Digestive System Flashcards
what are the main functions of the digestive system?
- take in food
- break food down to nutrient molecules
- absorb molecules into bloodstream
- rid body of indigestible remains
what is ingestion?
eating/taking food into the digesive tract
what is digestion?
insoluble food consisting of large molecules being broken down into soluble compounds
what are the 2 different types of digestion?
1) mechanical digestion
2) chemical digestion
what is mechanical digestion?
chewing food into smaller pieces
what is cheical digestion?
enzymes and acids to help breakdown the food
what is absorption?
the passage of foo dmolecules from digestive tract into the circulatory/lympthatic system to transport to the body cells

what is defecation?
the elimination/passing of feces from the rectum of the body

what is extracellular digestion?
outside of cell in the digestive tract
technically outside of the body
** we do this digestion**
what is intracellular digestion?
digestion taking place inside a cell
ex: phagocytosis
what is buccal cavity?
mouth cavity
what are the 2 groups of organs in the digestive system?
1) alimentary canal
2) accessory digestive organs
what is the alimentary canal?
continuous muscular tube running from mouth to anus
- digests food
- absorbs fragments through blood lining
what are the organs involved in digestion with the alimentary canal?
1) mouth
2) pharynx
3) esophagus
4) stomach
5) small intestine
6) large intestine
7) anus
what are accessory digestive organs?
1) teeth
2) tongue
3) gallbladder
4) digestive glands
helps with the process of digestion
what are the boundaries of the buccal cavity?
anterior- lips
lateral- cheeks
superior- soft/hard palate
inferior- tongue
what composes of the buccal cavity?
soft palate
hard palate
tongue
epiglottis
esophagus
trachea
uvula

what are the associated organs of the buccal?
mouth
tongue
salivary glands
teeth
what is mastication?
chewing of food to make smaller food particles
what is a bolus?
mixing of food with saliva for easy swallowing
what are the major salivary glands?
parotid
submandibular
sublingual

what are the functions of saliva?
- cleanses the mouth
- dissolves food chemicals
- moistens food
- contains enzyme amylase that begins digestion of starch
what is deglutition?
swallowing
what is the buccal stage with deglutition?
voluntary contractin of the tongue
what are the 2 Pharyngeal-esophageal phases with deglutition?
involuntary phases
• Controlled by swallowing centre in medulla and lower pons
what are the steps/stages of deglutition?
1) buccal phase:
upper esophageal sphincter is contrcted (closed)
tongue presses against hard palate, forcing bolus down towards oropharynx
2) pharyngeal-esophageal phase begins:
tongue blocks mouth
soft palate and uvula rise, closing nasopharynx (nose)
larynx rises so epiglottis blocks the trachea
upper esophageal sphincter relax (opens) so food starts entering esophagus
3-5) pharyngeal-esophageal phase continues:
constrictor muscles of pharynx contract forcing food into esophagus inferiorly
upper esophageal sphincter contracts after food enters

what is the esophagus?
muscular collapsible tube that extends from the pharynx to the stomach
where is the esophagus located?
in front of vertabral column
behind trachea

what is the esophageal sphincter?
the point where the esophagus connects to the stomach
physiological sphincter
what is peristalsis?
rhythmic muscular movements that pushes food down the esophagus when entered
how does peristalsis work?
when circular muscles contract, longitudinal muscles relax which pushes the food down

what are the 4 major parts of the stomach?
1) cardia
2) fundus (left)
3) body
4) pylorus (right)

what part of the stomach is the cardia?
the part where the esophagus is joined
what part of the body is the fundus?
the rounded part of the stomach slightly above and to the left of the cardia
what part of the stomach is the body?
the large central portion of the stomach
what part of the stomach is the pylorus?
the lower part of the stomach attached to the first part of the small intestine
how is the pylorus’ opening controlled?
the pyloric sphincter
This is a band of circular muscle that can open or close controlling movement of food from the stomach into the duodenum
what are the functions of the stomach?
- Holding area for food (helps with rate of digestion)
- produces gastrin
- Gastric juice production, converts the bolus to acid chyme (pH 2)
- Digestion of proteins & lipids
**very small amounts of digestion**
what is pepsinogen?
lines the stomach to not eat stomach when empty
what is the digestive processes carried out in the stomach?
- carries out breakdown of food
- holding area for food
- delivers chyme (broken down bolus) to small intestine
- pepsin carries out enzymatic digestion of proteins (rennin in infants)
what are some facts about the liver?
- largest gland in the body
- has 4 primary lobes
- falciform ligament
- round ligament
what are the 4 lobes of the liver?
- left lobe
- right lobe
- falciform ligament
- round ligament

