HIstology Lecture 2-Epithelial Tissues and Glands Flashcards
(95 cards)
What are the four basic/primary types of tissue?
1.) Epithelial tissue 2.) Connective tissue 3.) Muscular tissue 4.) Nervous tissue
Define “tissues”
group of cells and their extracellular matrix that work together to perform a function
____ or more tissues forms an organ
2 or more tissues forms and organ
Function of epithelial tissue
Covers/protects body surfaces, organs, ducts, and glands
Function of connective tissue
protects and supports the body. Multiple types with a lot of extracellular matrix.
Function of muscular tissue
made of contractile cells with moderate extracellular matrix in order to move the body
Function of nervous tissue
detects changes and conditions inside and outside of the body. It responds to stimuli by generating action potentials. It is made up of many differnt cells with long processes and no extracellular matrix.
Name the two main categories of Epithelial Tissue and describe them.
- ) Covering or Lining Epithelium-covering external body surfaces (skin), lines GI tract, respiratory tract, and internal body cavities (pleural cavity), as well as organs
- ) Glandular Epithelium-covers secretory and duct portions
What are 6 functions of Epithelial tissue?
- ) Secretion- thinking of the stomach, some of these cells produce secretions
- ) Absorption- thinking about intestinal epithelial (absorbs nutrients)
- ) Filtration- thinking about the kidney filtering the blood
- ) Excretion- although we filter the blood there is still stuff in the blood that we need to pull out and excrete
- ) Transport- some epithelium have cilia in order to transport (repiratory tract and mucus)
- ) Protection- multiple layers of cells for chemical, mechanical and bacterial protection (skin)
What are the (6) characteristics of Epithelial Tissues? (What makes epithelium, epithelium?)
1.) Cellularity-made up of lots of cells (almost entirely of cells, almost no ECM) 2.) Specialized Contacts between cells 3.) Polarity -free or apical surface/pole/domain -lateral surface/domain -basal surface/pole/domain 4.) Supported by Connective Tissue – lamina propria 5.) Avascular, but Innervated 6.) Regeneration
To define the subclasses of epithelium, look at the morphology. Naming epithelium is based on what two morphological features?
1.) number of cell layers 2.) cell height/shape
Epithelium which all cell layers sit on the basement membrane between the epithelial tissue and connective tissue
Simple
Epithelium which one the deepest layer of cells sits on the basement membrane between the epithelial tissue and connective tissue
Stratified
Epithelium which appears stratified, but in fact all cell layers sit on the basement membrane between the epithelial tissue and connective tissue
Pseudostratified
Epithelium which appears flat, the width is greater than the height, nuclei are flattened
Squamous
Epithelium which appears box shaped, tall as they are wide, and the nucleus is centered and round
Cuboidal
Epithelium which appears taller than they are wide, column shaped, the nucleus is associated with basal side of cell and is slightly elongated
Columnar
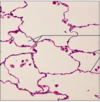
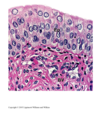
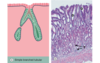
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Simple cuboidal
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Stratified squamous
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Ciliated Pseudostratified
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Simple squamous
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Simple Cuboidal
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Non-Ciliated Simple Columnar
How would you classify the cells in the image?

Ciliated Simple Columnar