Lecture 12: (Part II) B cell activation and antibody production Flashcards
(54 cards)
_______ of a primary RNA transcript results in the formation of mRNA for the membrane or secreted form of the u heavy chain
Alternative processing
B cell differentiation results in an increasing fraction of the u protein produced as the _____ form
- secreted
- Not the polyadenylation sites
- one by the TP (Tail piece)
- one by the TM (transmembrane) and CY (cytoplasmic)
- Not the polyadenylation sites

which two Igs have a CH4
IgE and IgM
The CH2 of IgM and IgG has a binding site for
C1q
Isotype switching primarily ocurs in the the germinal centers and is driven by ____
- TFH cells
- (not that some may occur in extrafollicular B cells and this is driven by extrafollicular Th cells )
Abs specificity is unaltered in class switching. Why?
- Class switching involves chaing the constant regions of the heavy chains
- this leaves the light chains unaltered and they are what determines Ab specificity
B cells activated by TFH cell signals (CD40L, cytokines) undergo switching to different Ig isotypes. What cytokines lead to the switching of each antibody class?

IFN-gamma from ____ induces IgG switching and IL-4 from ____ induces IgE switching
- IFN-gamma from Th1
- IL-4 from Th2
CD40 with CD40L induces ____, which both isotype switching and affinity maturation are criticaly dependent on
activation induced deaminase
Immunodeficiencies related to the CD40-CD40L axis, the Ab response to protein Ag is dominated by ___ Abs
IgM (this is becaue there is limited isotype switching because inability to activate AID)
The molecular mecahnism of isotype switching is a process called switch recombination, in whihc the Ig heavy chain DNA in B cells is cut and recombined such that a previously formed VDJ exon that encodes the V domain is placed adjacent to a downstream C region, and the intervening DNA is deleted. These DNA recombination events involve nucleotide sequencs called switch regions, all of the heavy chains genes except ___ have this 5’ ends of each locus.
Delta (which codes for IgD)
Activation-induced cytosine deamninase (AID) function
- deaminates cytosines in single-standed DNA templates, converting C residues to uracil (U) residues
- (note then uracil N-Glycosylase (UNG) removes U residues to generate abasic sites where the APE1 endonuclease creates nicks that lead to a double-stranded break)
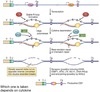
Affinity maturation is observed only in Ab responses to
- TD Ags
- (TFH cells and CD40:CD40L interactions are required for somatic hypermutation of Ig V genes to be initiated)
Are there fair more mutations in the IgG than IgM Abs
yes
Mutations in V genes increase with
time after immunization and with repeated immunization
B cells that have undergone somatic mutation migrate into the
FDC-rich light zone of the germinal center
B cells with high-affinity receptors for the Ags are best able to bind the Ag when it is present at low concentrations by follicular DCs, and these B cells survive preferentially because of several mechanisms:
- Ag Recognition by itself induces expression of anti-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family
- High-affinity B cells will preferentially endocytose and present the Ag for TFH cells in the GC which signal via CD40L to promote the survival of the B cells
- High-affinity B cells may activate endogenous inhibitors of Fas when their BCRs recognize Ag and thus be protected from death, while low-affinity B cells are killed
- Soem TFH cells express FasL, which can recognize Fas on B cells and induce apoptosis
Many tumros of B cells, B cell lymphomas develop from
- germinal center B cells
- (not this is caused by chromosomal translocations of various oncogenes into Ig gene loci)
- The DNA breaks associated with somatic hypermutation and isotype switching facilitate inorporation of oncogenes
Short-lived plasma cells
- are generated during T-independent responses
- may well be generated early during T-dependent responses in extrafollicular B cell foci
- are generally found in secondary lymphoid organs and in peripheral non-lymphoid tissues
Long-lived plasma cells
- are generated in T-dependent germinal center responses to protein Ag
- Are generated by signals from the BCR and IL-21 via a stage of their precursors called plasmablasts
Long-lived plasma cells are maintained by ____ allowing the cells to survive for long periods, often as long as the life span of the host
BAFF
Typically ____ weeks after immunization with T cell-dependent Ag, the long-lived plasma cells of the bone marrow beome a major site of Ab production
2-3 weeks
It is estimated that almost ___% Ab in the blood of a healthy adult is produced by long-lived plasma cells and is specific for Ags that were encountered in the past
50%
Memory B cells are generated mainly in the
germinal centers for T-dependent protein Ags