what is the falciform ligament?
part of the liver that separates larger right and smaller left lobes
what is the round ligament?
remnant of fetal umbilical vein
what are the function of the liver?
- produces bile
- fat/cholesterol absoption
- regulates blood glucose by storing glycogen
- detoxifies poisonous substances
- produces many plasma proteins
- stores fat soluble vitamins
- degrades hormones
what is the transport of bile from the liver to the gallbladder and the duodenum?
- small bile ducts in the right lobe join to form the right and left hepatic duct
- left/right hepatic duct - common hepatic duct
- common hepatic duct combines with cystic duct from gallbladder = common bile duct
- common bile duct is joined by the pancreatic duct = ampulla
- ampulla projects into duodenum

how does the hepatic portal system work with blood supply?
- veins from blood capillary networks of stomach, small intestine, and large intestine connects to hepatic portal system vein
- hepatic portal vein takes blood to the liver
- most of blood that liver receives is from hepatic portal vein to modify/detoxify blood before bringing it to the heart

what are the importances of the hepatic portal system?
- allows modification of nutrients absorbed
- liver removes toxins from the blood
- liver modiefies, stores and controls various nutrients in the blood/detoxifies blood
what gland is considered the soft gland?
pancreas
what are the three parts that the pancreas is divided into?
1) head
2) body
3) tail

what is the location of the pancreas?
lies just below the greater curvature of the stomach
- head of pancreas near the c-shaped curve of the duodenum
- body is the central portion, tail tapers to the left
what are the functions of the pancreas?
- produces pancreatic juice
- contains enzymes for digestion of fats, proteins, carbs, and nucleic acids
- HCO-3 (bicarbonate ion) neutralizes acid chyme
- produces glucagon (increase blood sugar) and insuline ( decreases blood sugar)
what is the most important organ for digestion?
small intestine
what is the distance that the small instestine runs through?
from pyloric sphincter - caecum
(end of stomach - start of large intestine)
what are the 3 parts of the small intestine?
1) duodenum
2) jejunum
3) ileum
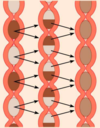
what are the circular folds in the small intestine?
permanent folds that force chyme to slowly spiral through lumen = allowing more time for nutrient absorption

what is villi?
fingerlike projections of mucosa that contains dense capillary bed and lymphatuc capillary (lacteal) for absorption

what is microvilli?
extensions of mucosal cell (brush border) that contains enzymes (brush border enzymes) used for final carbohydrate/protein digestion
AKA fingerlike projections of the cell

what is segmentation?
different parts of small intestine contract
mixes and moves contents towards ileocecal valve
food is moved forwards then backwards
parimarily mixes food and breaks it down mechanically to mix nutrients and enzymes
what are the 4 parts of the large intestine?
1) cecum
2) colon
3) rectum
4) anal canal

what are the functions of the large intestine?
- absorption of water, minerals adn vitamins
- formation of feces
what are the subdivisions of large intestine?
anal canal - anus
2 sphincters
what are the 3 sphincters of the anal canal?
1) internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle)
2) external anal sphincter (skeletal muscle)

what are the steps for regulation of defecation?
1) feces distend from rectum stimulating stretch receptors which transmit signals to spinal cord
2) parasympathetic motor fibres stimulate contraction of the rectum, relaxing th einternal anal sphincter
3) when its convenient to defecate, voluntary motor neurons are inhibited, relaxing the external anal sphincters so feces can pass

