Lecture12: (Part I) B cell activation and antibody production Flashcards
Ag activates mature naive B cells by binding to membrane ___ and __ on these cells
IgM and IgD


Heavy chain isotype switching and affinity maturation are increased in the ______ responses (multiple) to protein Ags
secondary responses
most mature naive B lymphocytes are follicular B cells which are also called
Recirculating B cells or B-2 cells
The _____ chemokine secreted by follicular DCs guides the movement of B cells to follicles
CXCL13
small soluble Ags (generally smaller than 70kD) are delivered to Follicular B cells through
afferent lymphatics and via conduits
Large Ags are delivered to follicular B cells by
subcapsular sinus Macrophages or by DCs in the medulla
In the spleen, Ags in immune complexes my bind to ____ complement receptors on marginal zone B cells
- CR2
- MZ B cells can transfer the immune-complex containing Ags to follicular B cells
Blood-borne pathogens may be captured by ______ in the blood and transported to the spleen, where they may be delivered to marginal zone B cells
Plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs)
Polysaccharide Ags can be captured by macrophages in the _______ of splenic lymphoid follicles and displayed or transferred to b cells in this area
marginal zone
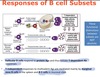
- ____ B cells respond to protein Ags and thus initiate T-dependeent Ab responses
- T-independent responses to multivalent Ags are mediated mainly by _____ B cells in the spleen and _____ in mucosal sites
- Follicular B cells respond to protein Ags and thus initiate T-dependent Ab responses
- T-independent responses to multivalent Ags are mediated mainly by marginal zone B cells in the spleen and B-1 cells in mucosal sites
B-1 cells, arise form the fetal liver by the ____ gestational week
eighth

A specialized type of helper T cell, called a _____, facilitates the formation of germinal centers (GCs) where activated B cells proliferate
- Follicular Helper T cells
Ab responses to ____ Ags require participation of CD4+ T helper lympocyte
- Protein Ags
- therefore, proteins are classified as T-dependent (TD) Ags
Ab responses to multivalent non-protein Ags with repeating epitopes, such as ____, some ____, and _____, do not require Ag-specific helper T lympocytes
- Polysaccharides, some lipids, and nucleic acids
- mutivalent Ags are called T-independent (TI) Ags
Follicular B cell survival depends on signals from the BCR as well as on inputs received from cytokine called _____
BAFF ( B cell-activating factor of the TNF family)
BAFF is mainly produced by
myeloid cells in lymphoid follicles and in the bone marrow


Extrafollicular B cell transcription factors
Blimp-1
Follicular/Germinal Center Transcription factors
Bcl-6

The generation of TFH cells requires sequential activation of T cells, first by ___ and then by ______. The TFH cells migrate into ____, where they
- The generation of TFH cells requires sequential activation of T cells, first by DCs and then by activated B cells. The TFH cells migrate into GCs, where they activate B cells
TFH secrete
- IL-21
- is required for GC development and generation of plasma cells
- IFN-gamma
- IL-4
TFH cells express
- ICOS (inducible costimulator)
- PD-1 (programmed death-1)
- IL-21
- IL-4
- IFN-gamma
- Bcl-6 (transcription factor)
Activated B cells migrate into the follicle and proliferate, forming dark zone of the germinal center. These B cells udnergo extensive isotype switching and somatic hypermutation of Ig ___ genes
Ig V genes
expression of ____ on B cells induces migration of cells toward the T cell zone
CCR7


