatum
- renal cell carcinoma
- malignant melanoma
- multiple sclerosis
- chronic granulomatous disease
Interferons
Antimicrobials:
Adverse Effects
- flu-like symptoms
- depression
- neutropenia
- myopathy
Interferons
Antimicrobials:
- Hepatitis C
- viral phosphoprotein (NS5A) inhibitor
- NS5A plays important role in replication
Ledipasvir
Antimicrobials:
- Hepatitis C
- inhibits synthesis of guanine nucleotides by competitively inhibiting inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase
- hemolytic anemia
- severe teratogen
Ribavirin
Antimicrobials:
- Hepatitis C
- HCV protease (NS3/4A)
- prevents viral replication
- photosensitivity reactions
- rash
Simeprevir
Antimicrobials:
- Hepatitis C
- inhibits HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B) acting as a chain terminator
- fatigue
- headache
- nausea
Sofosbuvir
_____ is the reduction of pathogenic organism counts to safe levels.
Disinfection
_____ the inactivation of all microbes including spores.
Sterilization
Disinfection and Sterilization:
- pressurized steam at > 120°C
- sporicidal
- may not reliably inactivate prions
Autoclave
Disinfection and Sterilization:
- denature proteins and disrupt cell membranes
- not sporicidal
- Alcohols
- Chlorhexidine
Disinfection and Sterilization:
- oxidizes and denatures proteins
- sporicidal
Chlorine
Disinfection and Sterilization:
- free radical oxidation
- sporicidal
Hydrogen Peroxide
Disinfection and Sterilization:
- halogenation of DNA, RNA, and proteins
- may be sporicidal
- Iodine
- Iodophors
Disinfection and Sterilization:
- impair permeability of cell membranes
- not sporicidal
Quaternary Amines
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy
Take Really Good Care to keep Children SAFe.
- Tetracyclines
- Ribavirin
- Griseofulvin
- Chloramphenicol
- Clarithromycin
- Sulfonamides
- Aminoglycosides
- Fluoroquinolones
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
- discolored teeth
- inhibition of bone growth
Tetracyclines
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
teratogenic
- Ribavirin
- Griseofulvin
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
Gray Baby Syndrome
Chloramphenicol
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
embryotoxic
Clarithromycin
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
kernicterus
Sulfonamides
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
ototoxicity
Aminoglycosides
Antimicrobials to Avoid in Pregnancy:
cartilage damage
Fluoroquinolones


