Histology Lecture 3-Connective Tissue Flashcards
(53 cards)
Types of Connective Tissue:
1.) Embryonic Connective Tissue 2.) Adult Connective Tissue
Types of Embryonic Connective Tissue:
1.) Mesenchyme 2.) Mucous
Types of Adult Connective Tissue:
1.) Connective Tissue Proper 2.) Specialized Connective Tissue
Types of Connective Tissue Proper:
1.) Loose (areolar) 2.) Reticular 3.) Dense Regular 4.) Dense Irregular 5.) Adipose
Types of Specialized Connective Tissue:
1.) Blood 2.) Supporting Connective Tissue (bone and cartilage)
Functions of Connective Tissue:
1.) Binds, Supports, and Strengthens other body tissues 2.) Protection- surrounds organs and bones 3.) Insulation of internal organs 4.) Compartmentalization of organs 5.) Transport nutrients and oxygen 6.) Storage of Energy Reserves (adipose) 7.) Immune Responses (blood)
All Connective Tissue has what common characteristics?
1.) cells in an extracellular matrix (protein fibers and ground substance) 2.) common origin (all CT comes from mesenchyme) 3.) degrees of vascularity (can be avascular, poorly vascularized, or highly vascularized)
What is mesenchyme?
Embryonic connective tissue that is: -loosely organized CT -has elongated, undifferentiated cells with cytoplasmic processes -has viscous ground substance Mesenchyme can differntiate into other types of cells other than CT cells
What is the general composition of connective tissue?
Cells with a large amount of extracellular matrix between them.
The ECM is made up of:
1.) Protein fibers 2.) Ground substance
The protein fibers found in the ECM of connective tissue are:
1.) Collagen 2.) Reticular fibers 3.) Elastic fibers
Describe Ground Substance:
amorphous material between fibers, provides medium through which diffusion can occur, can be fluid, semifluid, gelatinous, or calcified (no diffusion), GS is hydrophilic
What are the components of the Ground Substance in the ECM?
1.) Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) (ex. hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate) 2.) Proteoglycans 3.) Multiadhesive Glycoproteins (ex. laminin and fibronectin)
What is the major product or activity of fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, and odontoblasts?
production of fibers and ground substance
What is the major product or activity of plasma cells?
productions of antibodies
What is the major product or activity of lymphocytes?
production of immunocompetent cells
What is the major product or activity of eosinophils?
participation in allergic and vasoactive reactions modulation of mast cell activities and the inflammatory process.
What is the major product or activity of Neutrophils?
phagocytosis of foreign substances, bacteria
What is the major product or activity of macrophages?
secretion of cytokines and other molecules, phagocytosis of foreign substances and bacteria, antigen processing an presentation to other cells.
What is the major product or activity of mast cells and basophils?
liberation of pharmacologically active molecules (histamine)
What is the major product or activity of adipose cells?
storage of neutral fats and thermogenesis
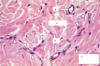
What type of cell is indicated by the black arrows? What does this type of cell do?

Type of cell: fibroblast
Activity: produces ECM fibers
What is the most common cell type in connective tissue?
fibroblast cells
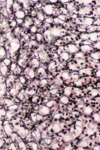
What type of cells can be seen in this image?

Active fibroblasts (seen coming away from ECM which indicates that they are active)