IMM 1 immunological mechanisms of diabetes Flashcards


changing the concept of T2D


T2D: key concepts
caused by? where?
characterized by what?
Deleterious complications that arise from elevated blood sugar?
what factors contribute to development of T2D?
T2D prevalence rises with what? so that means a role of?
threat to global health why?

insulin sensitivity in health
lean insulin-sensitive individuals, normal secretion is sufficient to? (3)
adipose macrophages and kupffer cells do what?
resulting serologic state characterized by what serum concentrations?

recognized that what two things are causally linked to insulin resistance?
Obesity is characterized by?

immune cell infiltration in adipose tissue in obesity
in leanness what cells present? predominates?
in chronic obesity what cells present? predominates?

Factors regulating macrophage polarity and insulin resistance
in leanness- adipocyte secretes what? these promote? what type are these? which secrete what? may secrete? FFAs present?
Obesity- induces changes in what? resulting in? FFAs present? will also cause the release of what?
what cell is activated by this? produces what? induces what state?



how do we lose beta cells in T2D?
serum levels?
leads to?
death leads to?

pathogenic role of M1 M in islet inflammation and beta cell dysnfunction
what long chain fatty acid induces b-cell dysfunction? via?
b-cells sense this FA via what pathway? this recruits what? to where? how?
newly recruited ____ differentiate into ____ that play pivotal role in b- cell dysfunction via (3)

Genetics of T2D
T2D multifactorial disease arising from the presence of what? where? and what else?
risk if in family?
Concordance rate?
what population has a much higher prevalence of T2D than general population?
concordance rate is showing in twins the prevalence of the disease in both twins. if 100 % then it is entirely genetic. but since its not then there are other factors. Since dizygotic twins have a lower concordance rate then that means the genes do play a role

environmental factors in T2D
twin studies show important role in what two things (non genetic) in development of T2D
B- 2 things that increase T2D
E- what factor would increase risk?

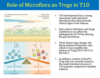
role of microflora in T2D
and on the horizon?

T1D
chronic autoimmune disease characterized largely by?

T1D (history)
initiating events in T1D?
insulin target for?
biomarkers for T1D?
later what discovered to have major role?

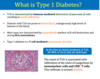
What is T1D
characterized by? resulting in?
patients with T1D are prone to?
most cases are characterized by (immunological)
type 1 diabetes is what mediated?
at time of clinical symptoms of T1D how much b cells destroyed?
onset of T1D associated with infiltration of what by?
infiltrate is termed?
physiological contributions to T1D
just waht are three tissues? and main thing that is wrong?

environmental factors contributing to T1D?
Concordance rate? suggests?
incidence is? suggests?
type of evidence linking environment and T1D?
incidence by country?

T1D
prenatal triggers/ protective factors
postnatal
promoters of progression?
factors slowing progression?
(know the blue)

role of infections in T1D
Bacteria?
virus? (3)
virus act by what mechanisms?
adjuvant- agent that modifies the affects of other agents

breast-feeding vs cow milk
correlation?
cow milk when may contribute to T1D? what else may result?
what disclaimer?

other environmental factors T1D
(3)

role of microflora in T1D
major evidence supporting connection is represented by?
important what was or wasnt well represented in gut biota in T1D patients?
this explains what symptoms?

genetic factors contributing to T1D
risk before 20 if sibling affected? general pop?
concordance?
what grouping seen?