Anatomy Lecture 3-Overview of the Cardiovascular System Flashcards
3 important capillary beds to consider:
1.) the body=systemic circulation 2.) the heart=cardiac circulation 3.) the lungs=pulmonary circulation
Major function of the cardiovascular system
transportation of water, Oxygen, CO2, nutrients, waste products and hormones
Label A-H

A.) Pulmonary Trunk
B.) Arch of aorta
C.) Right atrium
D.) Superior vena cava
E.) left ventricle
F.) apex of heart
G.) Right ventricle
H.) Left atrium
In the standard PA view:
The upper limit of the heart is near the _______ _______ (anteriorly) and the intervertebral disc between ___/___ vertebrae (posteriorly).
In the standard PA view:
The upper limit of the heart is near the sternal angle (anteriorly) and the intervertebral disc between T4/T5 vertebrae (posteriorly).
In the standard PA view:
the Inferior base/Apex of heart is roughly at _____ intercostal space and sits on the diaphragm.
In the standard PA view:
Inferior base/Apex of heart is roughly at 5th intercostal space and sits on the diaphragm.
In the standard PA view:
The right ventricle and the left ventricle (apex) together form the _________ ________ (on the superior surface of the diaphragm)
the right ventricle and the left ventricle (apex) together form the inferior border (on the superior surface of the diaphragm)
In the standard PA view:
the superior vena cava, right atrium and inferior vena cava form the ______ ______ from the R 3rd costal cartilage to the R 6th costal cartilage)
In the standard PA view:
the superior vena cava, right atrium and inferior vena cava form the right border (from the R 3rd costal cartilage to the R 6th costal cartilage)
in the standard PA view:
Aortic arch, pulmonary trunk and left auricle form the ______ ______ (2nd intercostal space to the apex of the heart at the 5th intercostal space – midclavicular line)
In the standard PA view:
Aortic arch, pulmonary trunk and left auricle form the left border (2nd intercostal space to the apex of the heart at the 5th intercostal space – midclavicular line)
The superior border of the heart is at the ____ costal cartilage on the Right of the sternum and the ____ intercostal space on the Left of the sternum.
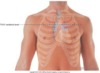
The superior border of the heart is at the 3rd costal cartilage on the Right of the sternum and the 2nd intercostal space on the Left of the sternum.
In the heart, the greatest pressure is associated with _______ emptying (first big hump) (systolic-120). The smallest pressure is associated with ______ filling (diastolic-80)
In the heart, the greatest pressure is associated with ventriculcar emptying (first big hump) (systolic-120). The smallest pressure is associated with ventricular filling (diastolic-80)
Systole is the ______ of the heart.
Diastole is the ______ of the heart
Ventricluar diastole is the _____ of the ventricles
Atrial diastole is the _____ of atria
Systole is the contraction of the heart.
Diastole is the dilation or filling of the heart
Ventricluar diastole is the filling of the ventricles
Atrial diastole is the filling of atria
Label A-H
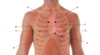
a. ) auscultation position for aortic valve
b. ) aortic valve
c. ) tricuspid valve
d. ) auscultation position for tricuspid valve
e. ) auscultation position for pulmonary valve
f. ) pulmonary valve
g. ) mitral valve
h. ) auscultation position for mitral valve
Label A-S
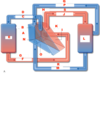
A.) Right pump
B.) Right Atrium
C.) Deoxygenated blood
D.) Pulmonary arteries
E.) Lungs
F.) Oxygenated blood
G.) Pulmonary veins
H.) Left atrium
I.) Left atrium
J.) oxygenated blood in aorta
K.) Left pump
L.) Body
M.) Deoxygenated blood in inferior vena cava
N.) valve
O.) right ventricle
P.) deoxygenated blood in superior vena cava
Q.) Superior vena cava
R.) inferior vena cava
S.) aorta
Trace the blood flow in the circulatory system beginning with blood from the body to the heart.
- ) From the body, deoxygenated blood (venous return) flows through the superior and inferior vena cava in to the right atrium.
- ) From the right atrium, the deoxygenated blood flows through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle.
- ) From the right ventricle, the deoxygenated blood flows through the pulmonary valve/semilunar valve into the pulmonary arteries.
- ) From the pulmonary arteries, the deoxygenated blood flows into the lungs.
- ) From the lungs, the now oxygenated blood flows through the pulmonary veins in to the left atrium.
- ) From the left atrium, the oxygenated blood flows through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle.
- ) From the left ventricle, oxygenated blood flows through the aortic valve and into the aorta.
- ) From the aorta, oxygenated blood flows to the body.
- ) From the body, deoxygenated blood flow back to the heart via the superior and inferior vena cava.
Ausculatation position for aortic valve is located at:
right sternal angle of 2nd intercostal space
auscultation position for tricuspid valve:
left sternal margin of 5th intercostal space
Auscultation position for pulmonary valve:
left sternal margin of 2nd intercostal space
Auscultation position for mitral valve:
mid clavicular of the left 5th intercostal space (hearing mitral valve at apex of heart)
locate the right atrium of the heart on both images


locate the pulmonary trunk

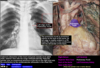
Label A-H
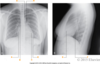
A.) Right Atrium
B.) Superior Vena Cava
C.) left ventricle
D.) apex of heart
E.) right ventricle
F.) left atrium
G.) arch of aorta
H.) pulmonary trunk


