Painful joints - Tutorial Flashcards
(36 cards)


Component of cartilage that allows distribution of weight?
Prevents wear and tear?

What is osteoarthritis?
Ialtered ________ homeostasis

3 stages of osteoperosis?
Explain each stage
- Fibrillation of cartilage.
- Eburnation of bone (polishing and grinding of bone on bone articulation)
- Sclerosis (bone below area of cartilage becomes more dense).
- Subcondral cyst: small fractures under eburnated bone –> joint fluid is forced into subarticular space –> fluid icites a host response and a fibrous capsule is made around it

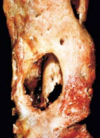
What is this joint showing?


What are these numbers shownig?


What are osteophytes?
What are the names of these in the DIP and PIP joints?



Treatment of osteoarthritis?

What disease is causing this to happen?

Rheumatoid arthritis
What causes rheumatoid arthritis?
Who is more likely to get it?
Which joints are involved?
What can be detected in the blood of these patients (diagnostic)?

What genetic involvement does rheumatoid arthritis have?
Is it purely genetic? Explain
Not purely genetic:
Smoking: promote citrullination of self protiens.
Infections: microbial antigens may promote disease and citrullination of proteins. EBV has been incriminated.

Which T cells are important for RA?
What cytokines to they produce and how does lead to pathogenesis of disease?
IFN-Y from Th1 activate macrophages.
TNF-a from macrophages stimulate synovial cells and chondrocytes to secrete proteases that destroy cartilage and ligaments, and stimulate osteoclasts to erode the bone.

What would you see with the histology of a pannus formation?


Local vs systemic affects of RA?

Explain the pathology going on here?
What is the condition?


Explain the pathology going on here?


Explain the pathology going on here?




Treatment of RA?

What is the main aetiological agent of osteomyelitis?
What is ostomyelitis?