what are complex carbs broken down into?
starch - glucose
what is amylase?
mainly shorter chains of starch
salivary amylase in mouth - maltose
pancreatic amylase in lumen - maltose
what is maltase?
breaks down maltose to glucose
sucrase digests sucrose
lactase digests lactose
what is the sequence for the breakdown of carbohydrates?
1) ploysaccharides
2) salivary amylase
3) pancreatic amylase
4) maltose
5) maltase
6) glucose
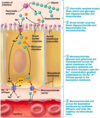
what are the mechanisms of monosaccharide absorption?
1) sodium enters apical membrane through concentration gradient
2) secondary active transport: taking in energy released from sodium to let glucose enter cell
3) facilitated diffusion is used to get into interstitial fluid/blood from basolateral membrane
what are proteins broken doen into?
amino acids
how is protein digested in the stomach?
pepsinogen - pspsin
pepsin: breaks down proteins into smaller peptides
how is protein digested in small intestine?
pepsin activated
uses 3 enzymes to digest
1) trypsin
2) chymotrypsin
3) carboxypeptidase
what is carboxypeptidase?
cuts off one amino acide at carboxyl end

what are aminopeptidase?
cuts off amino acid at amino end

what are dipeptidase?
splits dipeptides

what is the order of digestion of proteins in the small intestine?
1) proteins
2) polypeptides
3) peptides
4) amino acids
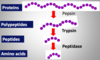
what is the difference of endopeptidases and exopeptidases?
endopeptidases: cuts peptide bonds within the protein molecule
exopeptidases: cuts peptide bonds at the ends of protein molecule (aminopeptidase/carboxypeptidase)

how is protein absorbed?
the exact same way as monosaccharides (carbs)

what are fats broken down into?
fatty acids/glycerol
what is the lingual and gastric lipase part of lipid digestion?
breaks down triglycerides
lingual lipase: breaks one fatty acid +dyglyceride
gastric lipase: breaks 2 fatty acids + monoglyceride
digests small amounts of lipids in stomach

what is pancreatic lipase in lipid digestion?
breaks down triclycerides to 2 fatty acids and monoglycerides
- bile salts help with emulsification
what is the function of bile?
breaks down fat to smaller globules for enxymes to attack/attach
what are pancreatic lipase?
anzymes that digest triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids
what are bile salts?
molecules that are polar at one end and non-polar at the other end
how does fat digest in small intestines if the fatty acid are long chains?
bile interacts with the chains to produce droplets called micelles
how do certain lipids absorb into cells?
short chain fatty acids are absorbed right throuh the cell
monoglycerides and long chain fatty acids diffuse with the help of bile salts (micelles)
in epithelial cell, the fatty acids and monoglycerids are reassembled into triglycerides, packaged into stuctures called chylomicrons
exported to cells through exocytosis to enter lacteals

what are the 2 types of nucleic acids?
RNA and DNA
in small intestine
what is the pancreatic enzyme that RNA is digested by?
ribonuclease
what is the pancreatic enzyme that DNA is digested by?
deoxyribonuclease
how is the secretion of digestive juices in human controlled?
both nervous and hormonal control
what control is short or long lived?
nervous control - short lived
hormonal regulation - more sustained
what is neural regulation during the cephalic phase of digestion?
nervou simpulses travel via vagus nerve to stomach
short live signal
no hormonal regulation at this stage
what is the gastric stage of digestion?
regulated by hormone gastrin produced by gastric glands
gastrin secretion stimulated by:
stomach digestion
partially digested protein
increased pH
caffeine
what are the hormones that contribute to the regulation of secretion of digestive juices for the intestinal phase of digestion?
secretin
cholecystokinin (CCK)
what is secretin?
hormone that goes into blood stream to the pancreas, and stimulates the flow of pancreatic juice
what is cholecystokinin?
hormone that goes into the bloodstream to the pancreas and the gall bladder to secrete pancreatic juice
what is the difference of CCK vs secretin?
CCK makes gall bladder contract to release bile
what is chylomicron?
newly formed tryglycerides from long chain monolycerides coated by protein to be released to lymphatic vessel by exocytosis


