Foundations in Immunology 3 Flashcards
What are properties of the adaptive immune system that is different to the innate immune system?
Very specific
Immunological memory
What antigen do B cells use to recognise free antigens?
BCR (surface IgM)
What receptor do T cells use when they are being shown an antigen?
MHC
How do antibodies from a memory cell bind to antigens compared to regular cells?
With much higher affinity
What is a naive B cell?
B cell that has not been exposed to an antigen
What happens once a naive B cell is exposed to an antigen?
Becomes a memory B cell or a plasma cell
What are the 2 kinds of adaptive immunity?
Active
Passive
What is active immunity?
Uses the hosts own immune cells
What is passive immunity?
Transfer of someone else’s immune cells
Which of active and passive immunity creates immunological memory?
Active immunity
What can active and passive immunity be further classified into?
Natural
Artificial
Where are B cells produced?
Bone marrow
What do B cells do on activation?
Differentiate into plasma cells
What are plasma cells?
Responsible for antibody production
Is it more important for B or T cells to be tolerant?
T cells because B cells need the help of T cells to make antibodies
What happens to B cells that recognise self antigens?
Die in bone marrow by apoptosis
What are epitopes?
Part of the antigen that antibodies bind to
How can epitopes differ from each other, other than their structure and what they bind to?
Some induce larger immune responses than others
What is an antigen?
Any substance capable of triggering an immune response
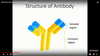
What does the structure of an antibody consist of?
Variable region
Constant region
What are the different antibody classes?
IgG
IgA
IgM
IgD
IgE
What is IgG good for?
Good opsoniser
What is IgA good for?
Protects mucosal surfaces, resistant to stomach acid
What is IgM good for?
Fixing compliment and opsonisation



