Embryology Lecture 2-Week 2 and 3 Development of Bilaminar and Trilaminar Disc Flashcards
By ______ post-fertilization - implantation into the endometrial wall is completed.
By 10 days post-fertilization - implantation into the endometrial wall is completed.
The trophoblast differentiate into:
The trophoblast differentiate into:
- ) Cytotrophoblasts
- Dervied from Trophoblasts
- Mitotic mononuclear cells
- Migrate to become Syncytiotrophoblasts - ) Syncytiotrophoblasts- -Multinuclear cells without cell membranes
- Responsible for erosion into the endometrium
- Produce the HCG preserving corpus luteum activity (secretion of E and P4)

Describe the establishment of embryonic and bilaminar structure:
After fertilization occurs:

- A small space is created within the embryoblast
- Amnioblasts surround this space enclosing the cavity
- This space will go on to become the amniotic cavity
- The embryoblast forms a flat bilayer structure, embryonic disc, consisting of two layers:
- ) Epiblast-Columnar cells
- ) Hypoblast-Small cuboidal cells
Describe the establishment of maternal blood communication:
- By Embryonic Day 11-12 the blastocyst will completely embed in the endometrium and the surface defect will close and heal
- Synctiotrophoblasts will penetrate deeper into the maternal capillaries termed sinusoids.
- This establishes uteroplacental circulation

Describe some support structures to the embedded blastocyst:
- Exocoelomic membrane- Lines inner surface of cytotrophoblasts
- Along with hypoblasts this forms the lining of the primitive yolk sac (also termed the exocoelomic cavity)

What is the function of the yolk sac?
to provide nourishment for the developing embryo
Describe the formation of the Extraembryonic Mesoderm:
- Cells intervene between the cytotrophoblast layer and the yolk cavity forming the extraembryonic mesoderm.
- This layer fills all space between the trophoblasts and the amnion and exocoelomic cavity.
- Within this mesoderm a space termed the extraembryonic cavity or chorionic cavity is formed surrounding the yolk sac and amniotic cavity.

It is within the _______ cavity that villi will develop to allow for uteroplacental circulation.
It is within the chorionic cavity that villi will develop to allow for uteroplacental circulation.
The extraembryonic mesoderm layer further differentiates into:

The extraembryonic mesoderm layer further differentiates into:
- Somatic layer- lines and supports/surrounds the cytotrophoblast and amnion
- Sphlanchnic layer - lines and supports/surrounds the yolk sac
_________ form the primary villi establishing communication with the chorionic cavity.
Trophoblasts form the primary villi establishing communication with the chorionic cavity

The hyoblast layer produces cells that migrate along the exocoelomic membrane and form a new cavity termed the _________. These migrating cells pinch off the yolk sac from the __________.
The hyoblast layer produces cells that migrate along the exocoelomic membrane and form a new cavity termed the secondary or definitive yolk sac. These migrating cells pinch off the yolk sac from the endometrium.

At the end of week 2:
- Chorionic cavity continues to expand.
- The somatic layer of mesoderm is now properly termed _______ _______.
- The connecting stock is now visible traversing the extraembryonic mesoderm.
- This connecting stock will go on to become the _______ _____.
At the end of week 2:

- Chorionic cavity continues to expand.
- The somatic layer of mesoderm is now properly termed chorionic plate.
- The connecting stock is now visible traversing the extraembryonic mesoderm.
- This connecting stock will go on to become the umbilical cord.
Early week 3 development is characterized by 6 things:
- Appearance of Primitive Streak
- Development of the Notochord
- Transition from two layer embryo to three layer embryo (gastrula)
- Establishment of body axes
- Further growth of the embryo
- Further development of uteroplacental circulation
Describe the formation of the primitive streak:
- Forms in the surface of the upper layer, the epiblast during week 3
- Establishes the body axis
- Becomes the site of gastrulation.

Describe the formation of the primitive groove and pit.
- The primitive streak deepens and can be properly termed the primitive groove as the sides bulge around it.
- At the cephalic end of the streak, an elevated area termed the primitive node forms and surrounds a small cavity termed the primitive pit.

Describe gastrulation:
- Cells of the epiblast layer migrate towards the primitive streak.
- They detach from the upper layer and move beneath it in a movement termed invagination.
- These cells have different fates
- Endoderm or endodermal layer
- Mesoderm or the mesoderm layer
- Ectoderm or ectodermal layer

- Cell migration continues _______ and _______ beyond the confines of the embryonic disc
- Cranially the cells pass on the sides of the prechordal plate between the tip of what will be the notochord and the oropharyngeal membrane
- Cranially migrating cells can be properly termed ________ _____.
Cell migration continues laterally and cranially beyond the confines of the embryonic disc.
- Cranially the cells pass on the sides of the prechordal plate between the tip of what will be the notochord and the oropharyngeal membrane
- Cranially migrating cells can be properly termed prenotochordal cells

Describe the formation of the Notochord:
- A mix of prenotochord cells and cells of the hypoblast develop the notochordal process.
- Cells from the endoderm replace the cells resident within the notochord process creating a solid cord of cells termed the definitive notochord.
- The notochord underlies the neural tube and will eventually induce development of the axial skeleton.

Describe Cephalo-Caudal Development:
- The cephalocaudal axis is now established
- The primitive streak will migrate caudally through development.
- Cells of the notochord and prenotochord regions extend cranially to the area of the prechordal plate and caudally to the primitive pit.
- Cloacal membrane forms at the caudal end of the embryonic disc.
- The posterior wall of the yolk sac forms a small diverticulum in the connecting stock termed the allantois, a rudimentary structure in humans.
- Both the oropharyngeal and cloacal membrane represent areas of tightly adherent ectoderm and endoderm. ** no mesoderm

After the notochord forms, the cephalocaudal axis is established, and the cloacal membrane has formed, what does the mesoderm differentiate into?
- Paraxial mesoderm near cranial end
- Intermediate mesoderm near midstreak region
- Lateral mesoderm plate closer to the caudal part of the streak
The primitive streak begins to disappear during which week of development?
The fourth week
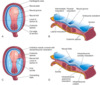
Describe how the circulatory connection between the placenta and the embryo is made (Uteroplacental circulation).
- The trophoblast layer is also transitioning as mesodermal cells penetrate the villi and grow into what is termed the secondary villus.
- By the end of the third week of development the mesodermal cells in the villus begin differentiation into blood cells and blood vessels forming the villous capillary system.
- The villus is now termed the definitive placental villus.
- Capillaries in the villus make contact with the capillaries in the mesoderm of the chorionic plate and in the connecting stalk
- These vessels now establish contact with the intraembryonic circulatory system and a connection is now made between the placenta and embryo.
- The cytotrophoblast cells are also continuing to penetrate the maternal endometrium.
- Communication is established between villous stems termed the outer cytotrophoblast shell.
- This shell will surround the trophoblast layer completely and affix the chorionic sac to the maternal endometrium.
- The chorionic cavity continues to enlarge and attaches to the trophoblastic cell by the connecting stock (umbilical cord), the connection between the placenta and embryo.



